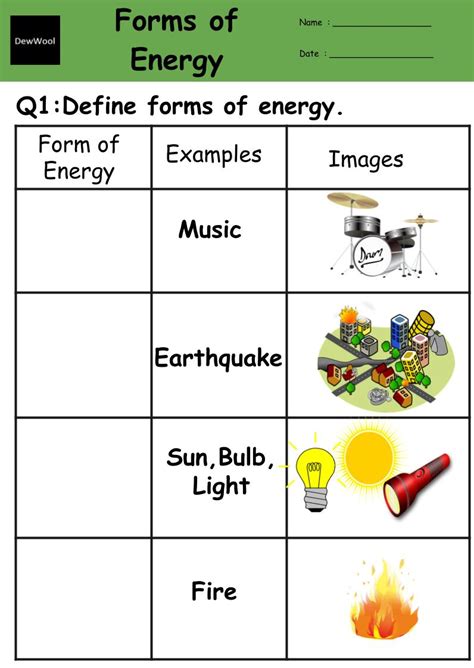
Forms of Energy Worksheet: Learn and Explore
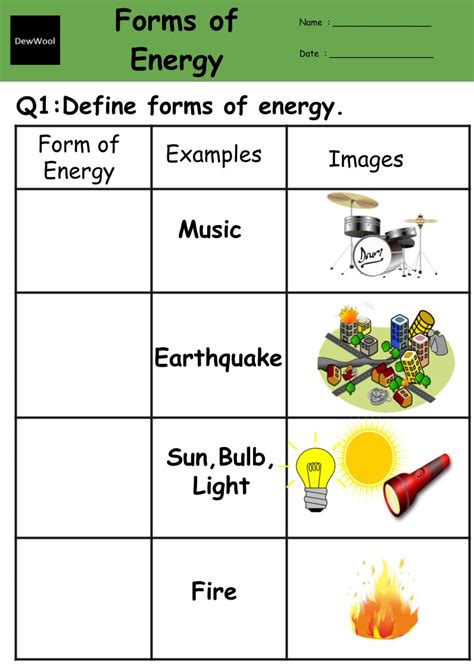
Understanding Different Forms of Energy

Energy is the ability to do work, and it comes in various forms. In this article, we will explore the different types of energy, their characteristics, and examples of each.
What are the Main Forms of Energy?

There are several main forms of energy, which can be broadly classified into two categories: kinetic energy and potential energy. Within these categories, there are several sub-forms of energy.
Kinetic Energy
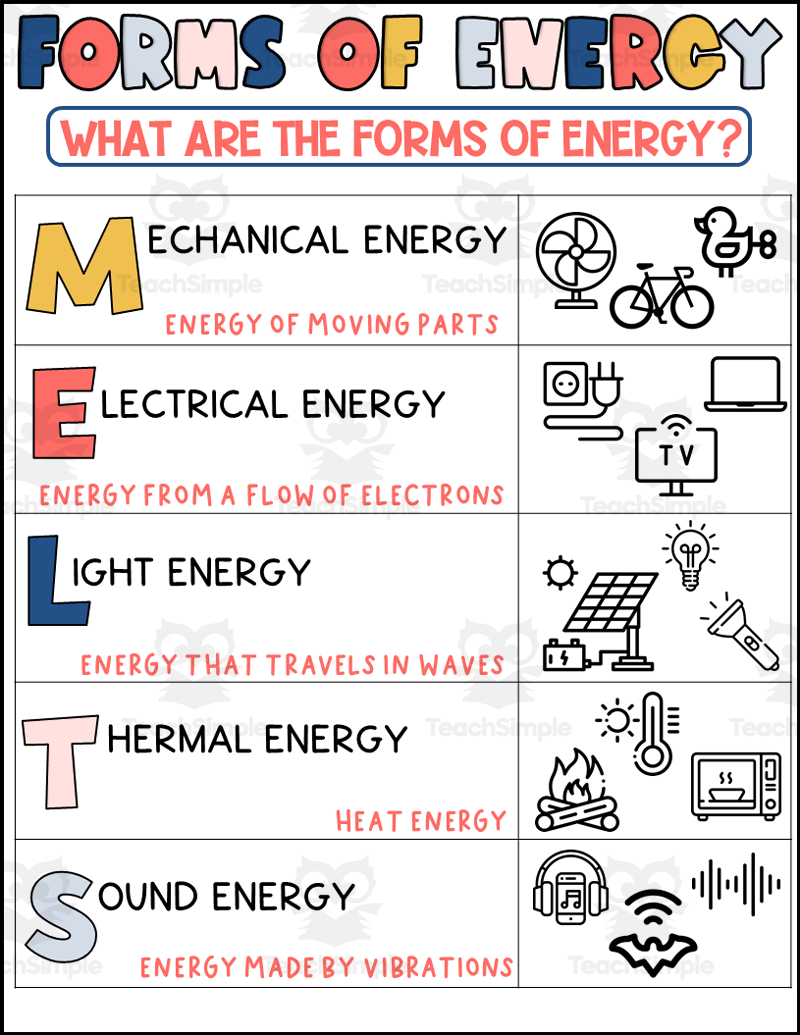
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. It is the energy an object possesses when it is moving.
- Thermal Energy: The energy an object possesses due to the motion of its particles. Examples include the heat from a fire or the warmth from the sun.
- Mechanical Energy: The energy an object possesses due to its motion or position. Examples include the energy of a rolling ball or a flying airplane.
- Electrical Energy: The energy that flows through a circuit, powering devices such as light bulbs and computers.
Potential Energy

