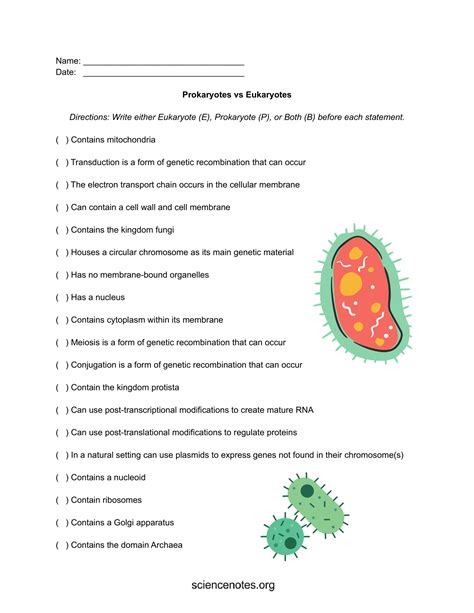
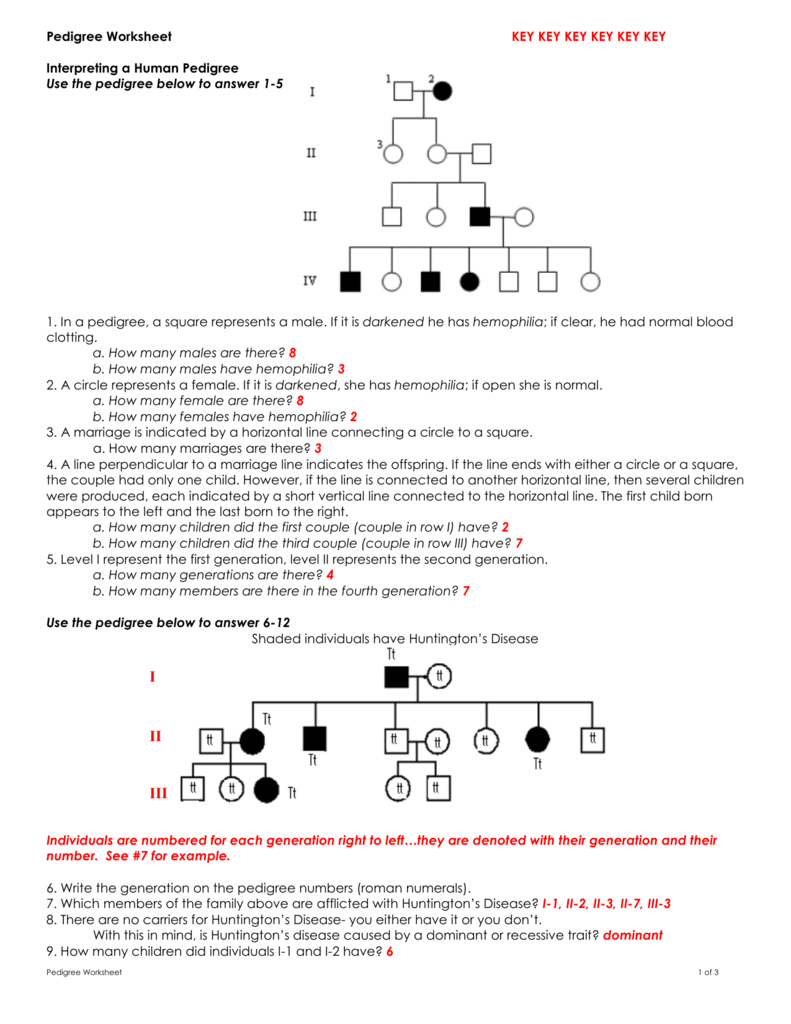
5 Tips to Easily Solve Genetics Pedigree Worksheets

If you're studying genetics, mastering the art of pedigree analysis is crucial for understanding how traits are inherited. Pedigree worksheets can be a valuable tool, but they often seem daunting at first glance. In this post, we'll explore five essential tips to help you solve genetics pedigree worksheets with ease, ensuring you can confidently trace genetic lineage and identify inheritance patterns.
Understanding the Basics of a Pedigree Chart

The first step to mastering pedigree worksheets is to understand the chart’s basic structure and symbols:
- Circles represent females.
- Squares represent males.
- A shaded symbol indicates an individual expressing the trait in question.
- A half-shaded symbol means a carrier (often used in X-linked traits).
- Horizontal lines between circles and squares symbolize marriage or mating.
- Vertical lines connect parents to their children.
- Roman numerals signify generations, while numbers represent individuals within a generation.
This visual structure helps in tracking the inheritance pattern effectively.
Tip 1: Identify Key Patterns of Inheritance

