Weather Processes Explained
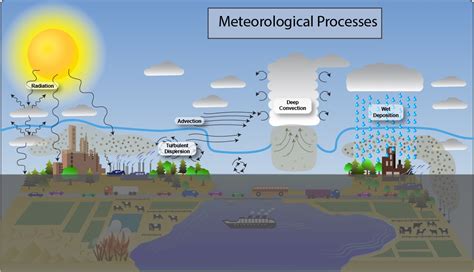
Introduction to Weather Processes

Weather is a complex and fascinating field of study that encompasses various atmospheric conditions, including temperature, humidity, cloudiness, wind, and precipitation. Understanding weather processes is essential for predicting and preparing for different weather conditions. In this article, we will delve into the world of weather and explore the various processes that shape our daily lives.
Atmospheric Components
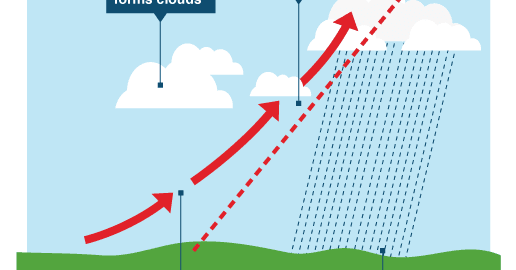
The atmosphere is composed of several layers, each with its unique characteristics. The troposphere is the lowest layer, extending up to 12 kilometers above the Earth’s surface. This layer contains about 75% of the atmosphere’s mass and is where weather occurs. The stratosphere lies above the troposphere, followed by the mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. Each layer plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate and weather patterns.
Temperature and Heat Transfer

Temperature is a critical factor in weather processes. It is measured using thermometers and is influenced by the amount of solar radiation the Earth receives. There are three main methods of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction occurs when there is direct contact between molecules, convection involves the movement of fluids, and radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. Understanding these processes is vital for predicting temperature changes and weather patterns.
Humidity and Precipitation

Humidity refers to the amount of moisture in the air. It is an essential component of weather, as it influences the formation of clouds and precipitation. There are several types of precipitation, including rain, snow, sleet, and hail. Precipitation occurs when the air is cooled to its dew point, causing the water vapor to condense into droplets. The type and intensity of precipitation depend on various factors, including temperature, humidity, and wind patterns.
Wind and Atmospheric Pressure

Wind is the movement of air from high to low-pressure areas. It is caused by the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface by the sun, which creates differences in air pressure. Atmospheric pressure is the weight of the air in the atmosphere, and it decreases with altitude. Wind plays a significant role in shaping our weather, as it influences the movement of weather systems and the distribution of heat around the globe.
Cloud Formation and Types

Clouds are collections of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air. They form when the air is cooled to its dew point, causing the water vapor to condense. There are several types of clouds, including: * Cirrus clouds: high-level clouds composed of ice crystals * Cumulus clouds: puffy, white clouds that can appear alone or in large clusters * Stratus clouds: low-level clouds that often cover the entire sky * Nimbus clouds: dark, rain-bearing clouds that can produce precipitation Understanding cloud types and formation is crucial for predicting weather patterns and precipitation.
Weather Forecasting
Weather forecasting involves the use of computer models, satellite imagery, and observational data to predict future weather conditions. Numerical weather prediction (NWP) models use complex algorithms to analyze data and make predictions. Satellite imagery provides visual information about cloud patterns, precipitation, and other weather phenomena. Radar and surface weather stations also provide valuable data for forecasting.
💡 Note: Weather forecasting is a complex and constantly evolving field, and advancements in technology have improved the accuracy of predictions.
Severe Weather Phenomena
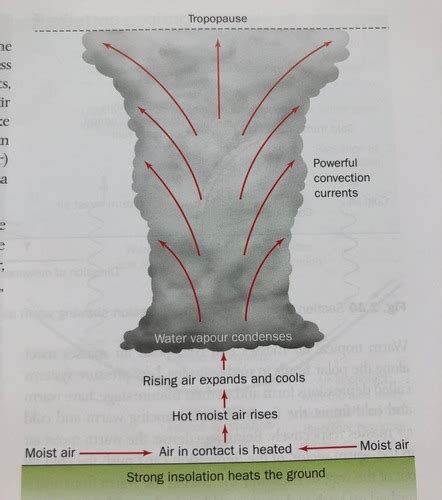
Severe weather phenomena, such as tornadoes, hurricanes, and blizzards, can have devastating effects on communities and ecosystems. Understanding the causes and characteristics of these events is essential for predicting and preparing for them. Tornadoes are rotating columns of air that touch the ground, causing damage and destruction. Hurricanes are tropical cyclones that form over warm ocean waters, bringing strong winds and heavy rainfall. Blizzards are severe snowstorms that can cause widespread disruption and damage.
| Severe Weather Phenomenon | Characteristics | Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Tornadoes | Rotating columns of air, high wind speeds | Destruction, injury, loss of life |
| Hurricanes | Strong winds, heavy rainfall, storm surges | Flooding, damage, loss of life |
| Blizzards | Heavy snowfall, high winds, low visibility | Disruption, damage, hypothermia |

As we conclude our exploration of weather processes, it is clear that understanding these complex phenomena is essential for predicting and preparing for various weather conditions. By recognizing the components of the atmosphere, temperature and heat transfer, humidity and precipitation, wind and atmospheric pressure, cloud formation and types, and severe weather phenomena, we can better appreciate the dynamic and ever-changing nature of our weather.
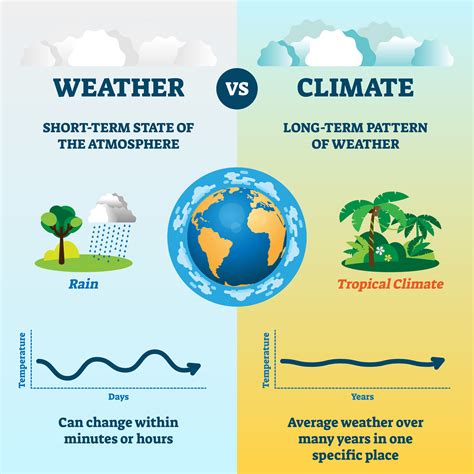
What is the difference between weather and climate?
+
Weather refers to short-term atmospheric conditions, while climate refers to long-term patterns and averages.
How do clouds form?

+
Clouds form when the air is cooled to its dew point, causing the water vapor to condense into droplets.
What is the role of wind in shaping our weather?
+
Wind plays a significant role in shaping our weather, as it influences the movement of weather systems and the distribution of heat around the globe.