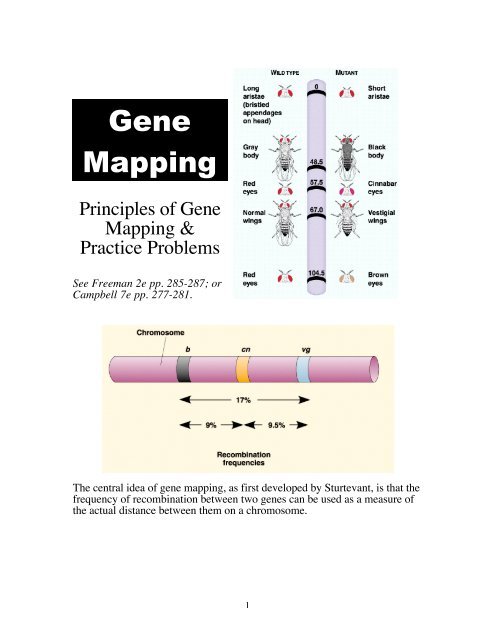
5 Essential Gene Mapping Worksheet Tips for Beginners

Embarking on the journey of gene mapping can be both exhilarating and challenging for beginners. Understanding the genome's secrets through gene mapping opens up a world of scientific exploration, from discovering the causes of genetic disorders to tracing the lineage of species. However, to navigate this intricate landscape effectively, newcomers need to equip themselves with fundamental knowledge and tools. This post offers five essential tips to help beginners in the field of gene linkage mapping, genetic distance, and inheritance patterns get a firm grasp on this complex science.
1. Understand the Basics of Gene Mapping

Before diving into the practicalities of genetic mapping, it’s crucial to get a solid understanding of the foundational concepts:
- Gene: A segment of DNA that codes for a specific protein or RNA molecule, responsible for traits.
- Locus: The physical location of a gene on a chromosome.
- Allele: Different forms of the same gene, leading to variations in traits.
Knowing these terms and their implications helps to decode the complexity of gene mapping. Additionally, familiarize yourself with key techniques like restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP), quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping, and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to better understand how genes and markers are mapped.
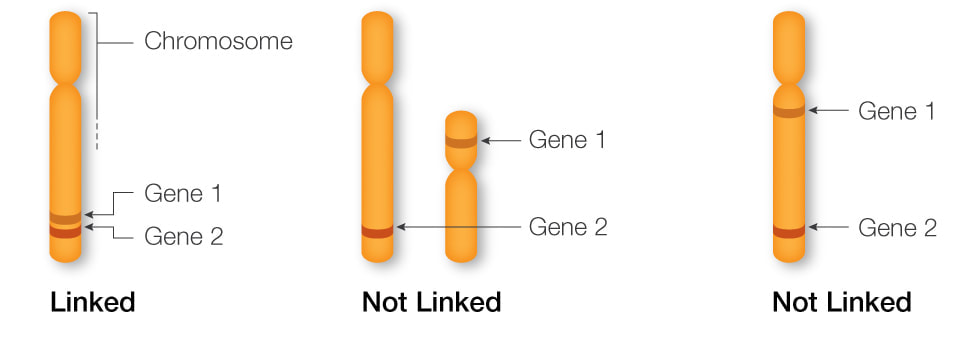
2. Master the Art of Pedigree Analysis
Pedigree analysis is an indispensable tool in gene mapping, allowing geneticists to track the inheritance of traits through generations:
- Identify Patterns: Learn to recognize patterns such as autosomal dominant, recessive, or sex-linked inheritance.
- Construct Pedigrees: Understand how to create and interpret pedigrees accurately, marking out the relationships, phenotypes, and genotypes of individuals in a family tree.
Pedigrees can reveal crucial information about the linkage between genes and their relative genetic distances, which are vital for mapping. Here’s a simple example of how you might record inheritance patterns in a pedigree:
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| ♂ | Male |
| ♀ | Female |
| □ | Unaffected Individual |
| ■ | Affected Individual |
| --|-- | Relationship (marriage or parent-child) |
| |▼ | Descendants |
3. Embrace Genetic Mapping Software

