Free Fall Physics Worksheet Answer Key Revealed
Free fall is a fundamental concept in physics, encapsulating the movement of an object where the only force acting upon it is gravity. Understanding this principle is crucial for students at various levels of education, from high school to college. This comprehensive worksheet answer key sheds light on the intricacies of free fall, providing clarity to those tackling physics problems or revising for exams. Here, we will explore the nuances of free fall, delve into the equations used to describe motion under gravity, and provide worked-out solutions to common problems found in educational settings.
Understanding Free Fall

Free fall refers to the state where an object moves under the sole influence of gravity, with no other forces altering its trajectory significantly. Here are key points to understand about free fall:
- The acceleration due to gravity (g) on Earth is approximately 9.8 m/s².
- In free fall, objects accelerate uniformly.
- The distance traveled by an object increases quadratically with time.
These points are not just theoretical; they translate into specific equations that allow us to predict motion:
| Equation | Variables |
|---|---|
| v = u + at | v (final velocity), u (initial velocity), a (acceleration), t (time) |
| s = ut + 0.5at² | s (displacement), u, t, a |
| v² = u² + 2as | v, u, a, s |

Worksheet Answer Key: Solving Free Fall Problems

Let’s dive into specific problems students might encounter in their physics worksheets:
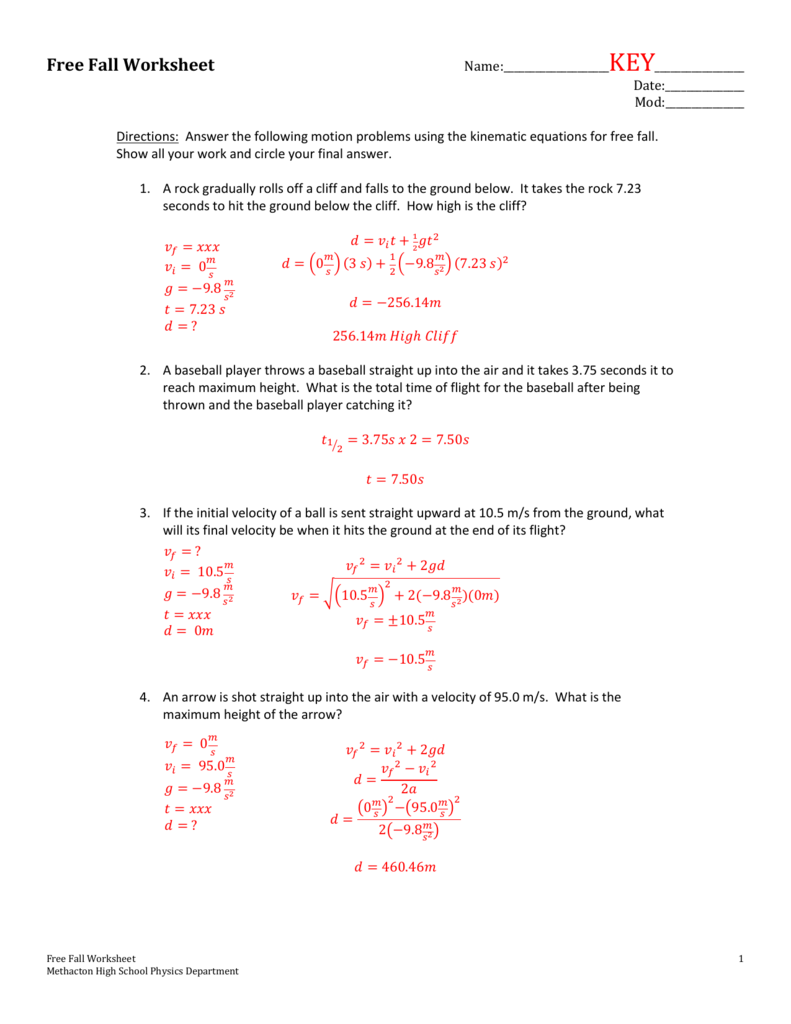
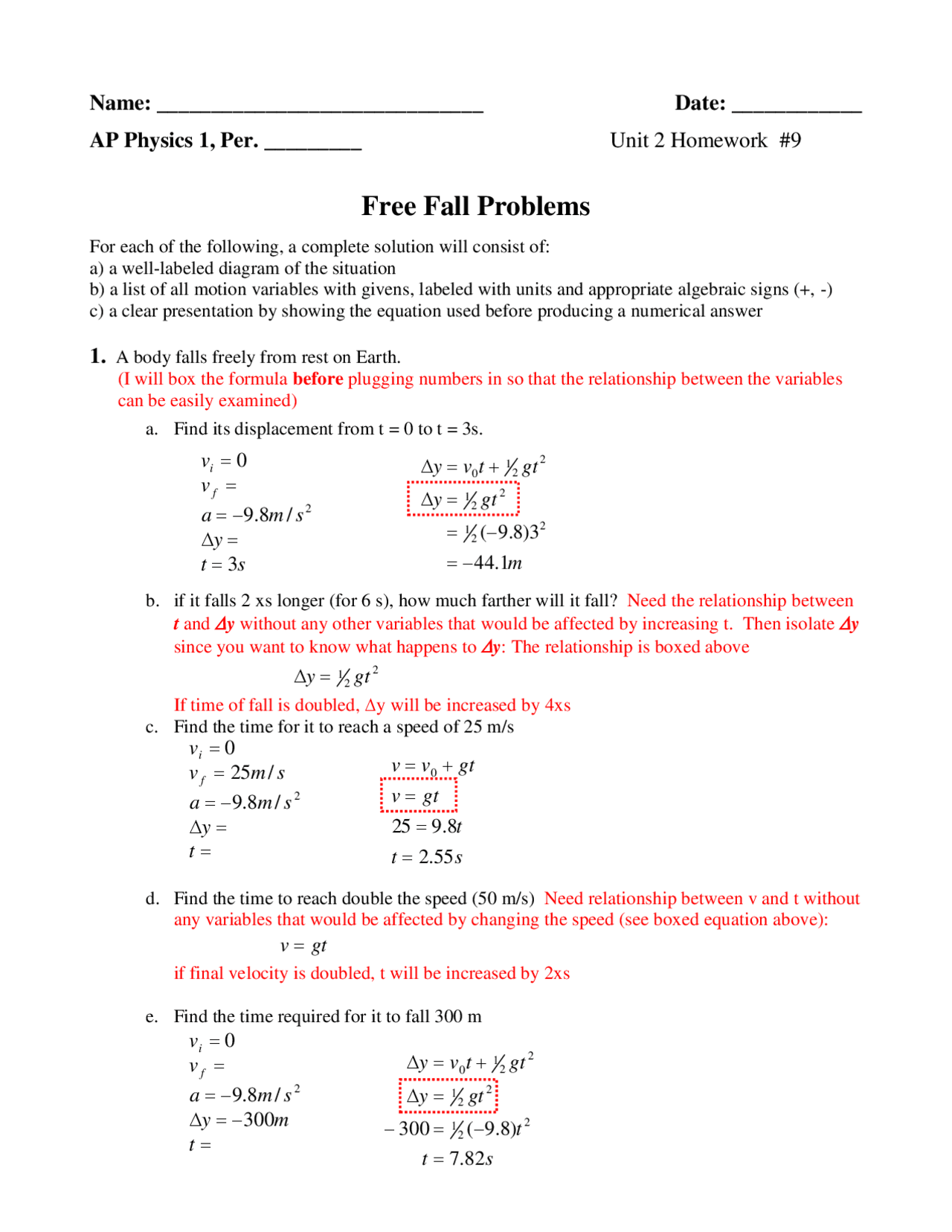
Problem 1: Time to Hit the Ground

