5 Steps to Master Equivalent Fractions on Number Lines

Understanding and mastering equivalent fractions is a foundational skill in mathematics, particularly when it comes to visual representation on a number line. This skill not only helps in solving more complex math problems but also enhances our ability to grasp concepts like addition, subtraction, division, and multiplication of fractions. Here, we will explore five steps to master equivalent fractions on number lines, making the learning process intuitive and practical.
1. Grasp the Concept of Fractions

Begin by ensuring you thoroughly understand what fractions are. A fraction represents a part of a whole, where the numerator represents the number of equal parts you have, and the denominator represents the total number of equal parts into which the whole is divided.
- Example: In the fraction 3⁄4, you have three parts out of a possible four.
📌 Note: Fractions represent division where the numerator is divided by the denominator.
2. Create Number Lines

Number lines are powerful visual tools for understanding fractions:
- Start with a basic number line from 0 to 1.
- Divide the number line into the number of segments equal to the denominator of your fraction.
- Place points on this line to represent different fractions.

📌 Note: Number lines help visualize fractions as points on a continuum.
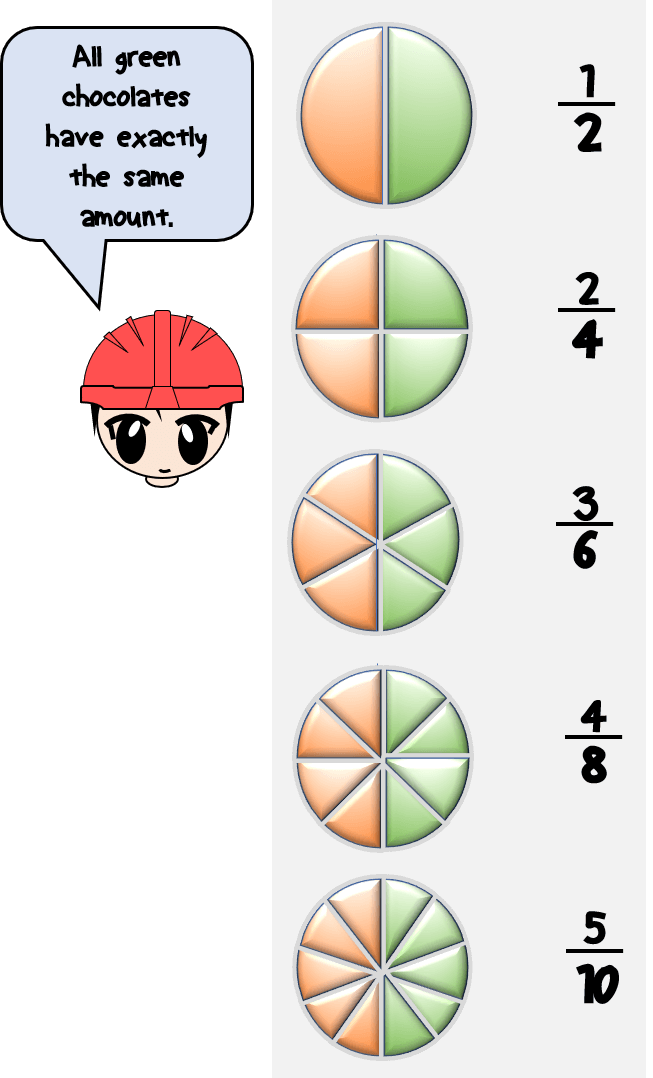
3. Identify Equivalent Fractions

Equivalent fractions are those that represent the same value but with different numerators and denominators. Here’s how to find them:
- Multiply or divide both the numerator and the denominator by the same non-zero number.
- Use the number line to compare these equivalent fractions.
Consider the fraction 1/2. Multiplying the numerator and denominator by 2, we get 2/4, which represents the same value as 1/2.
| Fraction | Equivalent Fraction |
|---|---|
| 1/2 | 2/4 or 4/8 |
| 3/4 | 6/8 or 9/12 |

📌 Note: Equivalent fractions can be simplified by dividing both the numerator and denominator by their greatest common divisor.
4. Practice Simplifying Fractions
Simplifying or reducing fractions is a key step in mastering equivalent fractions:
- Find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and denominator.
- Divide both by their GCD.
For instance, to simplify 6/8:
- The GCD of 6 and 8 is 2.
- Divide both by 2 to get 3/4.
5. Apply to Real-World Problems

Apply your understanding of equivalent fractions on number lines to real-world scenarios:
- Measure ingredients for recipes, where you might need to double or halve quantities.
- Calculate distances or time intervals in fractions when planning a journey.
By solving practical problems, you not only understand equivalent fractions better but also make math a part of your everyday life.
📌 Note: Real-world applications make learning more engaging and practical.
In summary, mastering equivalent fractions on number lines involves understanding the core concept of fractions, utilizing number lines for visual representation, identifying equivalent fractions through multiplication and division, practicing simplification, and applying these skills in real-world scenarios. This methodical approach not only enhances your mathematical proficiency but also aids in developing a deeper conceptual understanding of numbers and their relationships.
Why do we need equivalent fractions?

+
Equivalent fractions are essential for making comparisons between different quantities, performing arithmetic operations, and simplifying complex fractions.
How can I check if two fractions are equivalent without a number line?

+
Without a number line, cross-multiplying the numerators and denominators of the two fractions can show if they are equivalent. If the products are equal, the fractions are equivalent.
Can fractions ever have a denominator of zero?

+
No, a fraction cannot have a denominator of zero as division by zero is undefined in mathematics.