5 Essential Facts About Epithelial Tissue Worksheet Answers
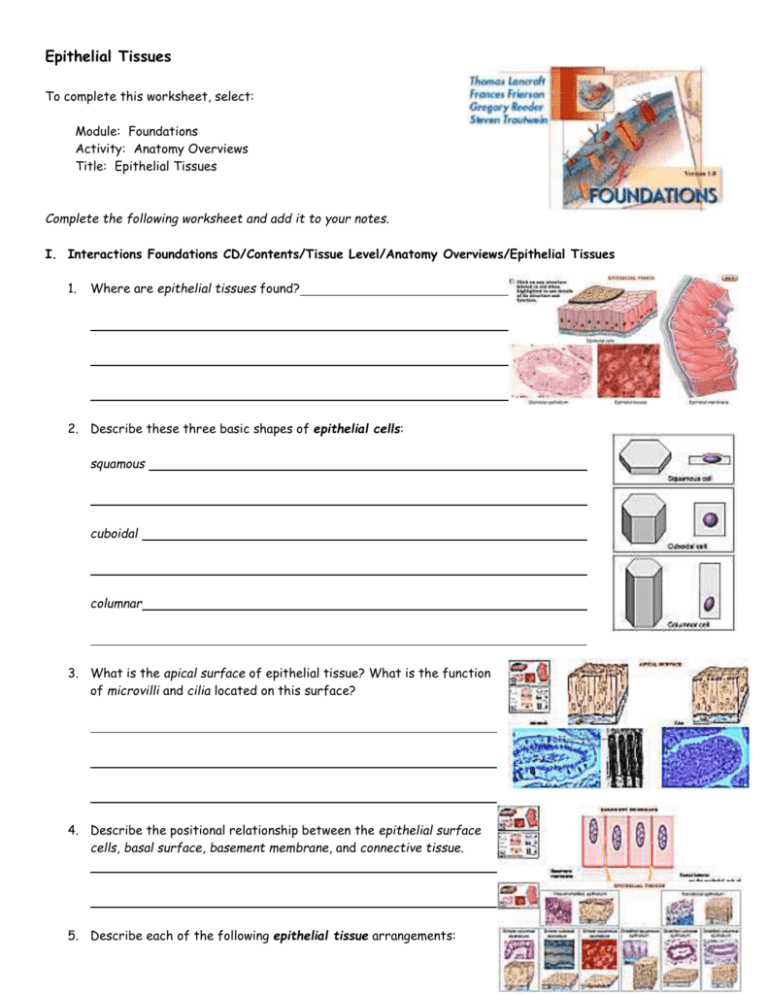
Epithelial tissue forms the covering or lining of organs, body cavities, and surfaces. This fundamental type of tissue plays vital roles in protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, and sensation. Here, we delve into five essential facts about epithelial tissue, focusing on its structure, function, types, and the significance of epithelial tissue worksheet answers in education and training.
The Basic Structure of Epithelial Tissue
- Cell Layers: Epithelial tissue can be single-layered (simple) or multi-layered (stratified).
- Cell Shapes: Cells are typically classified into squamous, cuboidal, or columnar shapes.
- Basement Membrane: The tissue adheres to an underlying basement membrane, which offers support and acts as a barrier.
⚠️ Note: The basement membrane is crucial for cell adhesion but not considered part of the epithelial tissue itself.
Functions of Epithelial Tissue
- Protection: Shields the body from the environment and pathogens.
- Transport: Regulates the passage of substances into and out of the body or organs.
- Absorption: In organs like the small intestine, epithelial cells absorb nutrients.
- Secretion: Some epithelial cells secrete substances, like those in glands.
- Filtration: Essential in organs like the kidney to separate waste from the blood.
