Fraction Vocabulary Worksheet: Essential Math Terms for Kids

Mastering basic math concepts like fractions is crucial for young learners, particularly for developing a solid foundation in mathematics. This article dives deep into fraction vocabulary, essential for kids who are stepping into the world of numbers and operations with fractions. Here, we aim to elucidate common fraction terms, why they matter, and how to use them effectively to understand fractions better.
What are Fractions?

At its core, a fraction represents a part of a whole. Imagine a delicious apple pie; if you divide it into 8 equal pieces, each piece is a fraction of the pie. Here's a basic explanation of fractions:
- Numerator: The number above the line, which tells how many parts you are considering.
- Denominator: The number below the line, indicating into how many equal parts the whole has been divided.
- Whole: The entire pie, object, or quantity which has been divided.
Essential Fraction Terms
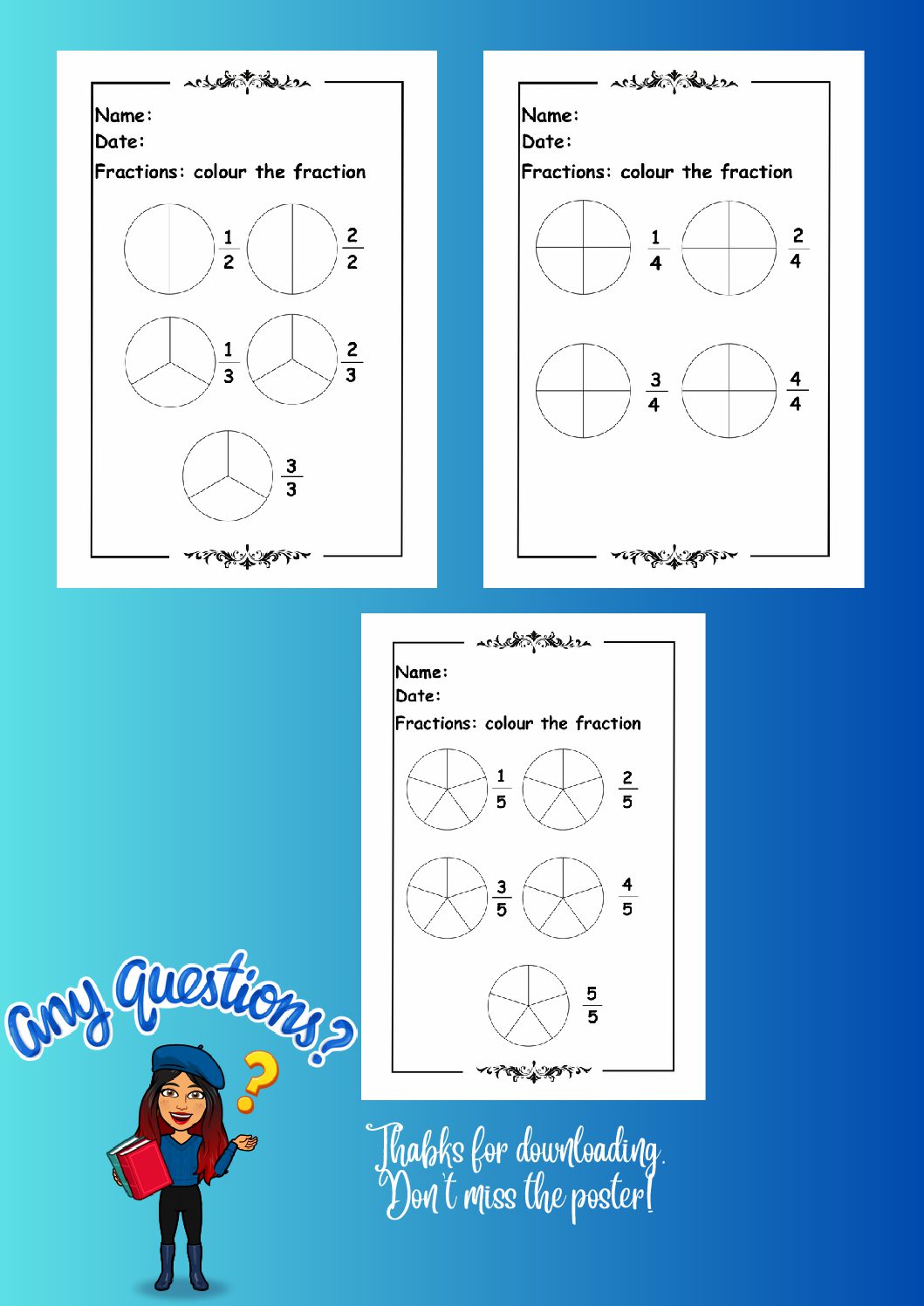
Numerator and Denominator

Understanding these two terms is the first step in learning fractions:
- The numerator indicates the number of slices we’re taking from the whole.
- The denominator represents how the whole is split up; essentially, it’s like the number of slices in the whole pie.

