5 Geometry Segment Addition Worksheet Answers You Need

Geometry can be an engaging and challenging subject, particularly when it comes to the intricacies of segment addition. Understanding how to use the Segment Addition Postulate effectively is crucial for success in this area of mathematics. This postulate states that given two points on a line segment, any point between them will divide the segment into two smaller segments whose lengths add up to the total length of the original segment. Here, we'll delve into the concept of segment addition, provide examples with worksheet answers, and explore common pitfalls to avoid.
The Basics of Segment Addition Postulate

The Segment Addition Postulate is fundamental in geometry, asserting that if point B lies on line segment AC, then the length of segment AC is equal to the sum of the lengths of segment AB and segment BC. Here's how it's often written mathematically:
AC = AB + BC
Here are some key points to remember:
- Collinearity: All points must lie on the same line or line segment.
- Betweenness: The point dividing the segment must be between the endpoints.
- Addition: The total length is the sum of the lengths of the smaller segments.
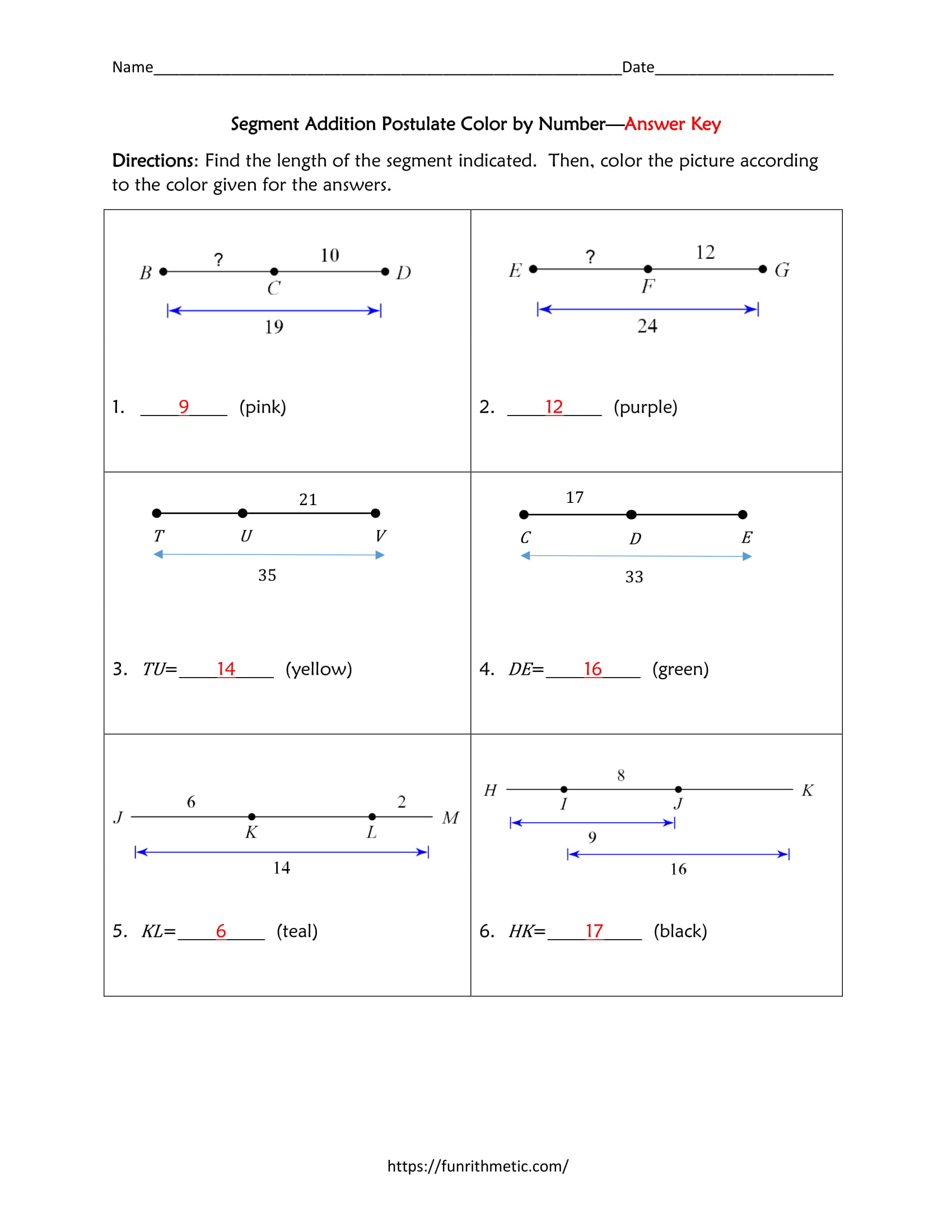
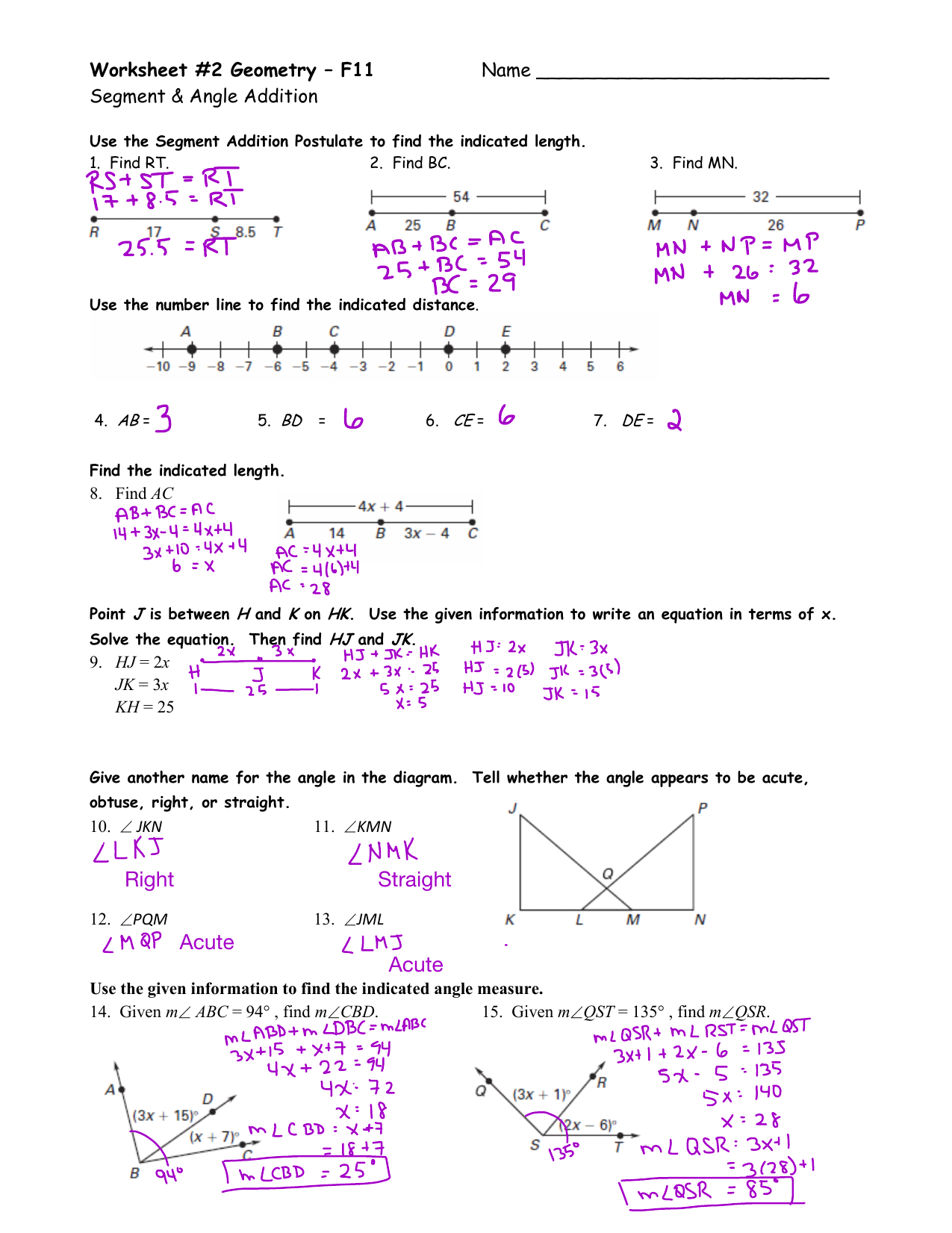
Worksheet Answers and Examples

