Geometry Vocabulary Worksheet: Master Key Terms Today

Understanding the language of geometry is like learning the alphabet of a new script. To master this field, one must first become fluent in its unique vocabulary. This comprehensive guide is designed to introduce you to key terms that will form the backbone of your geometry education. From points and lines to complex shapes and their properties, this worksheet aims to enhance your comprehension of geometric concepts, thereby laying a solid foundation for further exploration.
Essential Geometric Terms

Geometry revolves around shapes, dimensions, and positions, each defined by specific terms:
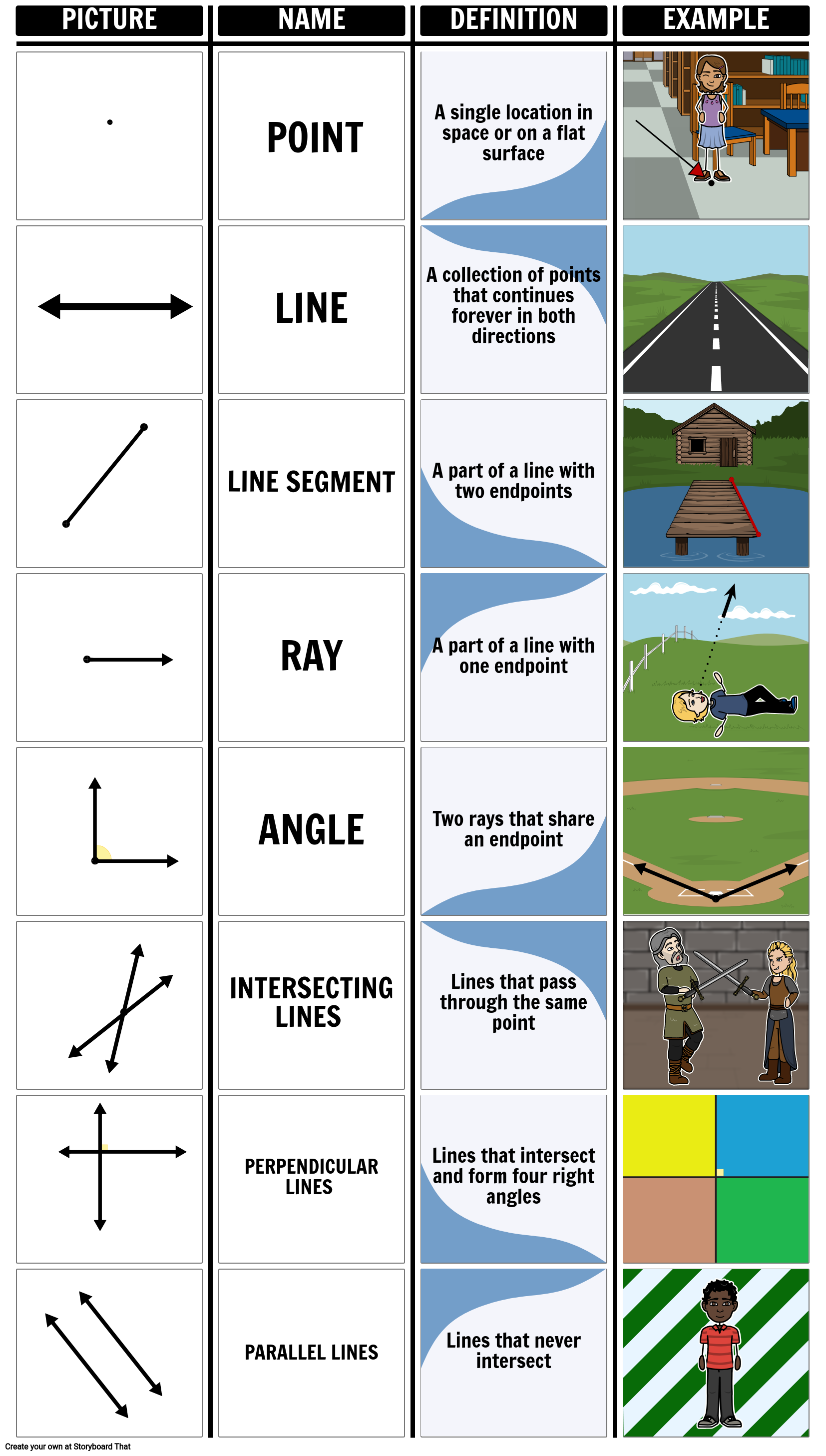
- Point: The most fundamental entity in geometry; a location in space with no dimensions.
- Line: A one-dimensional figure extending infinitely in both directions.
- Plane: A flat, two-dimensional surface that extends infinitely in all directions.
- Line Segment: A section of a line bounded by two points.
- Ray: Part of a line that starts at a single point (endpoint) and extends infinitely in one direction.
Understanding Shapes

Geometry is not just about lines and points; it also delves into various shapes and their properties:
Polygons

A polygon is a plane figure that is bounded by a closed path or circuit, which is made up of a finite sequence of straight line segments. Here are some common polygons:
- Triangle: A polygon with three sides.
- Quadrilateral: A polygon with four sides.
- Pentagon: A polygon with five sides.
- Hexagon: A polygon with six sides.
📝 Note: Regular polygons have all sides of equal length and all internal angles equal.
Circles and Ellipses
While not polygons, circles and ellipses are essential shapes in geometry:
- Circle: A round, two-dimensional shape with every point on its edge equidistant from its center.
- Ellipse: A set of all points for which the sum of the distances to two fixed points (foci) is constant.
Angles

Angles are crucial in defining the relationships between lines and shapes:
- Acute Angle: Less than 90 degrees.
- Right Angle: Exactly 90 degrees.
- Obtuse Angle: More than 90 but less than 180 degrees.
- Straight Angle: Exactly 180 degrees.
- Reflex Angle: Greater than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees.
Properties and Relationships

Geometry is filled with fascinating properties and relationships between its elements:
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines

- Parallel Lines: Two lines on a plane that do not intersect or meet at any point.
- Perpendicular Lines: Two lines that intersect at a right angle.
Types of Triangles

| Triangle Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Equilateral Triangle | All three sides and angles are equal (60 degrees each). |
| Isosceles Triangle | Two sides are equal in length. |
| Scalene Triangle | All sides are of different lengths. |

Congruence and Similarity

These concepts describe the likeness between shapes:
- Congruent: Figures that have the same shape and size.
- Similar: Figures that have the same shape but possibly different sizes.
📝 Note: For triangles to be congruent, all corresponding sides and angles must be equal.
Summary of Geometric Terms

To conclude, geometry is a language where understanding its vocabulary enhances our ability to describe, analyze, and solve spatial problems. From simple points to the complexity of polygons, circles, and angles, each term provides insights into the relationships and structures of space. By mastering these key terms, you are not only better equipped to delve into more advanced geometric concepts but also to appreciate the logical beauty of geometry's perfect order.
What is the difference between a line and a line segment?

+
A line extends infinitely in both directions, whereas a line segment is a part of a line bounded by two endpoints.
How are congruent and similar figures different?

+
Congruent figures are identical in size and shape, while similar figures maintain the same shape but can vary in size.
What are the types of triangles?

+
There are three main types of triangles based on their sides: Equilateral, where all sides are equal; Isosceles, with two equal sides; and Scalene, where all sides are of different lengths.



