Explore Harriet Tubman with Free Printable Worksheets
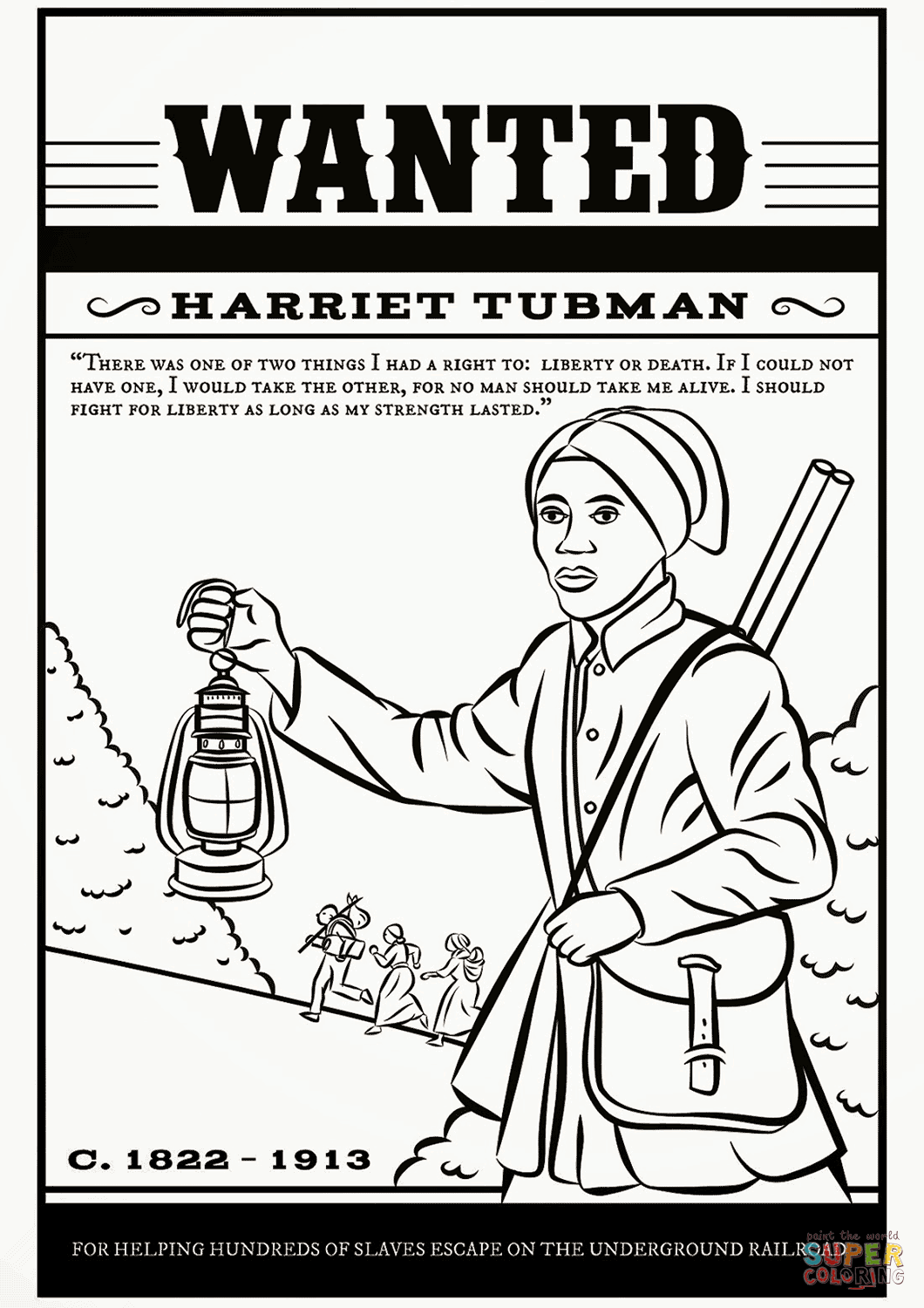
Harriet Tubman, born Araminta Ross around 1822 in Dorchester County, Maryland, is an emblematic figure of American history. Known for her heroic efforts in the Underground Railroad, Harriet Tubman not only liberated herself from the shackles of slavery but also made several daring missions to rescue around 70 enslaved people, including her own family members. This blog post delves into the life, achievements, and legacy of Harriet Tubman, offering educators, students, and history enthusiasts free printable worksheets to deepen their understanding of her remarkable journey.
Early Life and Slavery

