Master Worksheet for X and Y Intercepts

The concept of X and Y intercepts is fundamental in the study of algebraic equations and graph plotting in mathematics. Whether you're a student tackling algebra for the first time or a professional who often deals with data visualization, understanding these intercepts can streamline the interpretation and manipulation of linear equations. In this blog post, we'll explore in depth how to find, interpret, and apply X and Y intercepts in various contexts.
Understanding X and Y Intercepts

The X-intercept of a line or curve is the point where the function crosses or touches the x-axis. Here, the y-coordinate is zero. Conversely, the Y-intercept is the point where the function crosses or touches the y-axis, where the x-coordinate is zero.
Equations and Graphs

General Form of Linear Equation

The standard form of a linear equation is:
ax + by = c
Where:
- a is the coefficient of x
- b is the coefficient of y
- c is the constant term
To find the X-intercept, set y = 0 and solve for x:
ax = c
x = c/a
Similarly, for the Y-intercept, set x = 0 and solve for y:
by = c
y = c/b
Graphical Representation


Steps to Find X and Y Intercepts

- Isolate the Variable: Start by isolating the variable in question (X for X-intercept, Y for Y-intercept).
- Set One Variable to Zero: Set the other variable to zero to get either the X-intercept or Y-intercept.
- Solve for the Remaining Variable: Algebraically solve for the remaining variable.
Application in Real World Scenarios

Economic Models

In economics, intercepts can represent:
- Y-intercept: Fixed costs or starting value.
- X-intercept: Breakeven point where cost equals revenue.
📉 Note: In economic analysis, the X-intercept can be critical in determining at what quantity production becomes profitable.
Physics

Intercepts are often used in physics to:
- Determine initial conditions in motion problems, where the Y-intercept might indicate the initial position.
- Calculate time at which an object will cross a certain point (X-intercept).
Data Science

In data science, understanding intercepts:
- Helps in interpreting regression models by identifying the expected value of the dependent variable when all independent variables are zero.
Advanced Examples
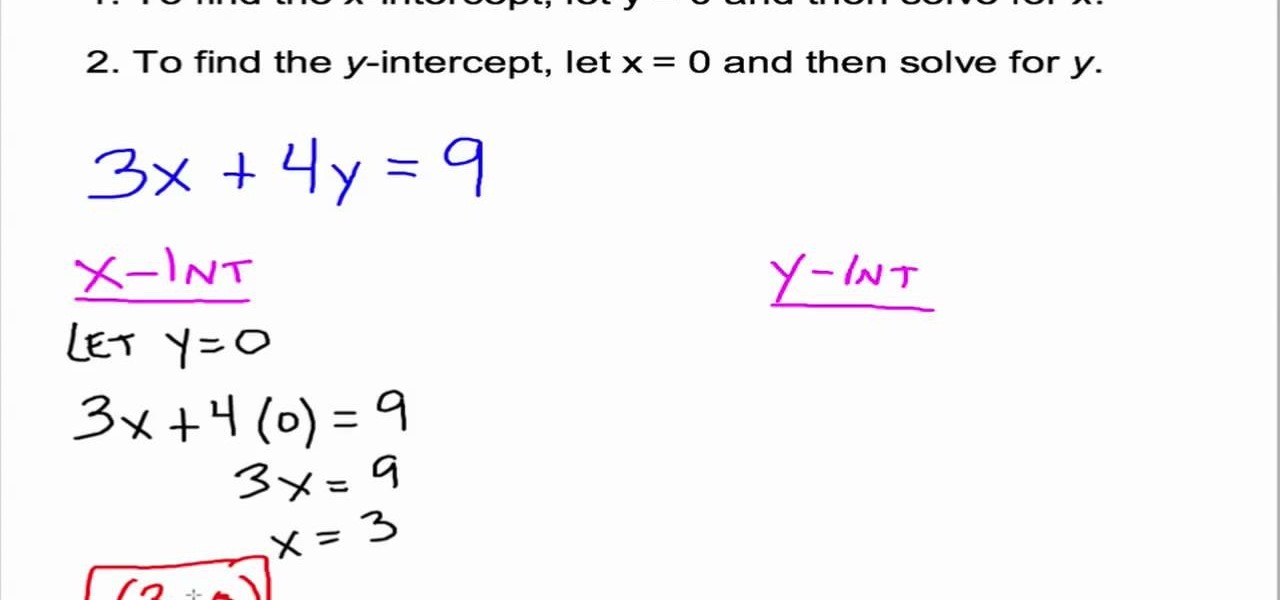
Quadratic Equations
The X-intercepts of a quadratic equation ax² + bx + c = 0 can be found using the quadratic formula:
x = (-b ± √(b²-4ac)) / (2a)
These solutions represent the points where the parabola crosses the x-axis.
Polynomials

