5 Key Steps for Federal Budget Approval Simulation
Navigating the complexities of federal budget approval can be daunting for policymakers, fiscal analysts, and citizens alike. While the exact procedures might differ based on the country, there are universal themes that govern how budgets are formulated, reviewed, approved, and implemented. Here are five key steps for understanding and potentially simulating a federal budget approval process:
1. Formulation of Budget Proposals

The genesis of a federal budget starts with agencies and departments crafting their individual budget requests. In a simulation:
- Participants would be divided into groups representing different government sectors.
- Each group would draft a budget proposal detailing expenditures, goals, and expected outcomes.
- They might consider economic forecasts, past spending patterns, and current policy initiatives.
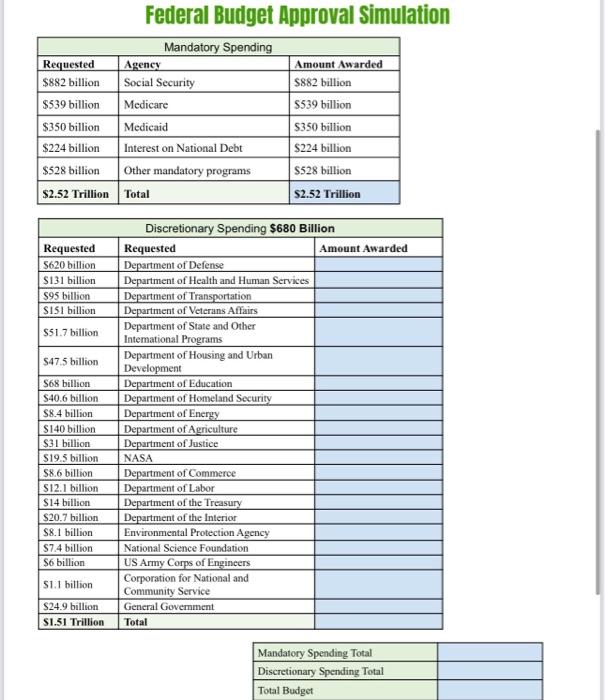
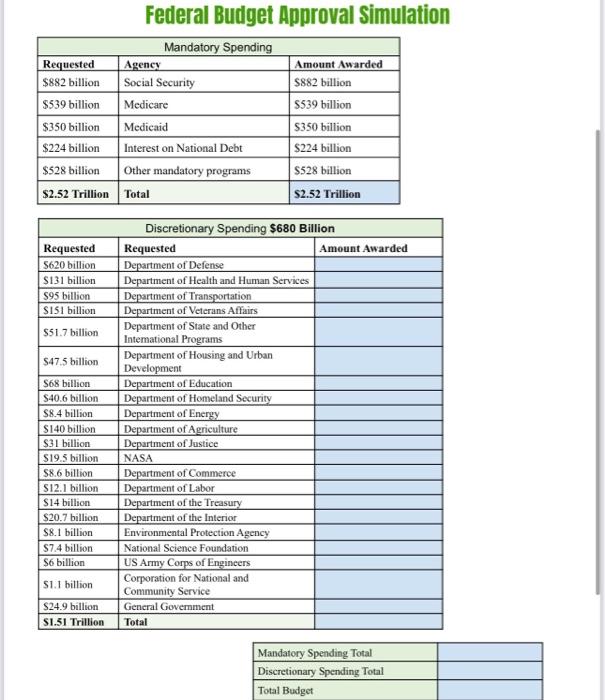
- Key considerations could include:
- Discretionary spending on programs like defense or education.
- Mandatory spending obligations like Social Security or Medicare.
🔍 Note: In real-life situations, political and lobbying influences can greatly affect these initial proposals.
2. Budget Review by the Executive

Once proposals are formulated, they go through an executive review, typically led by the President or Prime Minister:
- The simulation would involve participants simulating the executive branch, going through each proposal.
- Decisions on which proposals align with the administration’s priorities, cost-cutting measures, or increased investments.
- Consider trade-offs and fiscal policy implications.

