5 Tips for Estimating Math Sums and Differences
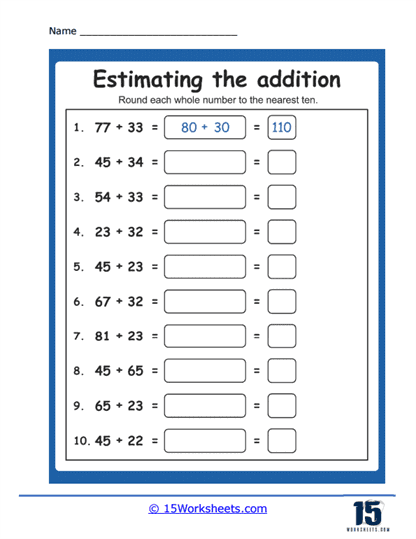
Mastering the art of estimating in mathematics can simplify complex problems and enhance your decision-making abilities. Estimation allows you to quickly evaluate sums and differences without precise calculations, making it a valuable skill in everyday situations. Here are five tips to improve your estimation skills in math:
1. Rounding Numbers

The first step to becoming adept at estimation is understanding how to round numbers effectively. Rounding not only simplifies numbers but also makes mental arithmetic much easier:
- Identify key digits: For rounding, focus on the digit in the place you’re rounding to and the next digit.
- Rounding rules: If the following digit is five or greater, round up; if less than five, round down.
💡 Note: When estimating, often round to the nearest ten, hundred, or thousand depending on the context of the problem.
2. Using Compatible Numbers

Compatible numbers are those that are easy to work with mentally. When you estimate, pick numbers that make calculations simpler:
- Pairing for ease: Find numbers that are close to each other or that make the arithmetic operation simpler, like turning 38 + 42 into 40 + 40.
- Adjust later: Remember to adjust your estimate if you’ve chosen numbers significantly different from the original ones.
3. Mental Clustering

Clustering involves grouping numbers together to make their sum easier to estimate:
- Identify clusters: Look for numbers that are close to each other and group them for simpler addition.
- Average them out: Estimate the sum by averaging the clustered numbers.
4. Front-End Estimation
This technique emphasizes the most significant digits, providing a quick ballpark figure:
- Focus on the largest units: Work with the digits in the highest place value first.
- Adjust for accuracy: After computing the front-end sum, adjust based on the remaining digits.
| Example Number | Front-End Estimation | Adjustment | Estimated Sum |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3579 | 3000 | +500 +70 +9 = 579 | 3579 |
| 2431 | 2000 | +400 +30 +1 = 431 | 2431 |
| Total | 5000 | 1000 | 6000 |

5. Benchmarking
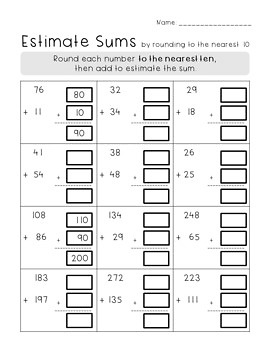
Using benchmarks helps anchor your estimations around known values:
- Choose reference points: Use familiar numbers as benchmarks. For example, when estimating distances, use well-known landmarks or cities.
- Relate to benchmarks: Relate your numbers to these benchmarks for a more accurate estimation.
⚠️ Note: Benchmarking can also help in understanding relative sizes or quantities, like using a pound or a kilometer as a reference.
These techniques are not just about cutting corners; they're about developing a mental toolkit for faster, more intuitive problem-solving. By practicing these methods, you'll find that your ability to estimate sums and differences improves significantly. Estimation isn't about getting the exact answer; it's about getting a reasonable approximation quickly, which is incredibly useful in both academic and everyday contexts.
Why is rounding important in estimation?

+
Rounding makes numbers easier to work with, simplifying calculations. This simplification allows for quicker mental arithmetic, which is crucial for effective estimation.
Can these techniques be applied to all levels of mathematics?

+
Yes, these estimation methods can be adapted to various levels of mathematics. From basic arithmetic to more complex problems in algebra or even calculus, these skills can aid in understanding and verifying results.
How can I practice these estimation skills?

+
Practice by incorporating estimation into your daily math exercises. Use estimation when you shop, estimate travel time, or even guess the number of people in a crowd. Regular application will enhance your skills.