In today’s digital age, mastering software tools for gene mapping can streamline your work:
- Genotyping Tools: Software like GATK and PLINK help in genotyping analysis, which is essential for constructing genetic maps.
- Visual Mapping: Tools like MapMaker or MapChart provide visual representations of genetic linkage.
- Data Management: Use databases such as Ensembl or UCSC Genome Browser to navigate complex genomic data.
💡 Note: Software can greatly reduce the time spent on manual calculations and plotting, but always cross-check the results manually to ensure accuracy.
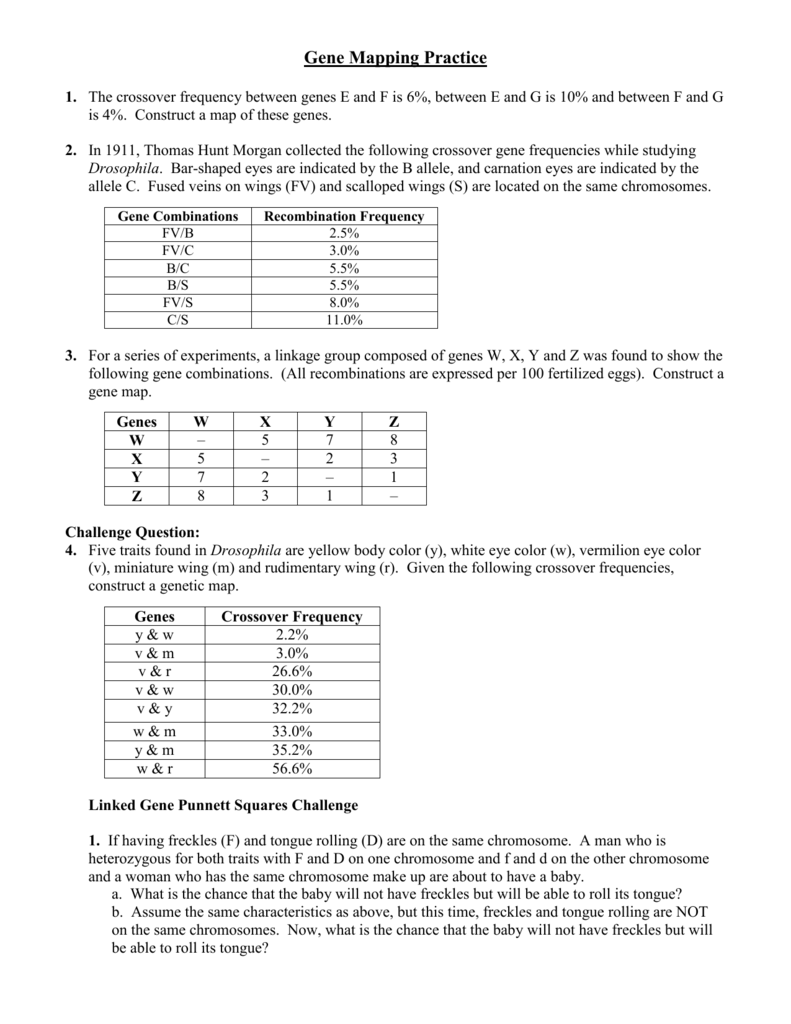
4. Analyze Recombination Frequencies and Genetic Distances

Understanding recombination is key to mapping genes. Here’s what you need to know:
- Recombination Frequency: The percentage of gametes that exhibit crossing over between two linked genes. This helps estimate the physical distance between genes.
- Genetic Distance: Measured in centiMorgans (cM), it reflects the likelihood of recombination. A higher distance implies a higher chance of crossing over.
Practical Example:
If the recombination frequency between genes A and B is 0.2 (20%), then their genetic distance would be approximately 20 cM.
🛑 Note: Always remember that genetic distances measured in cM are not equal to physical distances in base pairs on the chromosome.
5. Practice and Collaboration

The complexity of gene mapping requires not just theoretical knowledge but also:
- Practical Experience: Engage with real-world data sets through internships, lab work, or online platforms.
- Collaboration: Work with others in the field. Discussing your findings, methodologies, and results can offer new perspectives and insights.
Join forums, attend seminars, and participate in workshops to continually expand your knowledge base. Gene mapping is a dynamic field; staying current through practice and community involvement will keep you ahead.
In summary, for beginners venturing into the fascinating world of gene mapping, understanding the basics, mastering pedigree analysis, embracing digital tools, comprehending recombination, and gaining practical experience through collaboration are essential. By following these tips, aspiring geneticists can effectively navigate the intricate process of deciphering genetic codes. Keep learning, practicing, and engaging with the scientific community to continuously improve your skills in this ever-evolving science.
Why is pedigree analysis important in gene mapping?
+
Pedigree analysis helps trace the inheritance patterns of genes through generations, revealing linkage between genes, which is crucial for gene mapping.
What is the difference between a gene and an allele?

+
A gene is a segment of DNA that provides instructions for a particular trait. Alleles are different versions of the same gene that can result in variations of that trait.
How can software tools aid in gene mapping?

+
Software tools automate complex computations, manage large data sets, and provide visual aids, which reduce errors and increase efficiency in gene mapping projects.