Harriet Tubman’s early years were marred by the harsh realities of slavery. Here are some pivotal moments from her early life:
- Birth and Family: Born into slavery, Harriet was one of nine children. Her parents, Harriet Green and Ben Ross, instilled strong values of faith and resilience in their children.
- Early Hardships: At the age of 5 or 6, she was hired out to work as a nursemaid, which separated her from her family. A traumatic event in her youth involved an overseer throwing a 2-pound weight at another slave, striking Harriet in the head. This injury caused her to suffer from narcolepsy for the rest of her life.
- Change of Name: She took on the name Harriet when she married John Tubman around 1844, a free black man, though their marriage was strained due to her desire for freedom.
Escape to Freedom
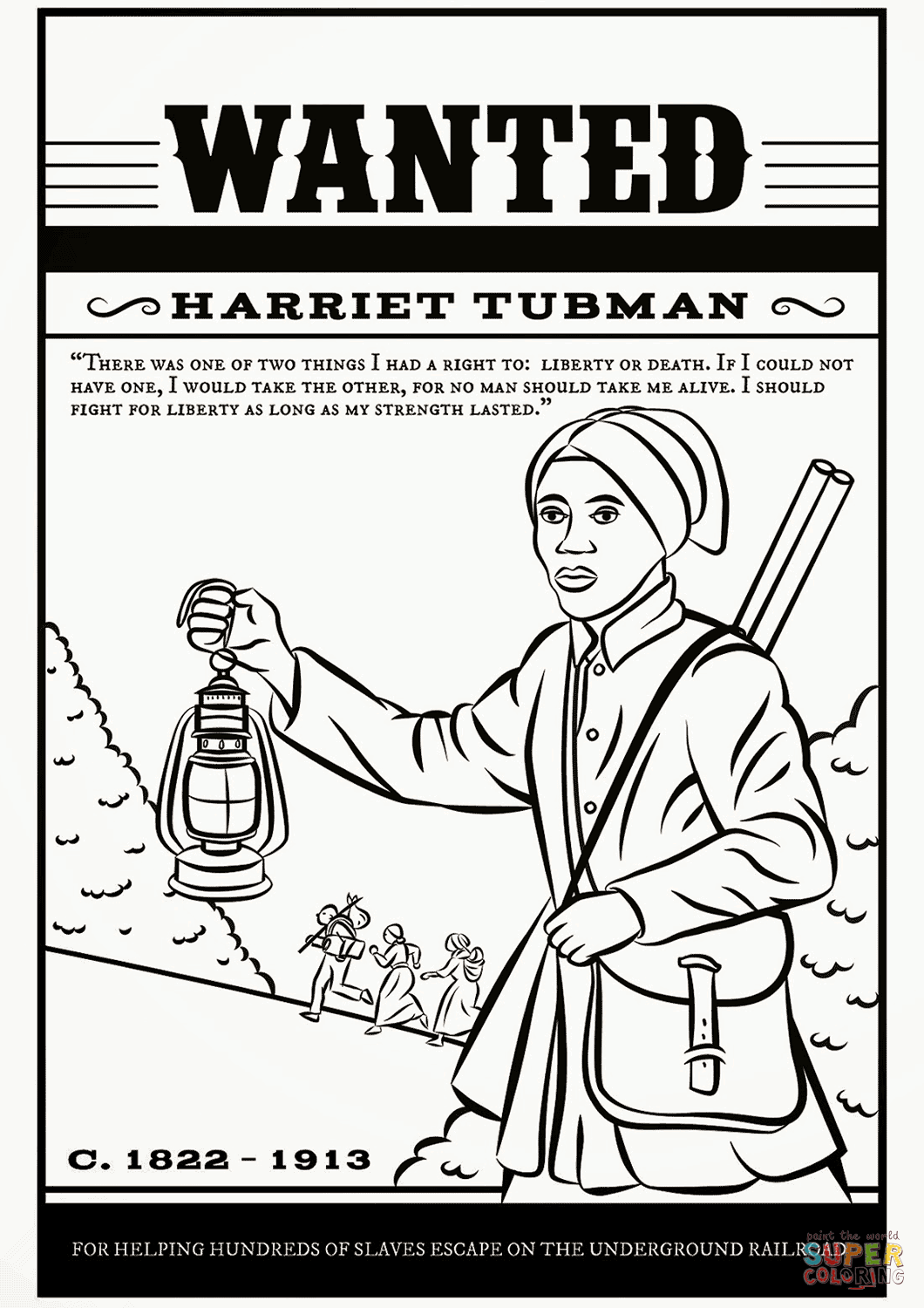
Harriet’s journey to freedom was fraught with peril but was successful:
- The Escape: In 1849, after learning she might be sold, Harriet decided to escape. She used the stars as her guide, making her way to Pennsylvania, a free state at the time.
- Underground Railroad: Feeling compelled to help others, Harriet returned to Maryland multiple times, using a network of safe houses and secret routes known as the Underground Railroad. She earned the nickname “Moses” for leading her people out of slavery.
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| September 1849 | Harriet Tubman escapes to freedom |
| 1850s | Harriet Tubman’s missions on the Underground Railroad |

