Fertile Crescent Map Worksheet Answers: Explore Ancient Lands Easily

Introduction to the Fertile Crescent

The Fertile Crescent is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, known for being the cradle of civilization, where agriculture and early urban societies first emerged. Encompassing the fertile lands stretching from the Nile Valley in Egypt, through the Levant, and down into Mesopotamia between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, this area was crucial for early human history due to its fertile soil and abundance of water, which supported the rise of major civilizations like Sumer, Akkad, Babylon, and Assyria.
In this blog post, we will delve into a comprehensive exploration of the Fertile Crescent through a worksheet format, providing answers, context, and a deeper understanding of this historically significant region. Whether you're a student, history enthusiast, or just curious about ancient lands, this guide will illuminate how these civilizations influenced not only their own time but the entirety of human development.
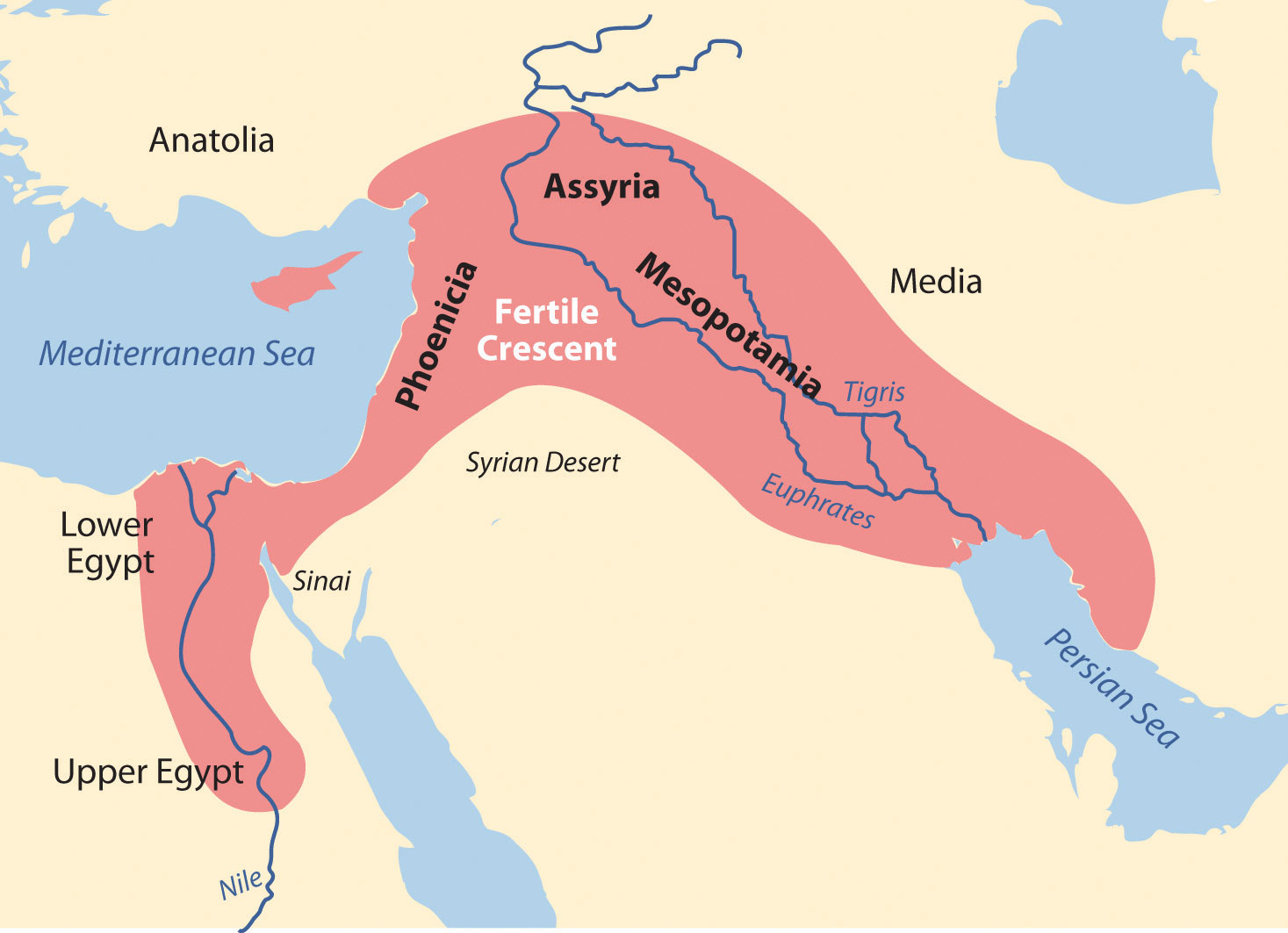
Fertile Crescent Map