Let's look at some typical questions you might find on a segment addition worksheet along with their solutions:
Example 1

Problem: If AB = 6 units, BC = 4 units, and point B lies on AC, find the length of AC.
Solution:
AC = AB + BC = 6 + 4 = 10 units
📝 Note: Ensure that the points B, A, and C are collinear for this problem to work.
Example 2

Problem: Given AC = 20 units, AB = 12 units, find the length of BC.
Solution:
AC = AB + BC 20 = 12 + BC BC = 20 - 12 BC = 8 units
Example 3

Problem: If AC = 25 units, BC = 9 units, find AB.
Solution:
AC = AB + BC 25 = AB + 9 AB = 25 - 9 AB = 16 units
Example 4

Problem: Points D, E, and F are collinear. If DE = 8 units, EF = 7 units, and DF = 15 units, verify the segment addition postulate.
Solution:
Since E is between D and F: DE + EF = DF 8 + 7 = 15 Thus, the postulate is verified.
Using the Postulate in Different Scenarios

The Segment Addition Postulate isn't just for basic calculations; it's also crucial in:
- Measuring Distances: When you're given partial measurements and need to find total length.
- Constructing Segments: For drawing lines with specific lengths or bisecting segments.
- Real-world Applications: Determining distances between cities, lengths of roads, or positions in physics.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
When working with segment addition, here are some common mistakes:
- Confusing point labels: Ensure that points are labeled correctly when solving.
- Not accounting for negative signs: Remember, direction doesn't change the length, but it does matter for coordinate geometry.
- Ignoring the Betweenness Property: Points must lie between endpoints, or the postulate won't apply.
⚠️ Note: Always check your work to ensure each calculation is correct and corresponds to the given points.
Wrapping Up the Understanding

Geometry, particularly the concepts around segment addition, is integral to understanding the spatial relationships between points and lines. By mastering the Segment Addition Postulate, students can enhance their geometric reasoning and problem-solving skills. This knowledge has practical applications beyond the classroom, from engineering to architecture and beyond. Keep in mind that practice, attention to detail, and a clear understanding of the postulates are the keys to success in geometry. Whether you're working on a problem set, preparing for an exam, or just enjoying geometric puzzles, the steps and examples outlined here should help you understand the basics of segment addition.
What is the Segment Addition Postulate?

+
The Segment Addition Postulate states that if point B lies on the line segment AC, then the length of AC is the sum of the lengths of segments AB and BC.
Can segment addition be applied to non-collinear points?
+
No, segment addition applies only to collinear points where one point lies between the other two.
How do you find a segment’s length if you know only one segment’s length and the total length?

+
Subtract the length of the known segment from the total length to find the length of the missing segment.
What are some real-world applications of segment addition?

+
Examples include determining distances between landmarks on a map, calculating the length of straight highways, or understanding force vectors in physics.
Can the Segment Addition Postulate be used to verify segment lengths?

+
Yes, if you have the total length and the length of one segment, you can verify the length of the remaining segment by ensuring the total length equals the sum of the segment lengths.