7 Free Printable Apple Tree Life Cycle Worksheets

The Marvelous Journey: Understanding the Apple Tree Life Cycle

The apple tree, a staple in many orchards and backyards, not only bears delicious fruit but also offers a fascinating look into the plant’s life cycle. From a humble seed to a fruit-bearing tree, the journey of an apple tree through its various stages of life is a marvel of nature. This blog post delves into the apple tree life cycle, providing free printable worksheets to educate and engage learners of all ages.
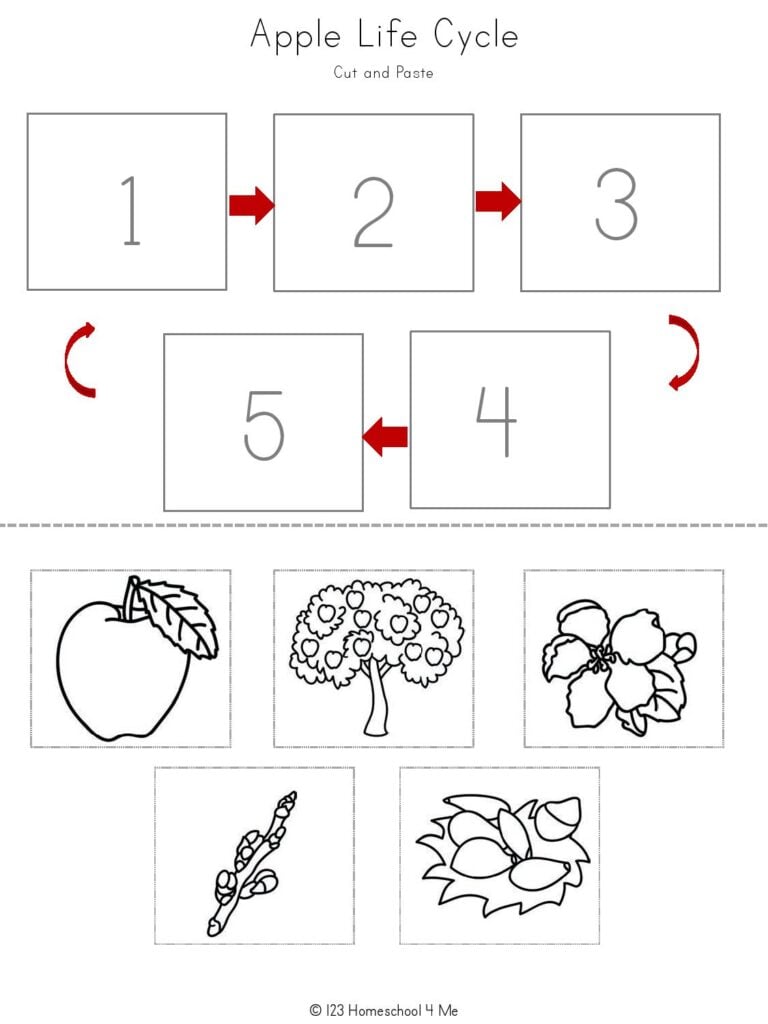
1. Seed Planting


The life cycle of an apple tree begins with a seed. For educational purposes, consider the following steps:
- Obtain Seeds: Either from an apple or through an educational kit.
- Preparation: Soak seeds in water for 24 hours to enhance germination.
- Planting: Plant the seeds in small pots or directly in soil, about 1 inch deep. Place the pot in a sunny area.
2. Germination and Seedling Growth


After planting, here’s what happens:
- The seed absorbs water and begins to swell.
- Roots emerge first, then the shoot pushes upward.
- Seedlings usually sprout in 2-6 weeks, varying with conditions.
🌱 Note: Not all seeds will germinate, so plant several to increase your chances of success.
3. Vegetative Growth
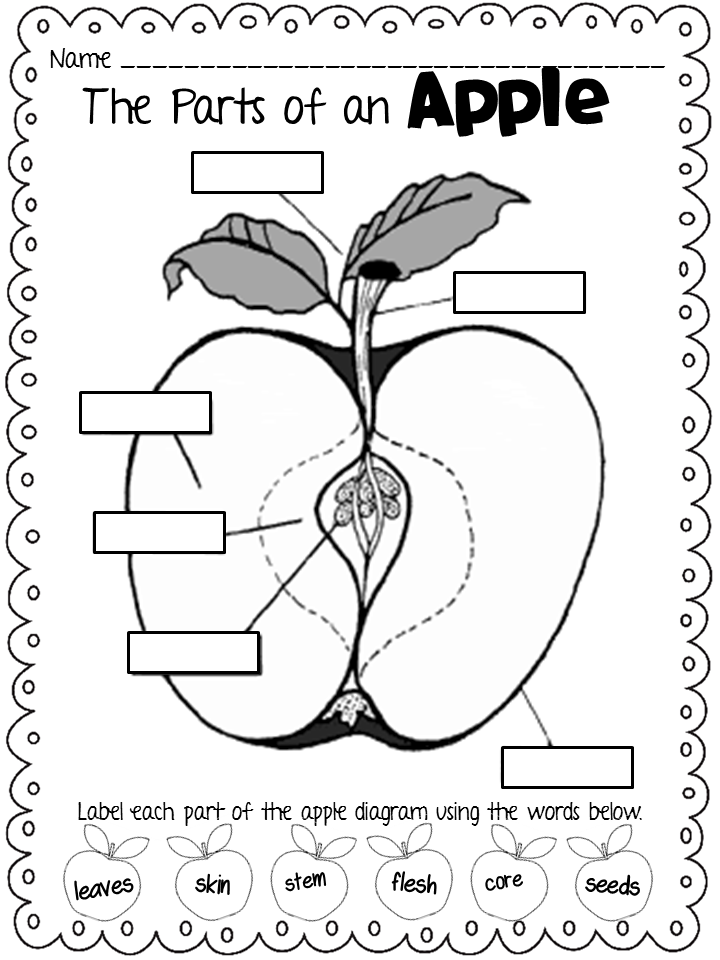
This phase is characterized by:
- Leaf Development: As the plant grows, leaves start to appear to photosynthesize.
- Stem Elongation: The tree increases in height through the elongation of its stems.
- Branching: Side branches start to grow, creating the tree’s characteristic shape.
🌿 Note: The growth rate depends on soil quality, sunlight, water, and nutrients.
4. Apple Blossom Stage


