5 Key Evidence of Evolution Worksheet Answers

When diving into the field of biology, particularly evolutionary biology, evidence plays a pivotal role in validating and substantiating theories and principles. The concept of evolution, first proposed by Charles Darwin, has stood the test of time through a wealth of scientific evidence. This article will explore five key types of evidence that not only support the theory of evolution but also make it an integral part of biology curriculum worldwide.
The Fossil Record


The fossil record is like a historical archive of life on Earth, providing physical proof of evolution over time. Here’s what it tells us:
- Transitional Forms: Species that show characteristics between two distinct groups, like Archaeopteryx which had both feathers and dinosaur features.
- Gradual Changes: Fossils show gradual changes in species over millions of years, for instance, the evolution from ancient whales with hind legs to modern whales without them.
- Mass Extinction Events: These events reset the evolutionary clock, leading to the rise and fall of dominant species.
Comparative Anatomy
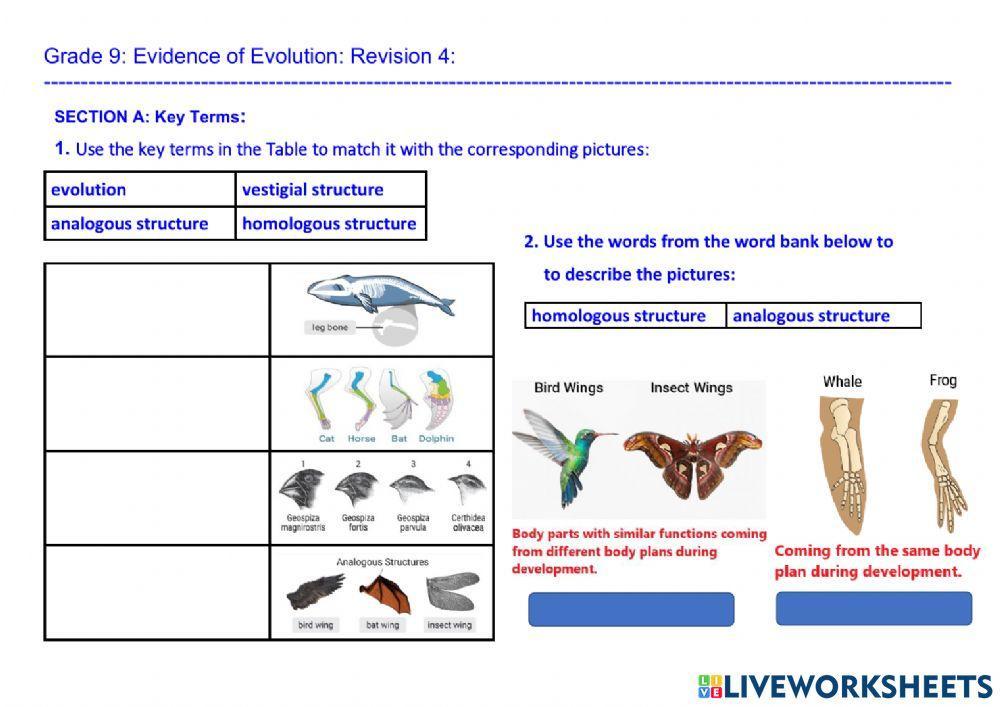

Comparative anatomy involves comparing the physical structures of different species:
- Homologous Structures: Organs or skeletal parts that are similar due to common ancestry, like the structure of limbs in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
- Vestigial Structures: Remnants of organs or structures that no longer have a function but once did, such as the human appendix or the pelvic bones in whales.
- Analogous Structures: Similarities in structure due to convergent evolution, not common ancestry, like the wings of bats and insects.
Embryology


Embryological development reveals striking similarities among different species, indicating common ancestry:
- Pharyngeal Gills: Early stages of vertebrate embryos all develop pharyngeal arches, which in humans develop into the jaw, ear, and throat.
- Tail: All vertebrate embryos have a tail at some point, which humans eventually lose before birth.
- Vestigial Structures: Structures that appear during embryonic development but disappear before birth, like the pronephros in human embryos.
Biogeography


Biogeography studies the distribution of species across the planet, offering clues to evolutionary history:
- Continental Drift: Species distributions align with ancient supercontinents, for example, marsupials found predominantly in Australia and South America.
- Island Endemism: Unique species found only on isolated islands, like the Galápagos Islands, suggesting in situ evolution.
- Range Disjunct: Species with a similar appearance but vast geographic separation, indicating past dispersal.
Genetics and Molecular Biology


The study of genetics and molecular biology offers the most compelling evidence of evolution:
- Genetic Variations: Natural selection acts on genetic variations, preserving some traits and eliminating others.
- DNA and Protein Sequences: Comparative analysis of DNA and protein sequences reveals how species are related. Closer relations indicate more recent divergence.
- Molecular Clocks: The rate of genetic mutation can be used to estimate the time when species diverged from their common ancestor.
🔍 Note: While the fossil record can provide a physical timeline, molecular evidence often offers a more precise estimate of evolutionary divergence times.
In reviewing these five key pieces of evidence, we can see how the theory of evolution is not just a hypothesis but a robust framework supported by diverse scientific fields. These pieces of evidence interconnect to form a comprehensive picture of life's history on Earth, each contributing to our understanding of how life has evolved over time.
What is the significance of transitional fossils in evolutionary biology?

+
Transitional fossils are crucial as they provide tangible evidence of how one group of organisms evolved into another. They show intermediate stages, offering proof of evolutionary transitions between species.
Can evolution occur through mechanisms other than natural selection?

+
Yes, other mechanisms like genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and non-random mating can also drive evolutionary changes, although natural selection is one of the primary forces.
How do vestigial structures support the theory of evolution?

+
Vestigial structures demonstrate that evolution has left remnants of once-useful features in organisms. These structures can be traced back to ancestors where these traits were functional, highlighting evolutionary changes over time.