For higher degree polynomials, finding exact X-intercepts might require numerical methods like the Newton-Raphson method or graphing calculators, which can visualize where the polynomial intersects the x-axis.
Interpretation of Intercepts

Linear Regression

In linear regression, the Y-intercept is the predicted value of the dependent variable when the independent variable equals zero. It often represents a base value or initial state in the model.
Linear Programming
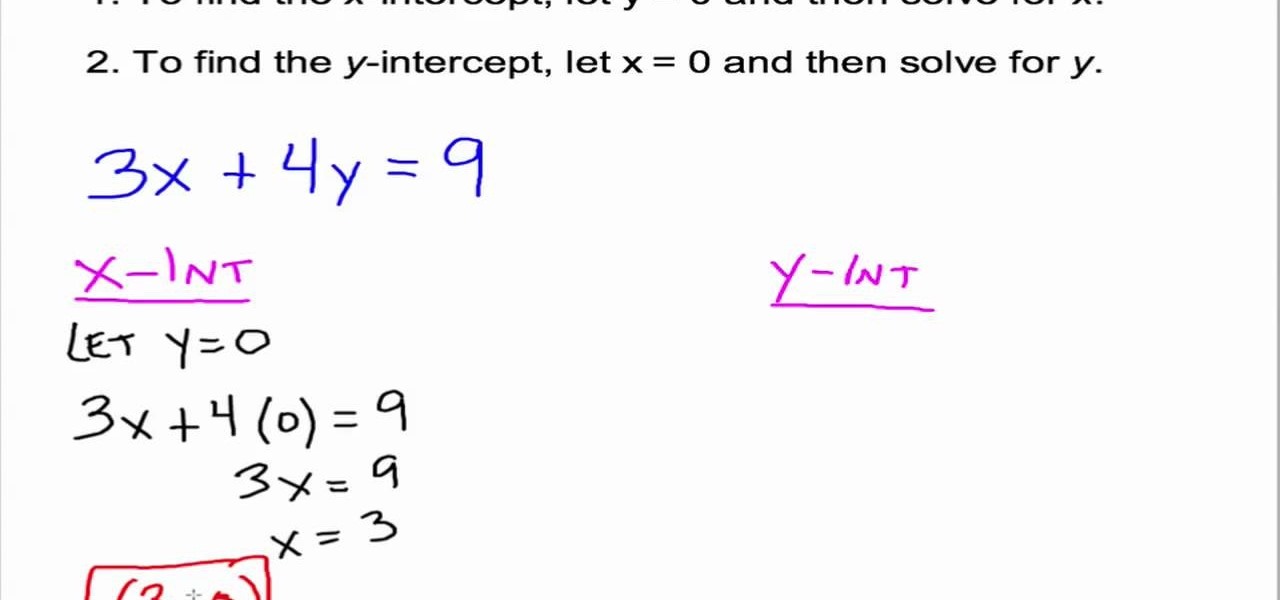
In linear programming, intercepts can help in defining the feasible region by plotting constraints. Each intercept represents where a constraint line touches an axis, providing bounds to the solution space.
The mastery of X and Y intercepts opens up a realm of possibilities for interpreting and manipulating equations in both academic and professional settings. From simple algebraic solutions to complex real-world applications in economics, physics, and data science, these intercepts are not just numbers but key insights into behavior, predictions, and optimizations.
What is the importance of X and Y intercepts in linear equations?

+
They help in plotting the graph, understanding where the line intersects the axes, and provide initial conditions or starting points for various applications.
How do you find X and Y intercepts algebraically?
+For X-intercept, set y = 0 and solve for x. For Y-intercept, set x = 0 and solve for y. This method applies to linear and some non-linear equations.
Can all equations have X and Y intercepts?
+Not all equations will have both X and Y intercepts. For instance, lines parallel to the x or y axis will have only one intercept or none at all.
Why might the Y-intercept be negative?
+A negative Y-intercept can indicate a base value below zero or a loss in economic models, or it can simply reflect the natural placement of the function on the coordinate plane.
What do X and Y intercepts tell us in the context of linear regression?
+In linear regression, the Y-intercept represents the expected value of the dependent variable when the independent variable is zero. X-intercepts can show where the model predicts zero outcome or a change in trend.