Before we dive into the answers, let’s set the scene with a map:

Geography of the Fertile Crescent

The geography of the Fertile Crescent was instrumental in its rise as a center of early civilization:
- Arable Land: Rich, fertile soil due to riverine alluvial deposits.
- Water Availability: The presence of the Nile, Tigris, and Euphrates Rivers provided necessary irrigation.
- Natural Barriers: Mountains, deserts, and the sea provided natural defenses.
- Trade Routes: Its position bridged Asia and Africa, making it a crossroads for trade.
Worksheet Answers

1. What Civilizations Emerged in the Fertile Crescent?

The Fertile Crescent was home to numerous influential civilizations:
- Sumerians: Known for developing the first known writing system (cuneiform), ziggurats, and the wheel.
- Akkadians: Established the first empire under Sargon the Great.
- Babylonians: Famous for their law code (Hammurabi’s Code), architecture, and mathematics.
- Assyrians: Known for their military prowess and complex administration.
- Phoenicians: Recognized for their maritime expertise, alphabet, and trade.
- Hittites: Early adopters of iron technology and known for their law codes.
2. What Were the Key Contributions of These Civilizations?
Here’s a table summarizing some key contributions:
| Civilization | Key Contributions |
|---|---|
| Sumerians | Cuneiform, Ziggurats, Mathematics, Astronomy |
| Akkadians | First Empire, Akkadian Language as Lingua Franca |
| Babylonians | Hammurabi's Code, Hanging Gardens of Babylon, Astrology |
| Assyrians | Military Innovations, Libraries, Administration |
| Phoenicians | Alphabet, Shipbuilding, Trading Networks |
| Hittites | Iron Technology, Law Codes, Chariot Warfare |

🌾 Note: The list of contributions is not exhaustive, as each civilization had many facets of development and culture.
3. How Did Geography Influence Development?

The unique geographical features of the Fertile Crescent played a pivotal role:
- Fertile Soil: Supported large-scale agriculture, leading to population growth.
- Rivers: Provided irrigation for farming, transportation, and trade.
- Defensibility: Mountains and deserts acted as natural barriers, protecting from invasions.
- Trade Routes: Positioned the region as a vital hub in ancient trade, fostering economic growth.
💡 Note: Geography not only shaped agriculture but also politics, warfare, and culture.
4. Why Was the Fertile Crescent Called the ‘Cradle of Civilization’?

The term ‘Cradle of Civilization’ refers to:
- Earliest Urban Centers: Cities like Uruk and Ur emerged here.
- Development of Writing: Writing systems like cuneiform were invented here.
- Legal Systems: Formalized legal codes such as Hammurabi’s Code.
- Agricultural Innovations: Systematic farming and irrigation techniques.
- Governmental Structures: Complex city-states, kingdoms, and eventually empires.
5. What is the Importance of the Fertile Crescent Today?

The legacy of the Fertile Crescent:
- Archaeological Sites: Places like Ur, Babylon, and Ugarit provide insights into ancient life.
- Linguistic Roots: Languages spoken today, like Arabic and Hebrew, trace back to this region.
- Cultural Heritage: The region is a crossroads of major religions and cultural practices.
- Historical Influence: Its developments shaped Western civilization’s sciences, laws, and arts.
🏺 Note: The archaeological wealth of the Fertile Crescent continues to be unearthed, shedding light on ancient human history.
In wrapping up, exploring the Fertile Crescent through this worksheet journey illustrates not only the geographical and historical significance of this area but also its profound influence on human progress. From the invention of writing to the establishment of legal systems, the contributions of these civilizations are foundational in our understanding of human history. We've looked at how the environment fostered innovation, the contributions each civilization made, and the lasting impact of the Fertile Crescent on contemporary society. It's a testament to the creativity, resilience, and ingenuity of ancient peoples, showcasing the importance of this region in the tapestry of world history.
Why is the Fertile Crescent considered important in the context of world history?
+
The Fertile Crescent is vital because it was the birthplace of some of the earliest civilizations, which developed key innovations in writing, agriculture, urban development, and legal systems, laying the groundwork for subsequent cultural and technological advancements.
What caused the decline of these ancient civilizations?

+
Various factors like environmental changes, overpopulation, invasions by neighboring groups, internal strife, and economic collapse have been cited as reasons for the decline of these civilizations. The exact causes differ for each civilization, but these elements often played a role.
How did agriculture contribute to the development of civilizations in the Fertile Crescent?

+
Agriculture allowed for food surplus, leading to population growth, specialization of labor, and the formation of complex societies. This stability enabled the development of writing, governance, and other cultural advancements.