Understanding how genes are inherited is key to solving pedigree charts:
- Autosomal Dominant: If one copy of a mutated gene is enough to express the trait, this pattern shows vertical inheritance. Look for instances where affected individuals occur in several generations, possibly with skipped generations.
- Autosomal Recessive: Traits that appear when two recessive alleles are present, often skip generations. Look for affected individuals being offspring of unaffected or carrier parents.
- X-linked Dominant: Traits inherited from affected fathers pass to all daughters but none of the sons.
- X-linked Recessive: A more common inheritance pattern, often affecting males more frequently than females since they have only one X chromosome.
- Y-linked: Traits that are passed from father to son through the Y chromosome.
🧬 Note: Always verify that the proposed inheritance pattern fits with the entire pedigree, as some traits might have variable penetrance or expressivity.
Tip 2: Start with What You Know

Begin your analysis by identifying individuals with clear genotypes:
- Identify individuals who are definitely affected by the trait or those who are certainly unaffected.
- From there, work backward to identify genotypes of their parents and siblings.
🧐 Note: This approach ensures that your analysis starts from a known point, reducing the probability of errors.
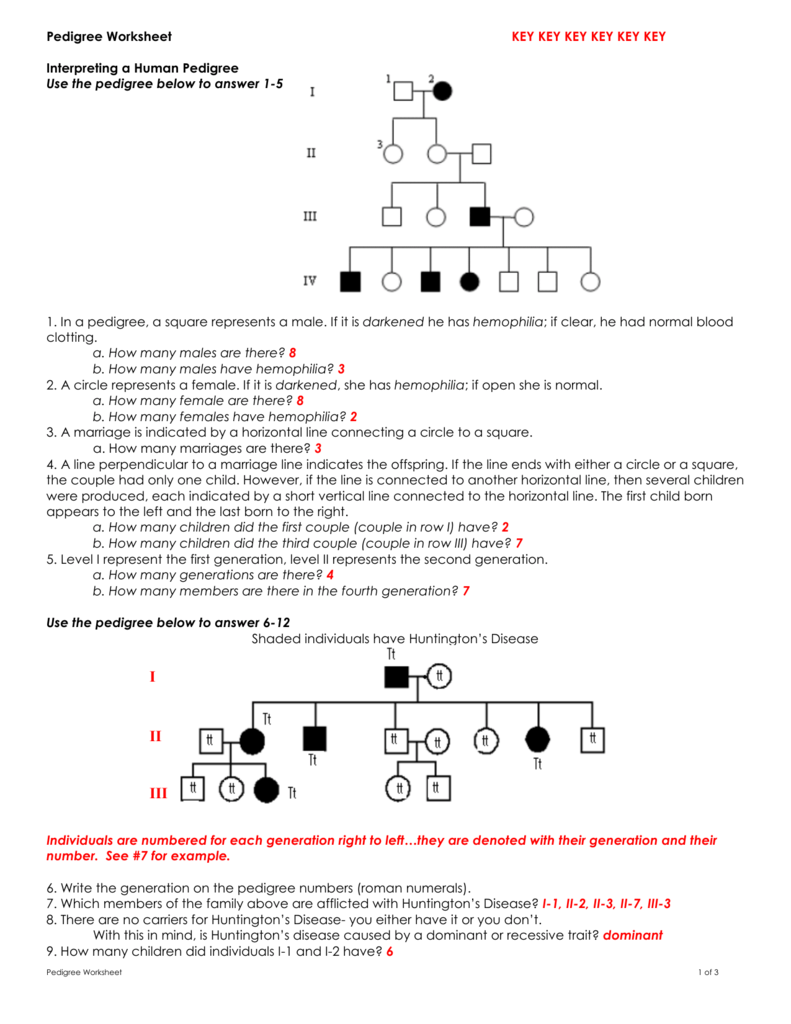
Tip 3: Use Punnett Squares for Confirmation
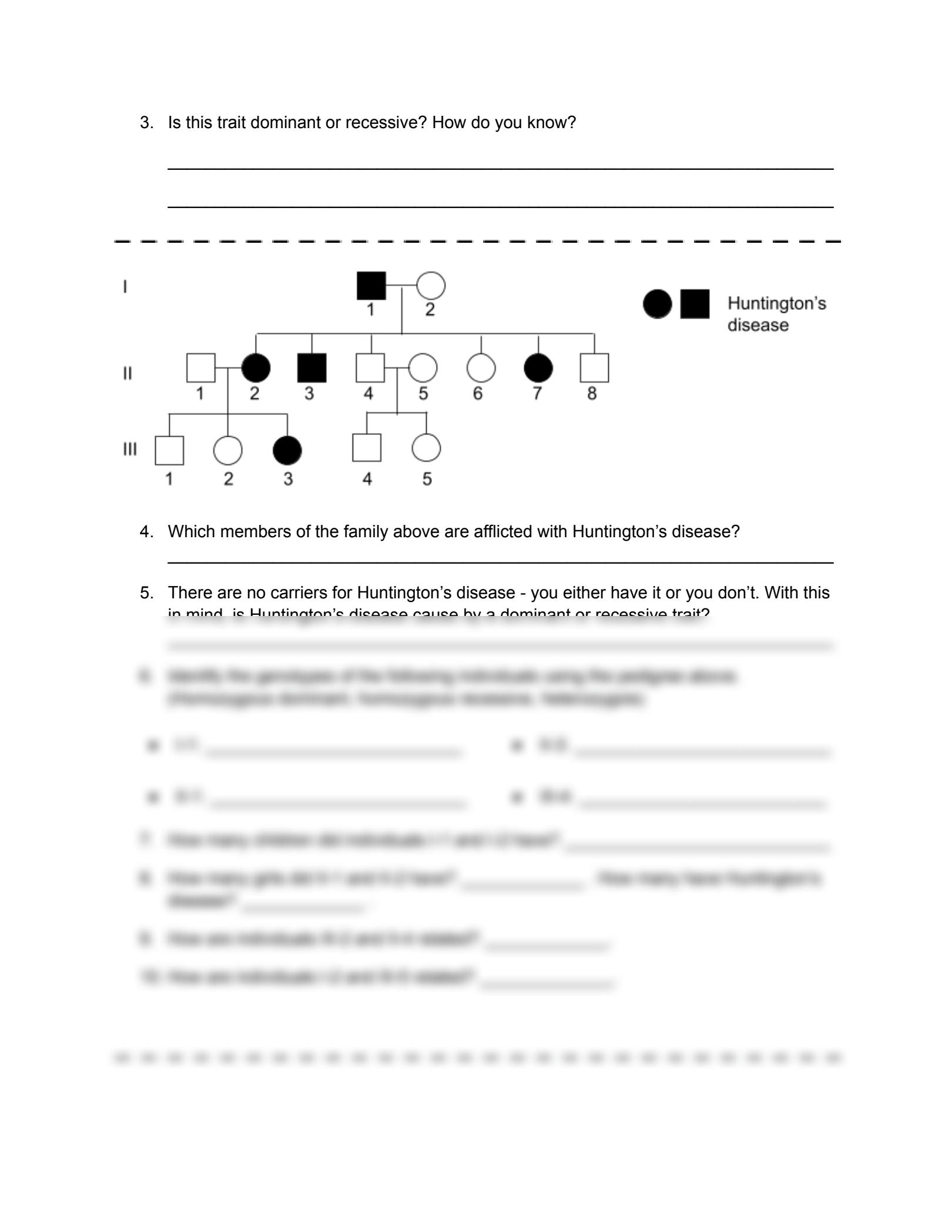
After identifying possible inheritance patterns, use Punnett squares to confirm the probability of certain genetic outcomes:
- Set up a square for each key mating pair in the pedigree.
- Fill in the genotypes of known individuals, then determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring.
Here’s an example of a Punnett square for an autosomal recessive trait:
| A | a | |
|---|---|---|
| a | Aa (carrier) | aa (affected) |
| a | Aa (carrier) | aa (affected) |

