Mastering Slope: Line Worksheet Tips

Mastering the concept of slope in mathematics is essential for understanding various aspects of algebra, geometry, and calculus. The slope of a line represents the steepness and direction of a line segment or curve, making it a fundamental concept in graphing and analyzing linear equations. This post will delve into strategies for mastering slope through line worksheet exercises, providing you with a step-by-step guide to understanding this pivotal mathematical principle.
Understanding Slope
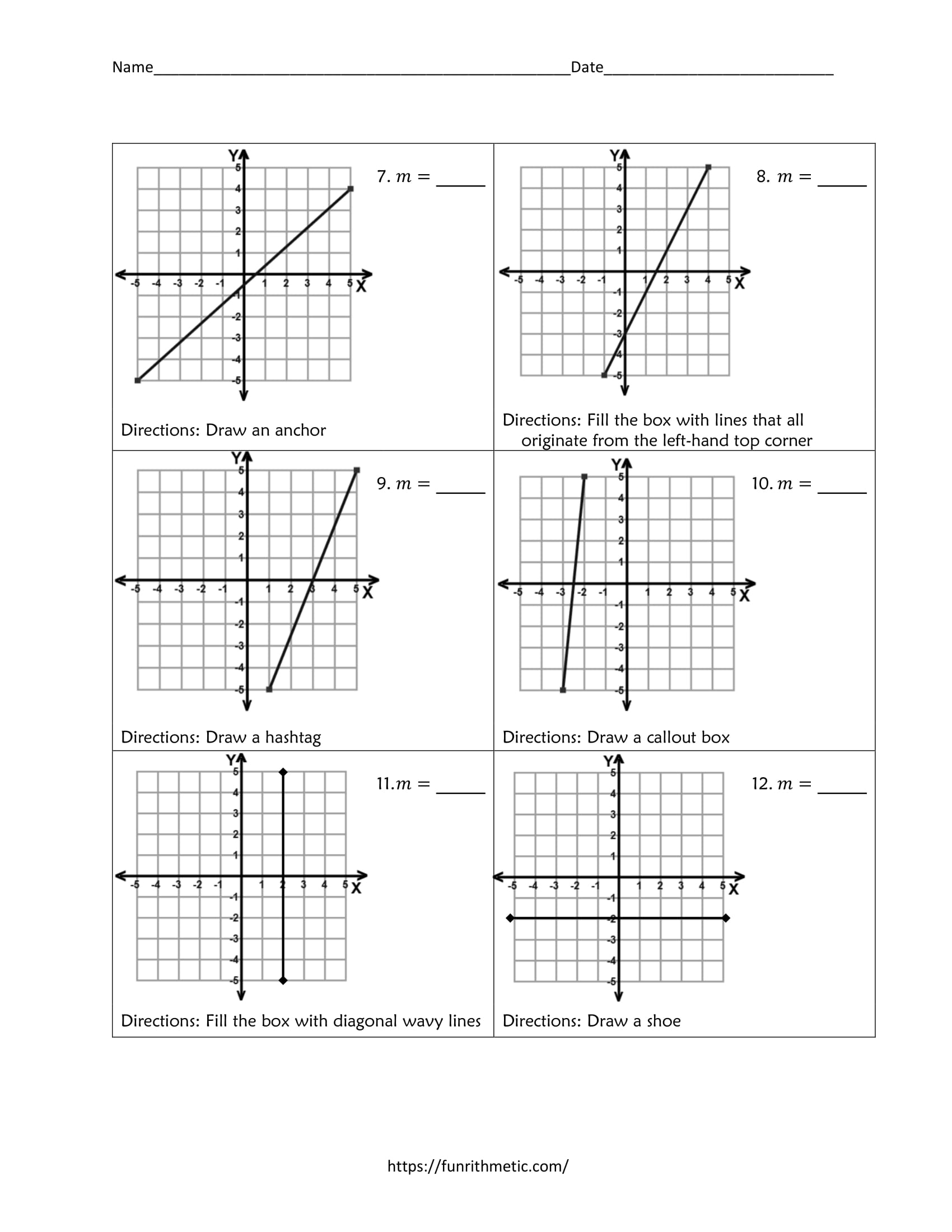
Before we dive into the worksheets, let’s solidify our understanding of what slope is:
- Definition: Slope is defined as the ratio of the “rise” (vertical change) to the “run” (horizontal change) between two points on a line.
- Formula: The slope (m) of a line between two points ((x_1, y_1)) and ((x_2, y_2)) is calculated using: [ m = \frac{y_2 - y_1}{x_2 - x_1} ]
- Positive vs. Negative Slope: A positive slope indicates a line that rises from left to right, while a negative slope means the line falls.
- Zero Slope: A horizontal line has zero slope.
- Undefined Slope: A vertical line has an undefined slope.
Working with Slope Worksheets

