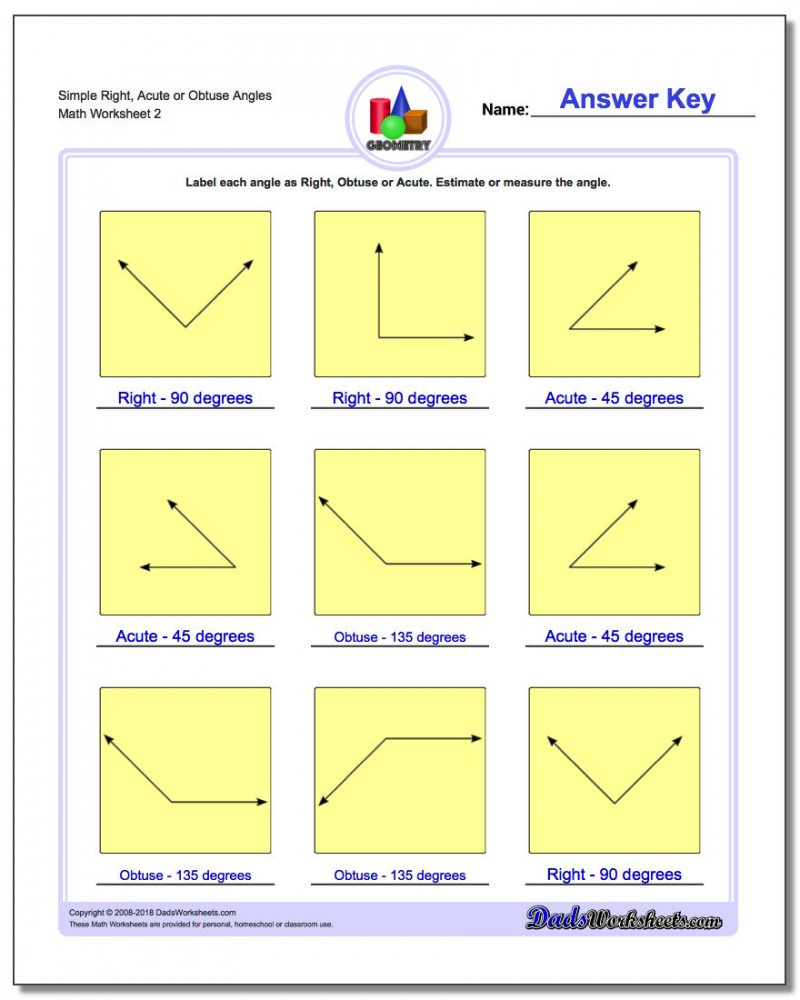
First Branch Legislative Worksheet: Master Your Civic Knowledge

In today's fast-paced society, understanding how legislation works can be both empowering and enlightening. For many, the first branch of government, often referred to as the legislative branch, remains an enigma. Today, we'll delve into the structure, functions, and significance of this crucial segment of government. Whether you're a student preparing for a civics class, a curious citizen, or someone keen on participating more actively in the political process, this comprehensive guide will help you master your civic knowledge.
What is the Legislative Branch?

The legislative branch is one of the three main divisions of the government, responsible for making laws. In the United States, this branch comprises:
- The Senate
- The House of Representatives
Each state elects two Senators to serve a six-year term, while representatives in the House are apportioned based on population, serving two-year terms.
The Structure of the Legislative Branch
The Senate

The Senate has several unique features:
- Equal representation with two Senators per state.
- Senators are chosen by state legislatures originally, but since the 17th Amendment, they are elected by popular vote.
- The Vice President acts as the President of the Senate with the ability to cast tie-breaking votes.
The House of Representatives

Here's what makes the House distinctive:
- Representation is based on population; larger states have more representatives.
- The Speaker of the House leads and sets the legislative agenda.
- Originating legislation related to revenue and taxation is an exclusive power.
Key Functions of the Legislative Branch

- Lawmaking: The primary role, where bills are proposed, debated, and potentially passed into law.
- Oversight: Ensuring the executive branch adheres to the law by conducting investigations and hearings.
- Representation: Voicing the concerns and interests of the public in national issues.
- Constituency Services: Assisting citizens with federal agency issues or casework.
📝 Note: The legislative process can be quite complex, involving committee stages, amendments, and reconciliation between the House and Senate versions of a bill.
Understanding the Legislative Process
How a Bill Becomes Law

The journey from an idea to legislation is intricate:
- Introduction of Bill: A member of Congress proposes the bill, which is then assigned to a committee.
- Committee Action: The bill is scrutinized, amended, and if approved, moves forward.
- Floor Action: Both houses debate, amend, and vote on the bill.
- Conference Committee: If the Senate and House versions differ, this committee reconciles the differences.
- Final Votes: Both houses vote again on the reconciled version.
- Presidential Action: The President can sign it into law, veto it, or take no action (a pocket veto if Congress adjourns).
Key Terms and Concepts

- Bicameral Legislature: A two-chamber legislature, like the U.S. with the Senate and House.
- Appropriations: Funds allocated by Congress to various federal programs.
- Filibuster: A tactic used in the Senate to delay or block legislation through extended debate.
- Cloture: A method to end a filibuster, requiring a supermajority vote.
The Importance of Civic Engagement

Engaging in the legislative process is vital for several reasons:
- Influence Policy: Your participation can impact the laws passed.
- Accountability: Holding elected officials accountable for their actions.
- Education: Learning more about how our government works, increasing your political literacy.
💡 Note: Use tools like the "Find Your Representative" feature on the official websites of your country to easily contact your elected officials.
Steps to Participate in the Legislative Process

- Stay Informed: Read legislative updates, watch committee hearings, and follow news outlets dedicated to politics.
- Communicate: Write letters, emails, or call your representatives to voice your support or opposition to specific bills.
- Attend Town Halls: These events allow direct interaction with your legislators.
- Join Advocacy Groups: Organizations often have direct lines to policymakers.
- Vote: Your vote is your most powerful tool for change.
As we conclude our journey through the legislative branch, remember that knowledge is power. Understanding this branch's role in our governance system equips you to engage more effectively in democracy. Whether you're watching legislation unfold or directly participating in the process, your involvement shapes the laws that govern our lives. Through this exploration, we've seen the complexity and beauty of our legislative system. It’s a system where every voice, when amplified through civic engagement, can make a difference. Keep learning, stay curious, and never underestimate the impact you can have on the democratic process.
Why does the U.S. have a bicameral legislature?

+
The bicameral system ensures that small states and large states have equal representation through the Senate and population-based representation in the House, providing balance.
How can I contact my representative?

+
You can find your representative’s contact information by visiting official government websites or using tools like ‘Find Your Representative’ provided by many civic organizations.
What is a filibuster?

+
A filibuster is a procedural tactic used by Senators to delay or prevent a vote on legislation, often by speaking for extended periods to block the process.
What happens if the President vetoes a bill?

+
Congress can override a veto with a two-thirds majority vote in both the House and Senate, allowing the bill to become law despite the President’s disapproval.
How can citizens influence the legislative process?

+
Citizens can engage through various channels like contacting representatives, participating in advocacy groups, attending public forums, and exercising their voting rights.