Tip 4: Check for Exceptions
Genetics isn’t always straightforward:
- Look for traits that do not fit neatly into an inheritance pattern. This might suggest other influences like incomplete penetrance, variable expressivity, or new mutations.
🔍 Note: Incomplete penetrance means that not everyone with the genotype expresses the phenotype. Variable expressivity refers to the same genotype showing different levels of trait expression.
Tip 5: Utilize Probability and Statistics

Genetics often deals with probabilities, so:
- Calculate the likelihood of different genotypes and phenotypes among offspring.
- Remember that small pedigrees might not reflect true probabilities, leading to what might look like exceptions.
The use of probability helps in validating or questioning the observed inheritance pattern.
As we delve into the intricate world of genetics and pedigree analysis, these five tips provide a structured approach to interpreting these charts. Whether you're dealing with human, animal, or plant genetics, understanding how to read and solve pedigree charts can significantly enhance your ability to grasp genetic concepts. This foundational knowledge not only aids in solving academic problems but also opens up applications in real-world scenarios like genetic counseling, where understanding inheritance patterns can have profound impacts.
Through mastering these tips, you'll find that genetics pedigrees become less like puzzles and more like fascinating puzzles with clear rules to unlock their mysteries. Remember, practice makes perfect, so regularly tackling pedigree problems will enhance your skills in genetic analysis, making complex genetic inheritance patterns easier to comprehend and solve.
What does it mean if a pedigree shows horizontal inheritance?

+
Horizontal inheritance suggests a pattern where the trait appears in individuals within the same generation but not necessarily in their offspring, which could indicate an autosomal recessive trait, where both parents must carry the allele for the trait to be expressed in their children.
How do I know if a trait is sex-linked?

+
Look for patterns where the trait affects one sex more frequently than the other, particularly if it follows a maternal inheritance in males (X-linked recessive) or affects all offspring of a father (Y-linked or X-linked dominant).
What is the significance of variable expressivity in pedigree analysis?
+
Variable expressivity means that individuals with the same genotype can show different severities of a trait. In a pedigree, this can appear as if individuals have different genotypes, making the analysis more complex but also more interesting as it reflects the real-world variability of genetic expression.
Can genetic counseling benefit from pedigree analysis?

+
Absolutely, pedigree analysis can predict the likelihood of passing on genetic conditions to offspring. It helps genetic counselors assess risk, provide options for prevention, and offer insight into family planning decisions.