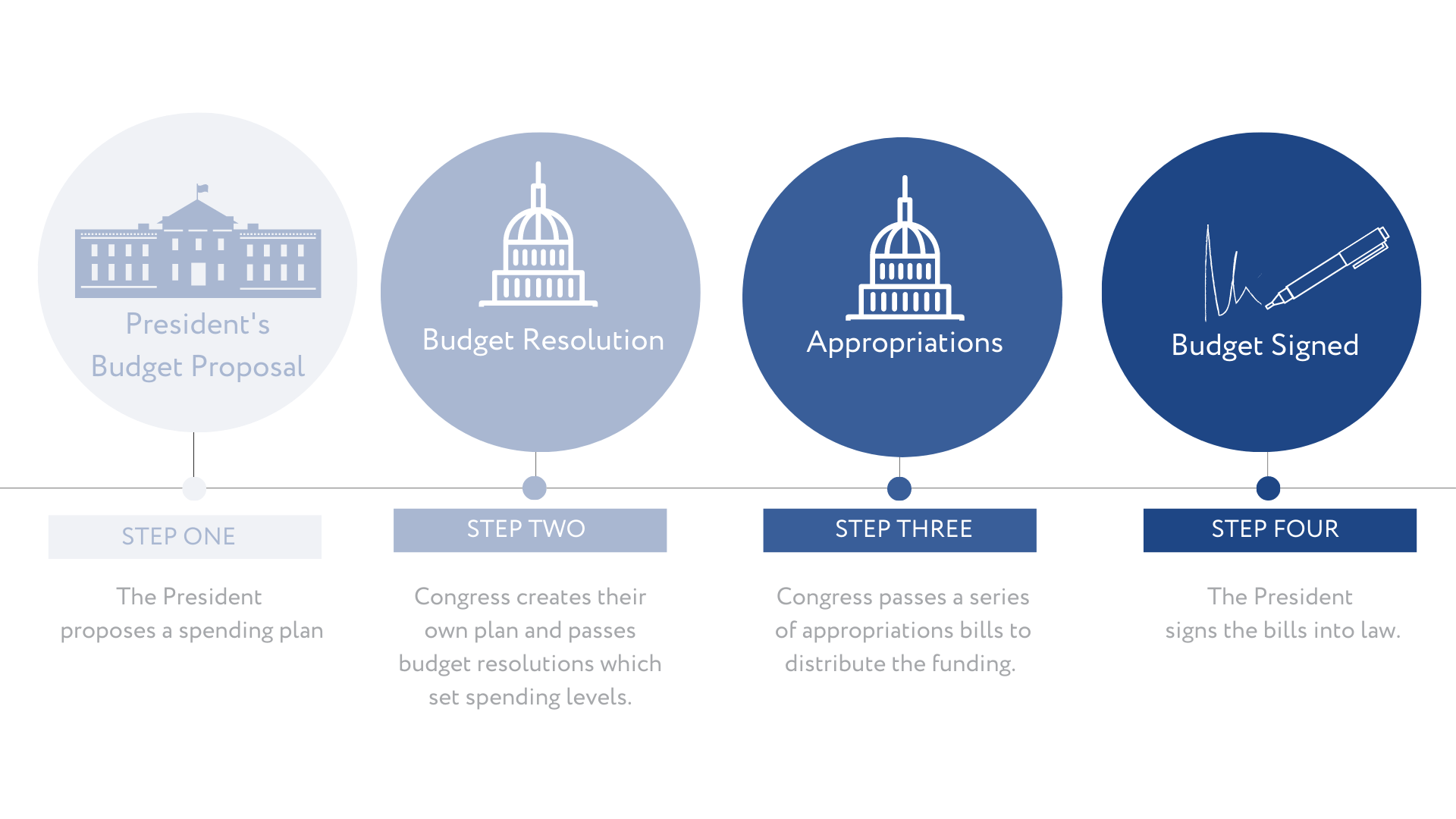
3. Legislative Review and Congressional Hearings

The executive’s budget is then submitted to the legislature, where a meticulous review takes place:
- In a simulation, groups would represent various legislative committees, scrutinizing the budget proposal.
- Participants would hold “hearings” to interrogate agency heads, discuss priorities, and modify the budget.
- Consider:
- Fiscal responsibility versus social needs.
- Short-term versus long-term economic health.
| Legislative Committees | Primary Focus |
|---|---|
| Appropriations | Allocating Funds |
| Budget | Fiscal Policy |
| Ways and Means | Revenue and Taxes |
💡 Note: In reality, these hearings are often politically charged, with legislators advocating for their districts’ interests.
4. Voting and Reconciliation

After extensive review, the budget goes to a vote, and if necessary, goes through reconciliation:
- Participants in the simulation would cast votes on the budget, demonstrating the complexities of a bicameral system.
- Conferences or negotiations would occur in the event of differences between chambers.
- Reconciliation could involve compromise or rejection of budget elements.

5. Approval and Implementation
Once the budget is passed, it moves to executive approval and implementation:
- In the simulation, the executive has the power to sign or veto the budget.
- If signed, participants simulate the implementation phase where agencies begin executing their budget allocations.
- Regular progress reports would be given, showing how the budget affects policy outcomes and economic health.
✅ Note: Implementation often reveals unforeseen challenges or benefits, leading to adjustments or supplemental funding requests in subsequent years.
To wrap up, this journey through the federal budget approval process, whether in reality or simulation, offers invaluable insights into governance, fiscal policy, and the nuanced interplay between different branches of government. By simulating this process, participants gain a tangible understanding of the power struggles, trade-offs, and the necessity for negotiation, all underpinned by the goal to allocate limited resources for the maximum public good.
Why should one simulate the federal budget approval process?

+
Simulating this process provides a deeper understanding of governmental operations, fiscal policies, and the dynamics of decision-making.
What are the challenges in real-life budget approval?

+
Real-life challenges include political polarization, short-term election cycles affecting long-term planning, unexpected crises, and public pressure on certain expenditures.
Can simulations accurately reflect reality?
+
While not perfect, simulations can mirror many aspects of the real process. They can include strategic delays, political compromises, and unforeseen fiscal hurdles.