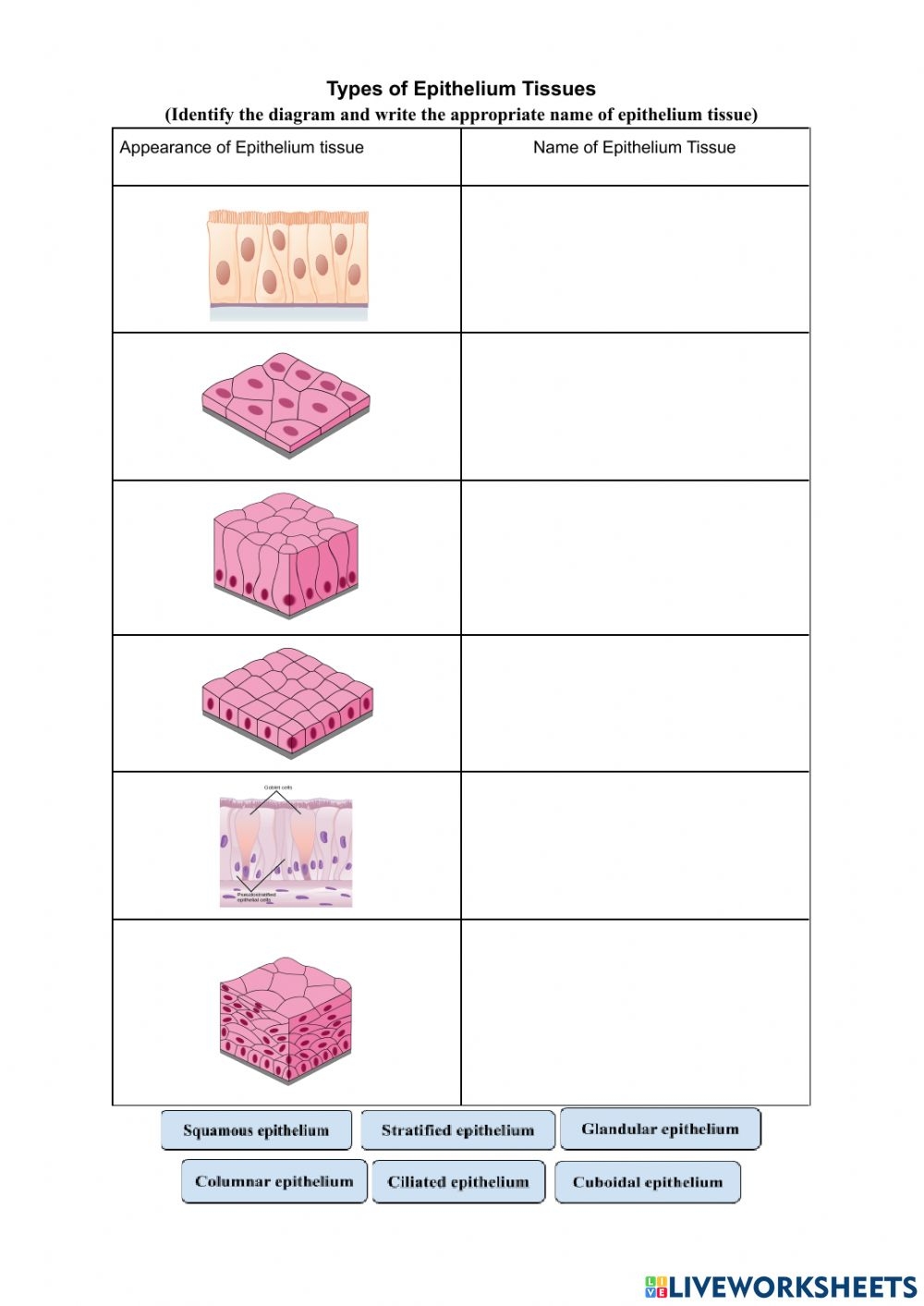
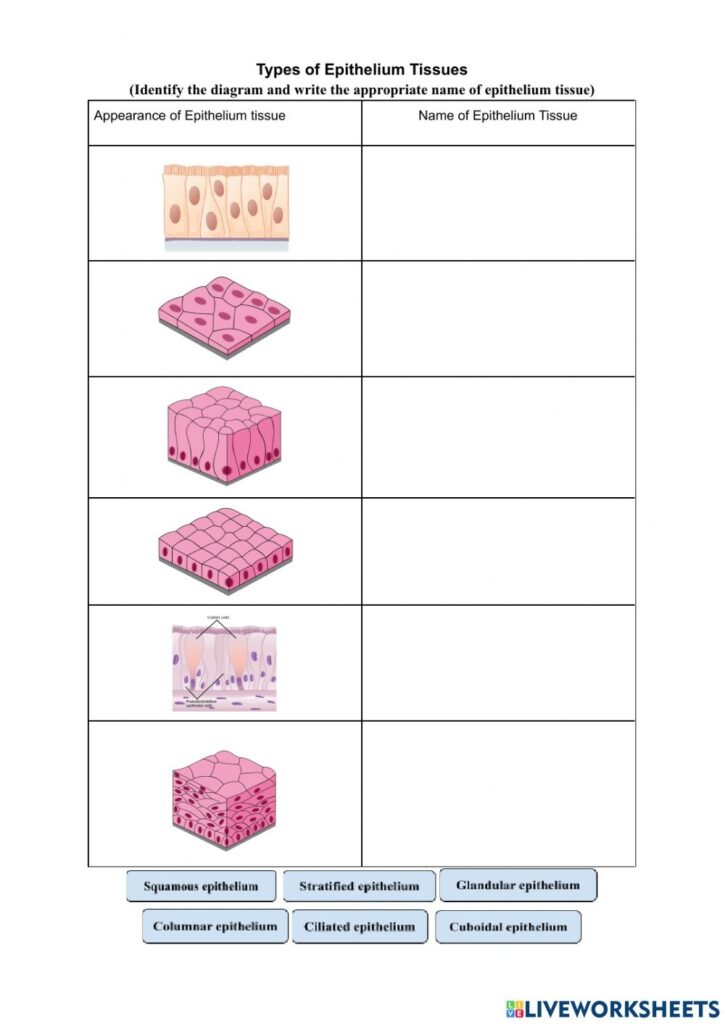