Potential energy is stored energy that has the potential to do work.
- Chemical Energy: The energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules. Examples include the energy from food and gasoline.
- Nuclear Energy: The energy stored in the nucleus of an atom. Examples include the energy from nuclear power plants and atomic bombs.
- Gravitational Energy: The energy an object possesses due to its height or position. Examples include the energy of water stored behind a dam or the energy of a ball at the top of a hill.
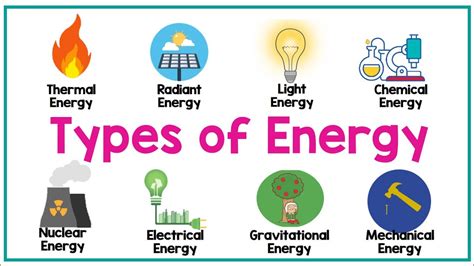
Other Forms of Energy
In addition to kinetic and potential energy, there are several other forms of energy.
- Radiant Energy: The energy of electromagnetic waves, including light and radio waves.
- Sound Energy: The energy of sound waves.
- Elastic Energy: The energy stored in stretched or compressed materials.
Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy Sources
Energy sources can be classified as renewable or non-renewable.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Energy sources that are sustainable and can be replenished naturally. Examples include solar energy, wind energy, and hydro energy.
- Non-Renewable Energy Sources: Energy sources that are finite and cannot be replenished naturally. Examples include fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas.
Energy Conversion

Energy can be converted from one form to another.
- Energy Transformation: The process of changing energy from one form to another. Examples include the conversion of chemical energy from gasoline to mechanical energy in a car engine.
- Energy Efficiency: The measure of how efficiently energy is converted from one form to another.
Conclusion
In conclusion, energy is a vital part of our daily lives, and understanding the different forms of energy is essential for harnessing and utilizing it effectively. By recognizing the various types of energy and their characteristics, we can better appreciate the importance of energy conservation and sustainable energy sources.
What are the main forms of energy?

+
The main forms of energy are kinetic energy and potential energy. Kinetic energy includes thermal energy, mechanical energy, and electrical energy, while potential energy includes chemical energy, nuclear energy, and gravitational energy.
What is the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy sources?

+
Renewable energy sources are sustainable and can be replenished naturally, while non-renewable energy sources are finite and cannot be replenished naturally.
What is energy conversion?

+
Energy conversion is the process of changing energy from one form to another. Energy transformation and energy efficiency are important concepts in energy conversion.
Related Terms:
- Forms of energy worksheet pdf