The relationship between the numerator and the denominator helps to understand what part of the whole a fraction represents.
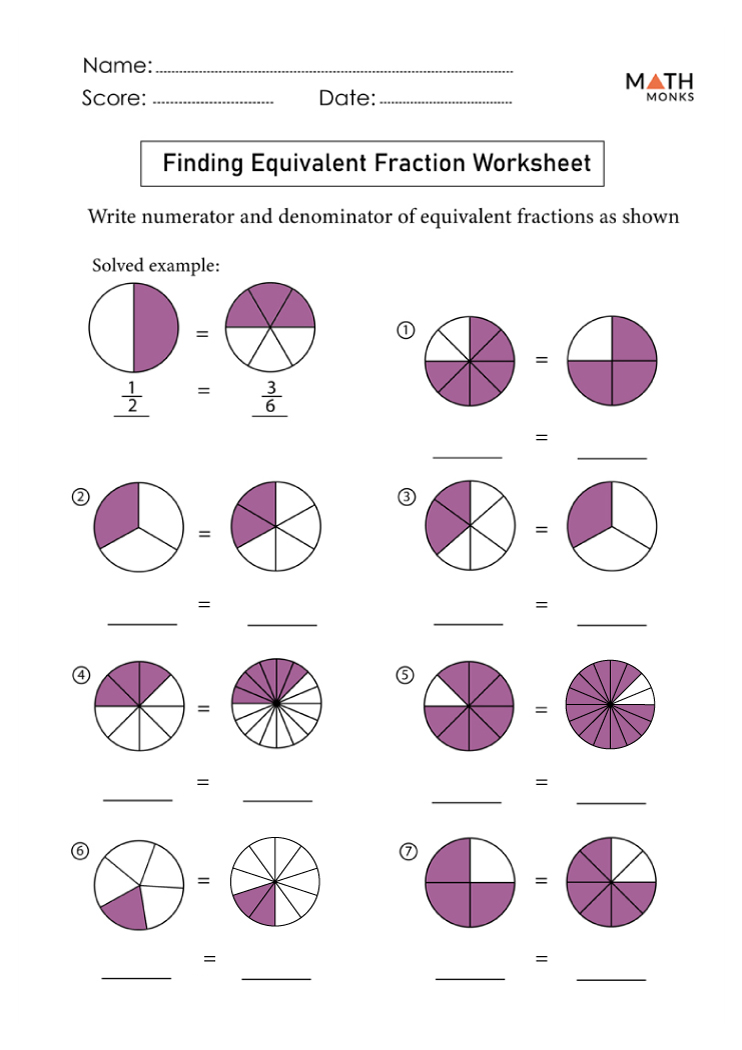
Equivalent Fractions

Two or more fractions represent the same value, even though they might look different. For example:
| Fraction | Equivalent Fractions |
|---|---|
| 1⁄2 | 2⁄4, 3⁄6, 5⁄10 |
These are equivalent because they simplify to the same fraction.
Simplifying Fractions

