Fetal Pig Dissection Guide: Complete Worksheet Answers
Embarking on a fetal pig dissection in a biology class can be a fascinating journey through the complexities of mammalian anatomy. This guide aims to serve as an invaluable companion, offering comprehensive answers to a fetal pig dissection worksheet, complete with explanations, diagrams, and important notes to ensure you grasp the intricacies of this biological exploration.
Getting Started with Fetal Pig Dissection

Before you dive into the dissection process, it's crucial to understand the tools and preparatory steps:
- Equipment: Dissection tray, dissection scissors, scalpel, forceps, blunt probe, gloves, and protective eyewear.
- Preservation and Handling: Fetal pigs are usually preserved in a solution that often includes formaldehyde. Handle with care, ensuring good ventilation.
- Initial Examination: Determine your pig's sex by locating the urogenital openings.
External Anatomy

Let's begin with the external features:
- Identify the snout, eyes, ears, and nostrils.
- Note the limbs, tail, and umbilical cord.
- Locate the mammary papillae in females and the urogenital openings for both sexes.
⚠️ Note: Handle the umbilical cord carefully to avoid damage to underlying structures.
Internal Anatomy - Muscles

After the external examination, proceed to dissect through the muscle layers:
- Superficial muscles: Identify the masseter, deltoid, biceps brachii, etc.
- Deeper muscles: Carefully expose and identify pectoralis major, rectus abdominis, and others.
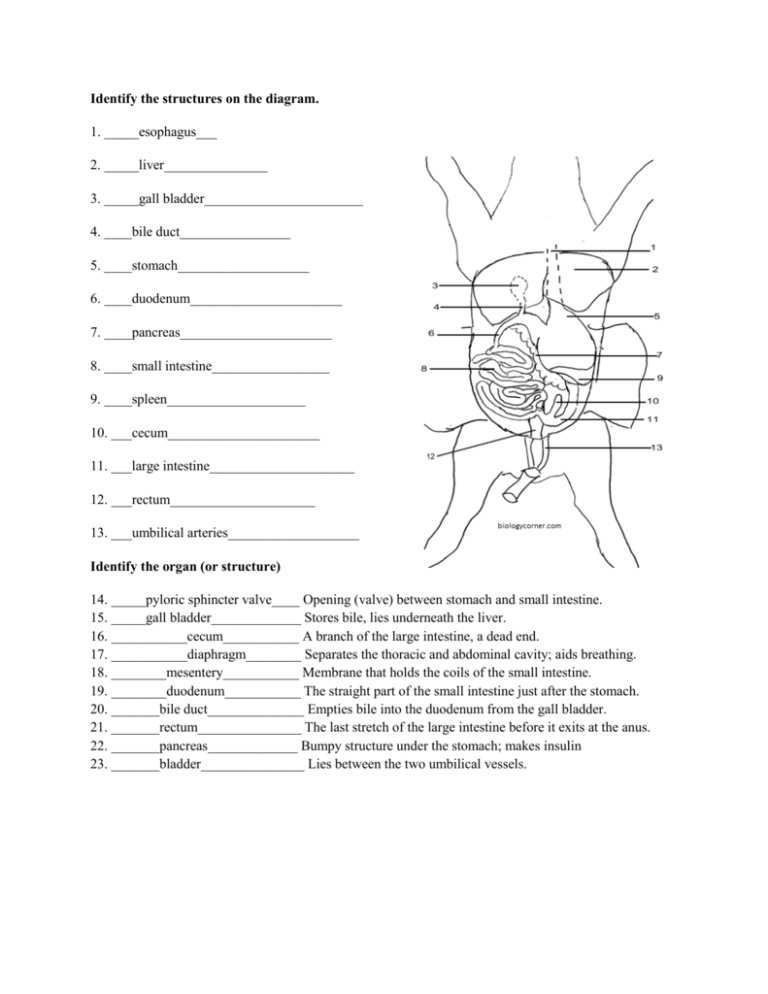
Internal Anatomy - Digestive System

The digestive tract offers a deep dive into how the pig processes food:
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Mouth and Esophagus | Initiation of digestion |
| Stomach | Chemical and mechanical digestion |
| Liver | Detoxification and bile production |
| Gallbladder | Bile storage |
| Small Intestine | Nutrient absorption |
| Large Intestine | Water absorption and waste consolidation |
| Anus | Waste expulsion |

🧪 Note: Note how the liver covers most of the abdominal organs and spans across multiple abdominal regions.
Internal Anatomy - Respiratory System

Understanding the respiratory system involves dissecting the:
- Trachea: Follow it from the larynx to the lungs.
- Lungs: Notice the pleural membranes, bronchi, and the respiratory exchange area.
Internal Anatomy - Cardiovascular System

Explore the heart's role in circulation:
- Identify the heart chambers: Atria (right and left) and ventricles.
- Trace major vessels: Aorta, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, and the vena cavae.
Internal Anatomy - Urogenital System

This system varies slightly between males and females:
- Urinary System: Locate the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
- Reproductive System: For males, find the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, and penis; for females, identify the ovaries, oviducts, uterus, vagina, and mammary glands.
In dissecting and studying the fetal pig, you are not only learning about its anatomy but also gaining insights into human physiology. This biological comparison can help demystify many aspects of our own body's workings.
Wrapping up your dissection journey, remember that your knowledge of the pig's systems not only informs you about their structure but also about how these structures function together to support life. This comprehensive understanding is key to appreciating the beauty of biological systems and the complexity of life itself.
Why do we dissect fetal pigs?

+
Fetal pigs are often used for dissection because their anatomy closely resembles that of humans, providing an excellent comparative study in anatomy and physiology.
What should I do if I cut something incorrectly?

+
Take it as a learning opportunity. Accidental cuts can reveal unexpected structures, but always try to follow the outlined dissection steps as closely as possible.
How do I properly dispose of the fetal pig after dissection?

+
Follow your institution’s waste disposal guidelines for biological specimens. Typically, this means placing the pig in a designated biohazard bag or container for incineration.