5 Steps to Master Equivalent Resistance Worksheets
Introduction to Mastering Equivalent Resistance
Understanding equivalent resistance in electrical circuits is not just a theoretical pursuit; it is the bedrock upon which practical electrical engineering and physics experiments are built. This blog post will guide you through the process of mastering equivalent resistance worksheets, providing you with a toolkit of knowledge that will enhance your understanding and application of electrical circuit theory.
Step 1: Understanding the Basics of Resistance

Before diving into the complexities of equivalent resistance, one must grasp the fundamental concept of resistance. Resistance (R) in an electrical circuit is opposition to current flow, measured in Ohms (Ω). Here’s what you need to know:
- Ohm’s Law: The current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across those points.
- Resistivity: Material-specific, influencing the resistance of a conductor.
- Resistor Colors: Each color band on a resistor corresponds to a digit or a multiplier, providing its resistance value.
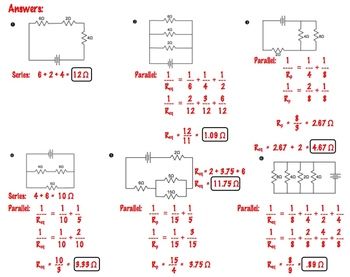
💡 Note: Always remember that resistance in series add up while resistances in parallel combine inversely.
Step 2: Series and Parallel Configurations

When working with equivalent resistance, understanding how resistors combine in series and parallel is crucial:
- Series Configuration:
- Total resistance (Rtotal) is the sum of individual resistances (R1 + R2 + …)
- Current is the same through all resistors
- Parallel Configuration:
- Total resistance is found using the reciprocal formula: 1/Rtotal = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + …
- Voltage drop is the same across each resistor
| Configuration | Formula |
|---|---|
| Series | Rtotal = R1 + R2 + … |
| Parallel | 1/Rtotal = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + … |

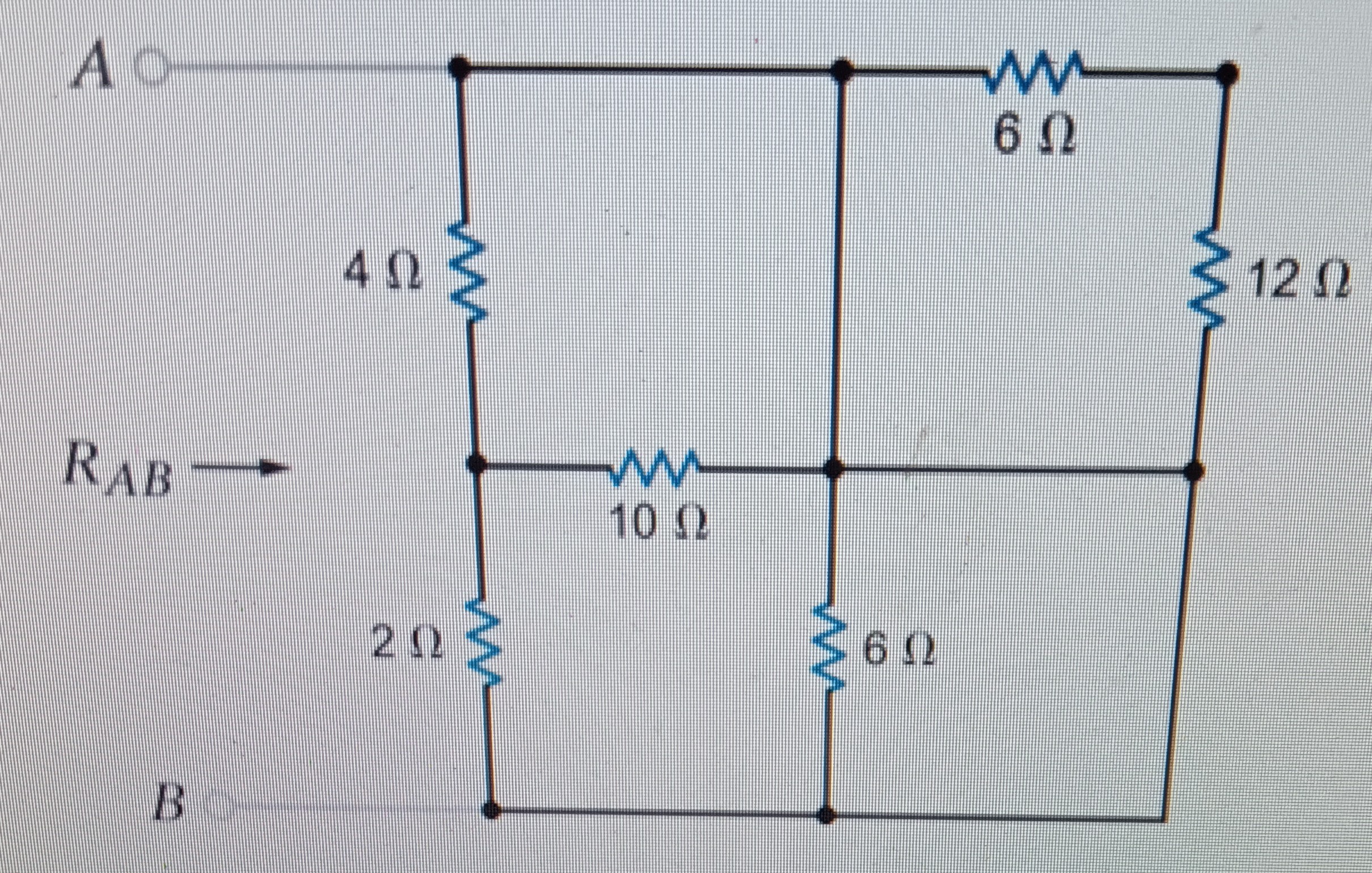
Step 3: Combining Series and Parallel Resistors