🌟 Note: Harriet Tubman’s escapes were not only physically challenging but also required incredible strategic planning and courage. Students can research more about her journey through interactive maps and biographical accounts.
Life After Slavery

After ensuring her own freedom, Harriet Tubman continued her fight in different arenas:
- Civil War Contributions: She served as a nurse, cook, and spy for the Union Army, even leading an armed assault on plantations along the Combahee River in South Carolina, freeing more than 700 enslaved people.
- Suffrage Movement: Post-war, she advocated for women’s suffrage, working alongside luminaries like Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton.
Legacy and Recognition

Harriet Tubman’s legacy extends beyond her time:
- Honors and Tributes: She has been commemorated with numerous awards, honors, and in popular culture through books, movies, and monuments.
- Influence: Her spirit of defiance and dedication to freedom influenced civil rights movements throughout history.
Throughout her life, Harriet Tubman embodied the fight against oppression, becoming a beacon of hope and action. Her story not only inspires but also serves as a teaching moment for values like bravery, resilience, and social justice. These free printable worksheets will help educators and students engage with Harriet Tubman's life in a more interactive and educational manner:
- Worksheet on the Underground Railroad
- Timeline of Harriet Tubman's Life
- Essay prompts on Harriet Tubman's contributions to American history
To summarize, Harriet Tubman's journey from slavery to freedom, her subsequent efforts to free others, and her enduring impact on American civil rights and gender equality movements serve as a profound testament to human spirit and resistance against injustice. Through understanding her life, we learn about courage, leadership, and the ongoing struggle for equality and justice.
How many people did Harriet Tubman help to freedom?

+
Harriet Tubman is believed to have personally led approximately 70 enslaved people to freedom through the Underground Railroad.
What was Harriet Tubman’s health issue caused by her injury?

+
Harriet Tubman suffered from narcolepsy, a sleep disorder where she would fall asleep at random times, caused by a head injury she received in childhood.
How did Harriet Tubman contribute during the Civil War?

+
During the Civil War, Harriet Tubman served as a nurse, cook, spy, and scout for the Union Army. She was also involved in the planning and execution of a military operation that freed over 700 enslaved people.