Here’s how you can effectively work through slope problems on worksheets:
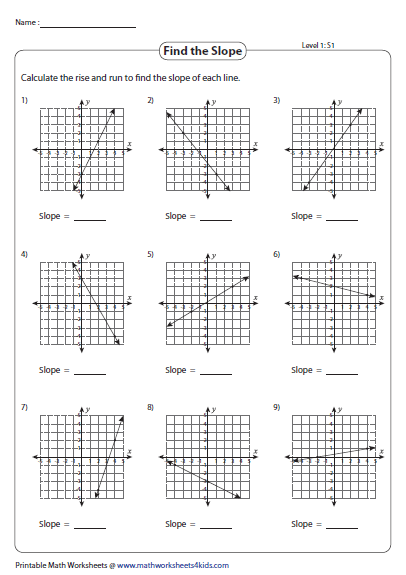
1. Identifying Slope from Graphs

- Read the Line: Look at the graph to visually determine the slope by the angle of the line.
- Use the Rise Over Run: Count the number of units the line rises or falls for every one unit it moves horizontally.
2. Calculating Slope Between Points

Follow these steps when calculating slope from two given points:
- Identify the coordinates of two points on the line.
- Apply the slope formula directly.
- Subtract the y-coordinates (rise) and the x-coordinates (run).
- Divide the rise by the run.
Here is a quick reference for calculating slope:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Identify points ( (x_1, y_1) ) and ( (x_2, y_2) ). |
| 2 | Calculate ( \Delta y = y_2 - y_1 ) (rise). |
| 3 | Calculate ( \Delta x = x_2 - x_1 ) (run). |
| 4 | Use formula ( m = \frac{\Delta y}{\Delta x} ). |

3. Slope-Intercept Form
The equation ( y = mx + b ) is a helpful tool for understanding how slope works in a line:
- m represents the slope of the line.
- b is the y-intercept where the line crosses the y-axis.
📌 Note: When finding the y-intercept, remember that it’s the value of (y) when (x) is zero.
4. Practice with Different Scenarios

- Parallel Lines: Lines are parallel if they have the same slope.
- Perpendicular Lines: The product of the slopes of two perpendicular lines is -1.
- Multiple Choice Slope Exercises: Use strategies like elimination or plug-in to quickly find the correct slope.
Tips for Success with Slope Worksheets

- Draw to Understand: Sketching the line can give you a better visual representation of the slope.
- Understand the Context: Know when slopes are relevant in real-world scenarios like hills or ramps.
- Memorize Key Slope Values: Knowing slopes like 1⁄2, 2, -3, etc., can speed up your calculations.
- Check Work: Always verify your slope calculations with another method or by reversing the point order.
✅ Note: Practice regularly; understanding slope becomes intuitive over time.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid

- Incorrect Calculation: Double-check subtraction order in the numerator and denominator.
- Division by Zero: Be cautious with vertical lines; remember they have an undefined slope.
- Overlooking Signs: Pay attention to the signs of (x) and (y) coordinates to correctly determine the direction of the line.
- Misinterpreting Graphs: Ensure you are reading the graph correctly, especially in terms of scale.
🚧 Note: Always read the problem thoroughly to understand what is being asked.
As we conclude our exploration of slope, remember that mastery in this area comes from consistent practice and a deep understanding of how slope influences the behavior of lines. Whether you are graphing, solving for equations, or understanding real-life applications, the concept of slope is integral. Keep practicing with various exercises, use the provided strategies, and watch as your confidence and proficiency in handling line equations grow. Happy learning!
What does slope tell you about a line?

+
Slope informs you about the steepness and direction of a line. A positive slope means the line rises from left to right, whereas a negative slope indicates a descent. The numerical value of the slope gives the angle’s sharpness; the larger the value, the steeper the line.
Can a slope be negative?

+
Yes, slope can be negative. A negative slope indicates that the line falls as you move from left to right, signifying a downward trend.
Why are slopes relevant outside of math?

+
Slopes are crucial in fields like physics (understanding forces and motion), economics (analyzing trends), architecture (designing structures), and civil engineering (calculating road grades), to name a few.