Real-world circuits often include a combination of series and parallel resistor arrangements:
- Identify Series: Recognize groups where resistors are connected one after the other without branching.
- Identify Parallel: Look for resistors that are connected at both ends, forming branches.
- Apply Series and Parallel Formulas: Calculate the equivalent resistance for each sub-group, then simplify by combining these values.
📝 Note: Breaking complex circuits into simpler, recognizable patterns helps in solving for equivalent resistance.
Step 4: Solving Equivalent Resistance Problems

Here are the practical steps to master equivalent resistance worksheets:
- Visualize the Circuit: Sketch or imagine how the resistors are connected.
- Label Resistors: Assign values to the resistors in your diagram for clarity.
- Choose the Simplification Path: Determine if you should start from the outside-in or inside-out for simplification.
- Simplify Step by Step: Use formulas to reduce the complexity of the circuit until you get a single resistance value.
- Verify: Plug back the calculated equivalent resistance into the circuit to ensure consistency with the expected result.
By following this methodology, your efficiency and accuracy in solving equivalent resistance problems will increase.
Step 5: Practice and Reinforcement

Like any skill, practice makes perfect:
- Vary Circuit Complexity: Solve problems of different levels to build both foundational knowledge and advanced understanding.
- Use Online Tools: Circuit simulators can provide visual and immediate feedback.
- Time Yourself: Practice under timed conditions to prepare for real exam scenarios.
- Learn from Mistakes: Analyze and understand the root cause of errors in your solutions.
Regular practice not only reinforces your knowledge but also builds your speed and confidence in tackling equivalent resistance problems.
By following these five steps, you will have developed a comprehensive understanding of equivalent resistance. Whether you are a student facing exams or an engineer designing circuits, this foundational knowledge will prove invaluable. Your ability to simplify complex circuits, calculate currents and voltages, and design efficient systems will be significantly enhanced. Remember, mastering equivalent resistance is not just about numbers; it's about understanding the flow of electricity in circuits, a skill that will serve you well in any field involving electronics or electrical engineering.
What if there are multiple branches in a circuit?

+
When a circuit has multiple branches, treat each branch as a single resistor in parallel. Simplify each parallel group first, then proceed to combine with any series connections.
How do I handle very complex circuits?
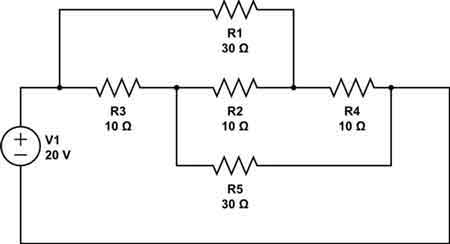
+
Start with the simplest part of the circuit, reduce it, then work your way towards the more complex sections. Use circuit analysis techniques like node voltage method or mesh current method when simplification becomes difficult.
Can I use software for equivalent resistance calculations?

+
Yes, software like LTSpice or even online calculators can verify your calculations, but it’s crucial to understand the manual process for learning and problem-solving.