As the tree matures, here’s what unfolds:
- The tree produces buds that eventually blossom into flowers.
- Each flower has both male and female reproductive organs, capable of self-pollination or cross-pollination with other apple trees.
- Pollination occurs with the help of bees, birds, or wind.
5. Fruit Development
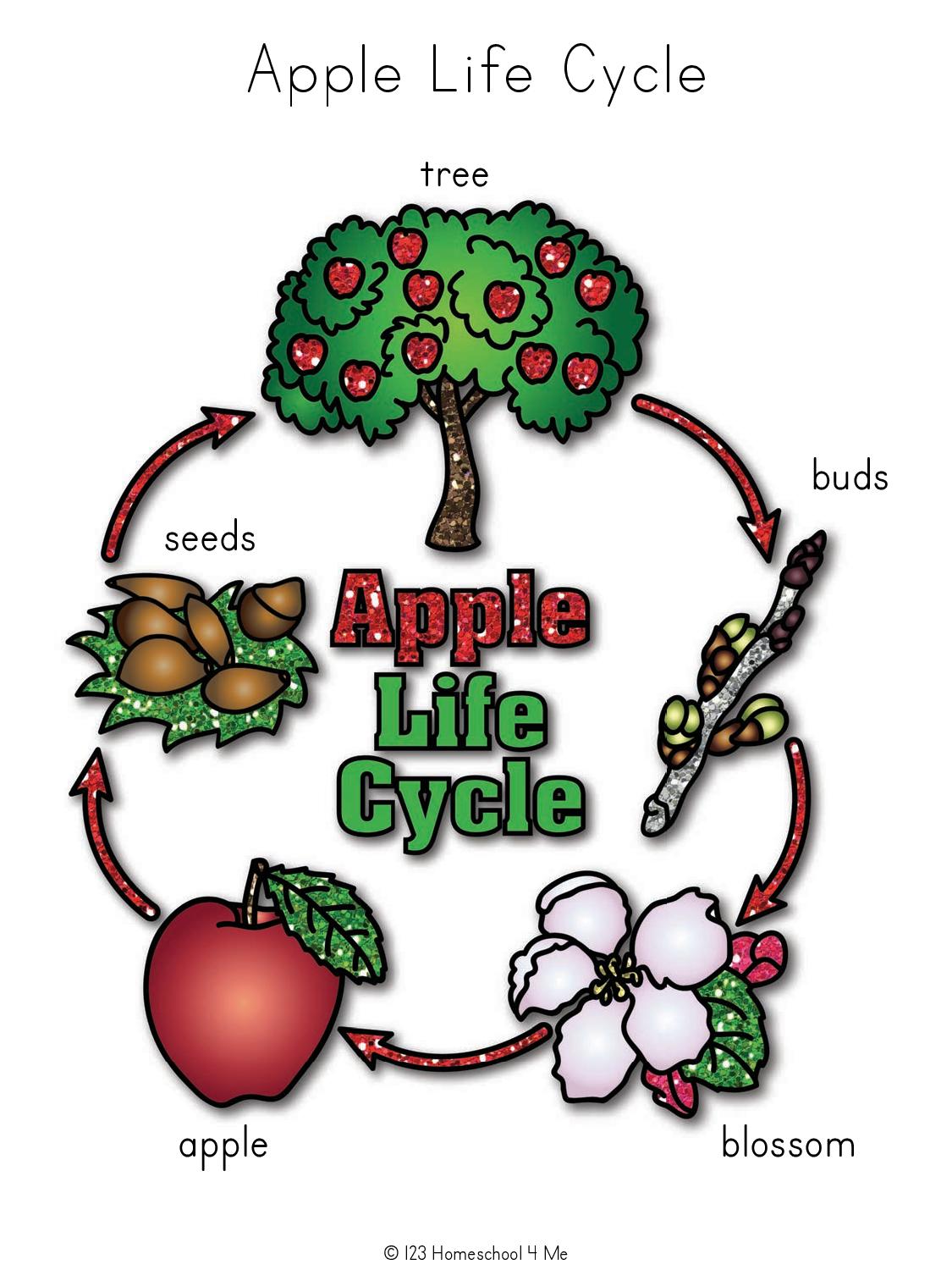
If pollination is successful:
- The flower’s ovary swells to form the apple.
- The apple ripens on the tree, taking about 3-6 months from bloom to harvest.
- Apples are usually ready for picking from late summer through autumn, depending on the variety.
6. Fruit Harvest