Also known as reducing fractions, this process involves dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common divisor (GCD). Here’s an example:
- Start with 8⁄12
- Both 8 and 12 share a GCD of 4
- 8 divided by 4 equals 2, 12 divided by 4 equals 3
- So, 8⁄12 simplifies to 2⁄3
Mixed Numbers
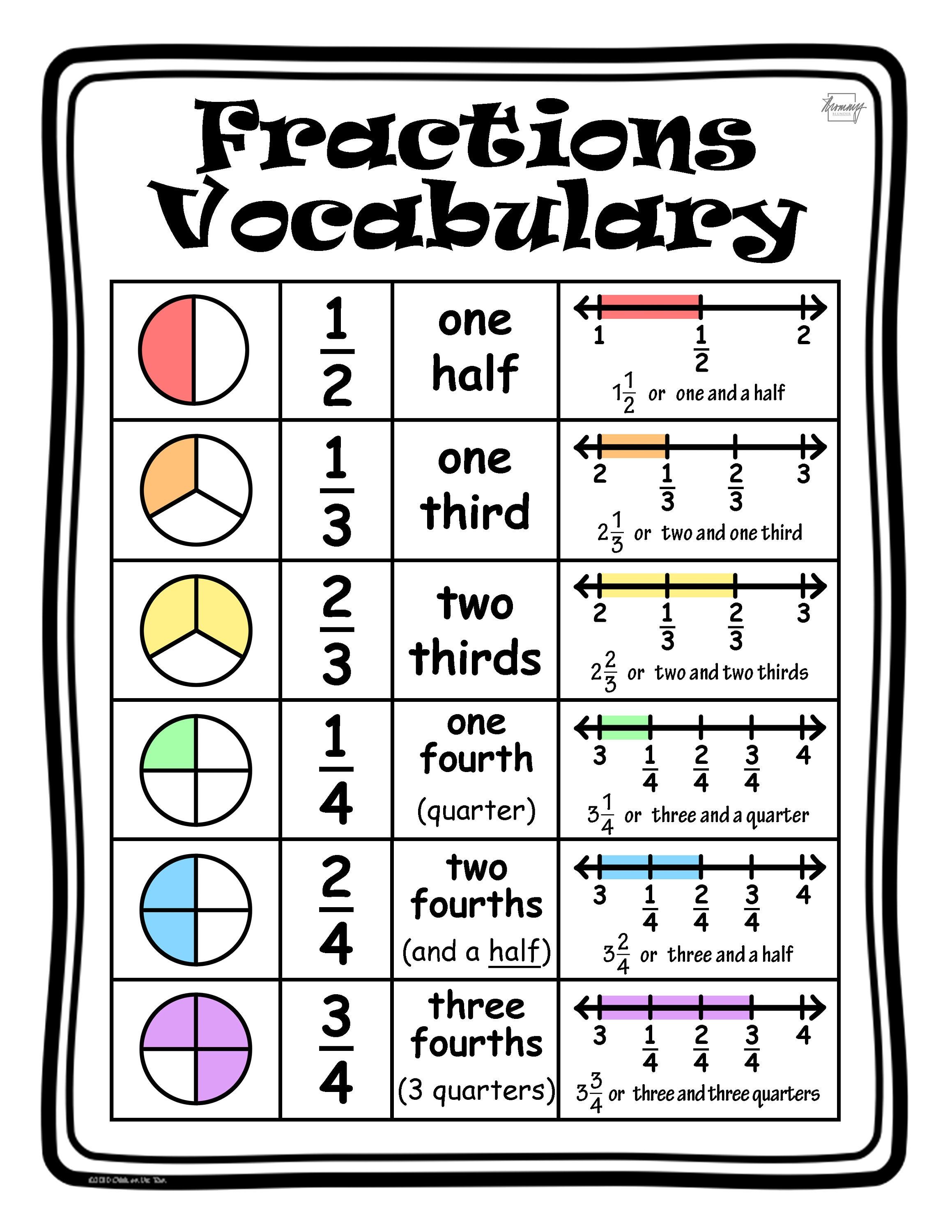
Mixed numbers consist of a whole number plus a proper fraction, like 2 and 1⁄4. These can be converted to improper fractions or vice versa:
- Conversion to Improper Fraction: Multiply the whole number by the denominator, add the numerator, and place this over the original denominator (e.g., 2 and 1⁄4 becomes 9⁄4).
- Conversion to Mixed Number: Divide the numerator by the denominator to get the whole number, the remainder becomes the new numerator, and the denominator remains the same (e.g., 9⁄4 equals 2 and 1⁄4).
💡 Note: Mixed numbers are useful for expressing quantities that are greater than one but still involve fractional parts.
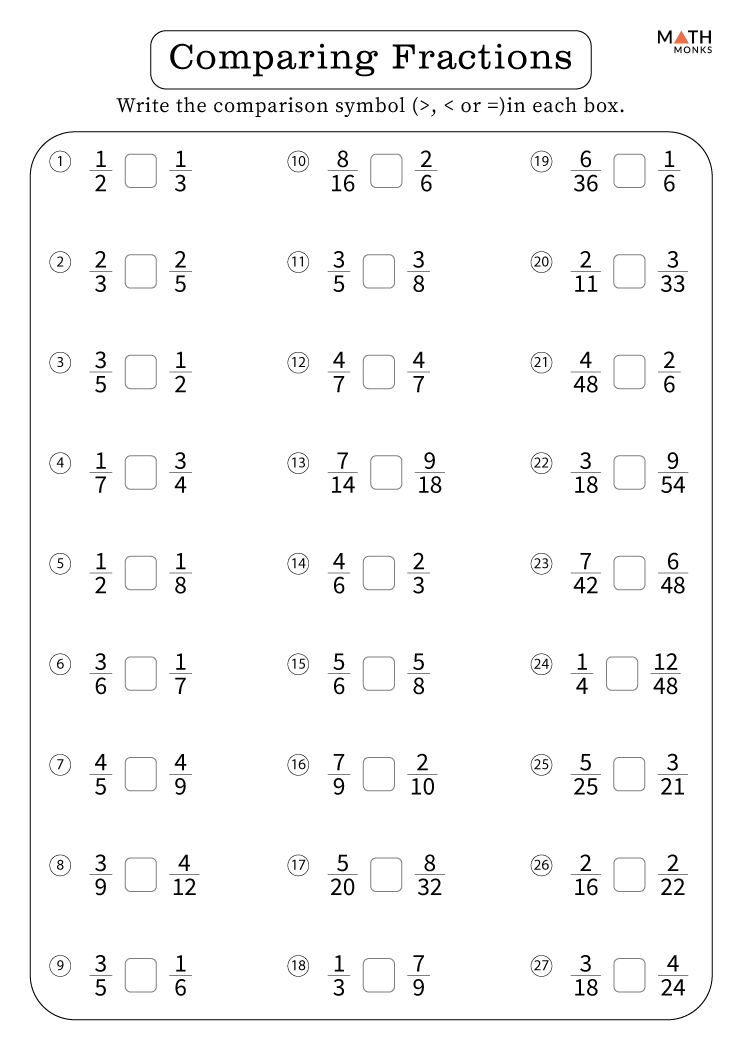
Comparing Fractions
To compare fractions, you can find a common denominator or convert them to decimals:
- Direct comparison can be achieved by ensuring fractions have the same denominator, which allows for a straight numeration comparison.
- Convert fractions to decimals or use a number line to visualize their value.
Proper and Improper Fractions