An object is dropped from a height of 100 meters. Determine how long it takes for the object to hit the ground.
To solve this:
- Use the equation s = ut + 0.5at².
- Given s = 100m, u = 0 m/s (dropped, not thrown), and a = 9.8 m/s².
- 0.5 * 9.8 * t² = 100 (since the displacement in free fall is always positive).
- Solve for t: t² = 100/(0.5 * 9.8)
- Therefore, t ≈ 4.52 seconds.
⏱️ Note: Remember to take the square root of both sides to find time.
Problem 2: Velocity at Ground Level
What is the velocity of an object just before it hits the ground if dropped from a height of 100 meters?
Steps:
- From Problem 1, we know the time to hit the ground is approximately 4.52 seconds.
- Use v = u + at, where u = 0 m/s.
- v = 9.8 * 4.52 ≈ 44.28 m/s.
Problem 3: Height Reached by a Thrown Object

An object is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity of 20 m/s. What is the maximum height it reaches?
- At the topmost point, the velocity is zero, so v = 0 m/s.
- Use the equation v² = u² + 2as.
- Solve for s: s = (0² - 20²) / (2 * (-9.8)) = 400 / (-19.6)
- Thus, s ≈ 20.41 meters.
In wrapping up our exploration of free fall, we've covered the basic concepts, essential equations, and practical problem-solving. The understanding of these principles not only helps in academic pursuits but also in comprehending the natural world around us. From dropping a ball to analyzing how far a meteorite might travel through Earth's atmosphere, free fall physics provides foundational knowledge for various scientific and engineering fields.
What is free fall?

+
Free fall is the motion of an object where gravity is the only force acting upon it, meaning that it accelerates uniformly towards the Earth or another gravitational body.
How is free fall different from regular falling?

+
Free fall refers to falling in the absence of any other significant forces like air resistance, ensuring only gravity influences the motion. Regular falling might include additional forces affecting the object’s descent.
Can free fall occur in space?
+
Yes, but in space, objects can be in “free fall” around massive bodies like planets or stars, essentially orbiting them due to gravity, where other forces are negligible compared to gravity.