The journey of the apple tree culminates with:
- Harvesting: Picking the apples when they’re ripe.
- Processing: Eating, cooking, or storing apples or preparing them for various uses.
| Month | Activity |
|---|---|
| March-April | Pruning, Soil Prep |
| May | Budding & Flowering |
| June-August | Fruit Setting & Growth |
| September-November | Harvesting |

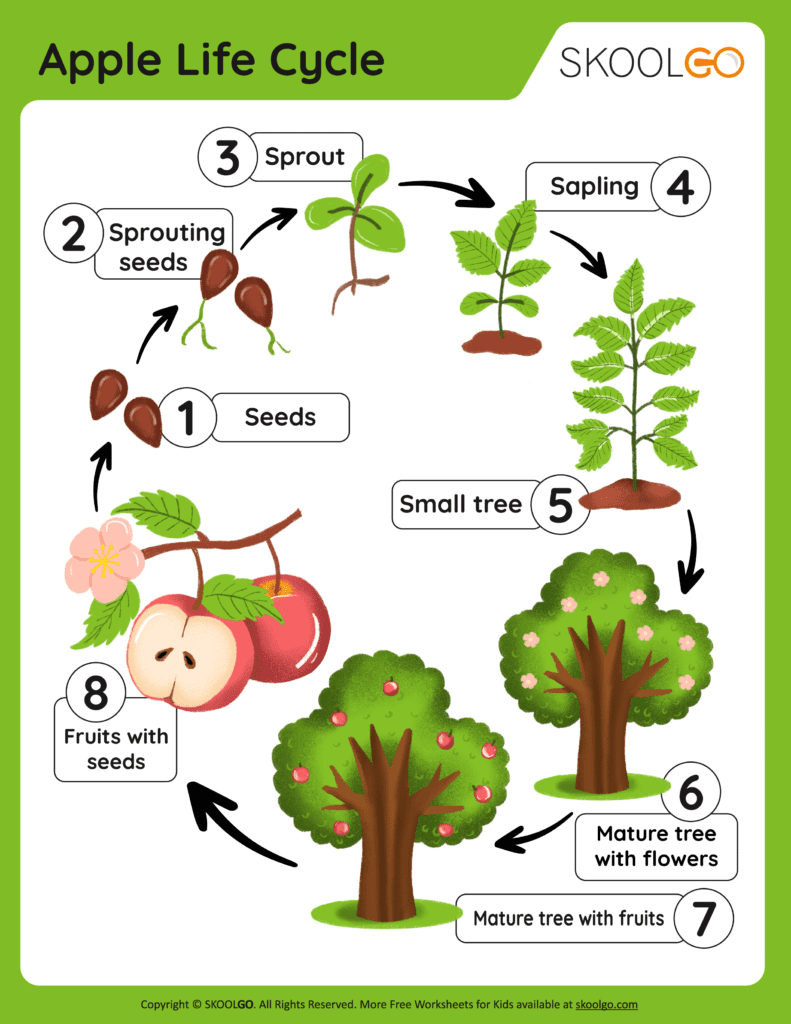
7. Distribution and End of Cycle

Upon harvesting:
- Apples are distributed for consumption or used in products.
- Seeds within apples can be replanted, continuing the cycle.
In summary, the apple tree life cycle is a marvelous journey from seed to fruit and back to seed. Through this cycle, we not only enjoy the fruits but also learn about plant reproduction, growth, and ecological interdependence. By understanding each step, we can appreciate the efforts involved in agriculture and the wonders of botany.
How long does it take for an apple tree to bear fruit?

+
It generally takes about 2 to 10 years for an apple tree to begin producing fruit, depending on the tree variety and growing conditions.
Can you grow an apple tree from the seed of an apple you eat?
+
Yes, but the tree might not produce the same type of apple as the parent tree due to genetic variability. Also, the process from seed to fruit can be quite lengthy.
What are the conditions for growing a healthy apple tree?

+
Apple trees require well-drained, fertile soil, full sun exposure, regular watering, and proper pruning to grow well. They also benefit from cross-pollination from other apple tree varieties.
What role do bees play in the apple tree life cycle?
+
Bees are crucial pollinators for apple trees. They transfer pollen from one flower to another, facilitating cross-pollination, which is necessary for fruit development in most apple tree varieties.
How does climate affect apple trees?

+
Apple trees need a certain number of chilling hours during winter to break dormancy and bloom in spring. Too warm or too cold conditions can negatively impact flowering and fruit quality.