Recognizing the difference between proper and improper fractions is essential:
- Proper Fraction: When the numerator is smaller than the denominator, e.g., 3⁄5.
- Improper Fraction: The numerator is equal to or greater than the denominator, e.g., 5⁄3.
How to Teach Fraction Vocabulary to Kids

Teaching fraction vocabulary to kids involves a combination of visual aids, real-world examples, and engaging activities:
- Use everyday items: Cutting a pizza or an apple pie into equal parts visually represents fractions.
- Interactive Worksheets: Provide kids with fraction vocabulary worksheets where they match terms with their definitions or solve fraction problems.
- Storytelling: Create stories or scenarios where fractions play a role (e.g., dividing a candy bar among friends).
Engage them in activities that make learning both fun and relevant.
Math is not just about numbers; it's a language, a way to describe relationships between quantities. Understanding fraction vocabulary is akin to learning the grammar of this language, allowing kids to express complex ideas with precision. By focusing on key terms like numerator, denominator, equivalent fractions, simplifying, mixed numbers, comparing, and distinguishing between proper and improper fractions, young learners are better equipped to navigate the vast terrain of mathematics with confidence and skill.
As they grow, these foundational concepts will serve as building blocks for more complex mathematical operations, from algebra to calculus. The process of mastering fraction vocabulary opens up a world where numbers become tools to analyze, solve problems, and comprehend the environment around us.
As the finale, remember that teaching fractions is not just about memorizing terms but understanding their application in real life. The skills developed through learning fractions will support a child's journey through various stages of education and beyond, making it an invaluable area of focus in their early math education.
Why are fractions important in math?
+
Fractions are essential because they help us understand and work with parts of whole numbers, ratios, proportions, measurements, and division problems that don’t result in whole numbers. They are foundational for higher math like algebra, geometry, and beyond.
What is the difference between a mixed number and an improper fraction?

+
A mixed number is a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction, while an improper fraction has a numerator that is equal to or greater than its denominator, representing more than one whole.
How can equivalent fractions be useful?

+
Equivalent fractions allow us to compare and add or subtract fractions with different denominators by converting them to a common base. This simplification can make complex problems much easier to solve.