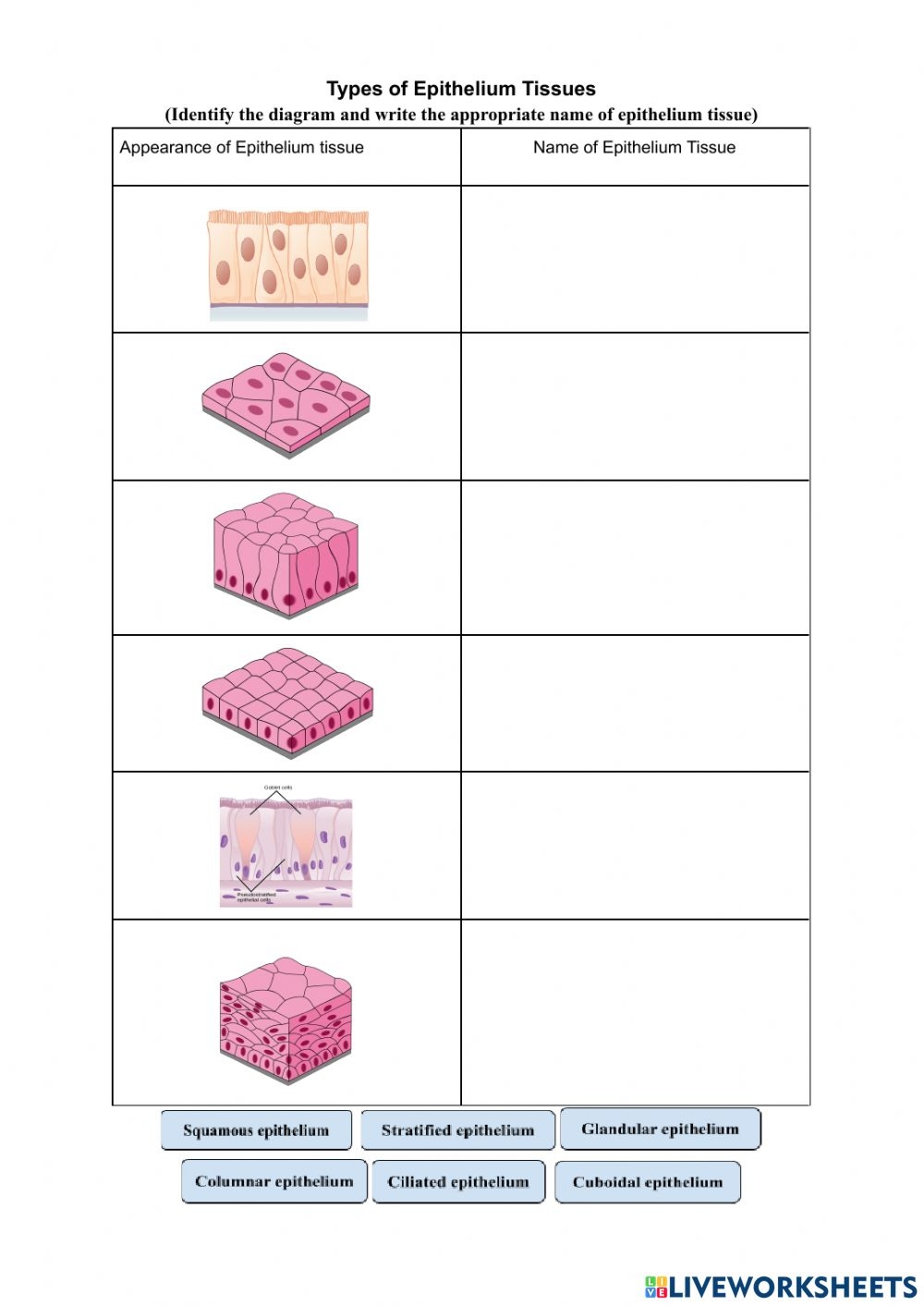
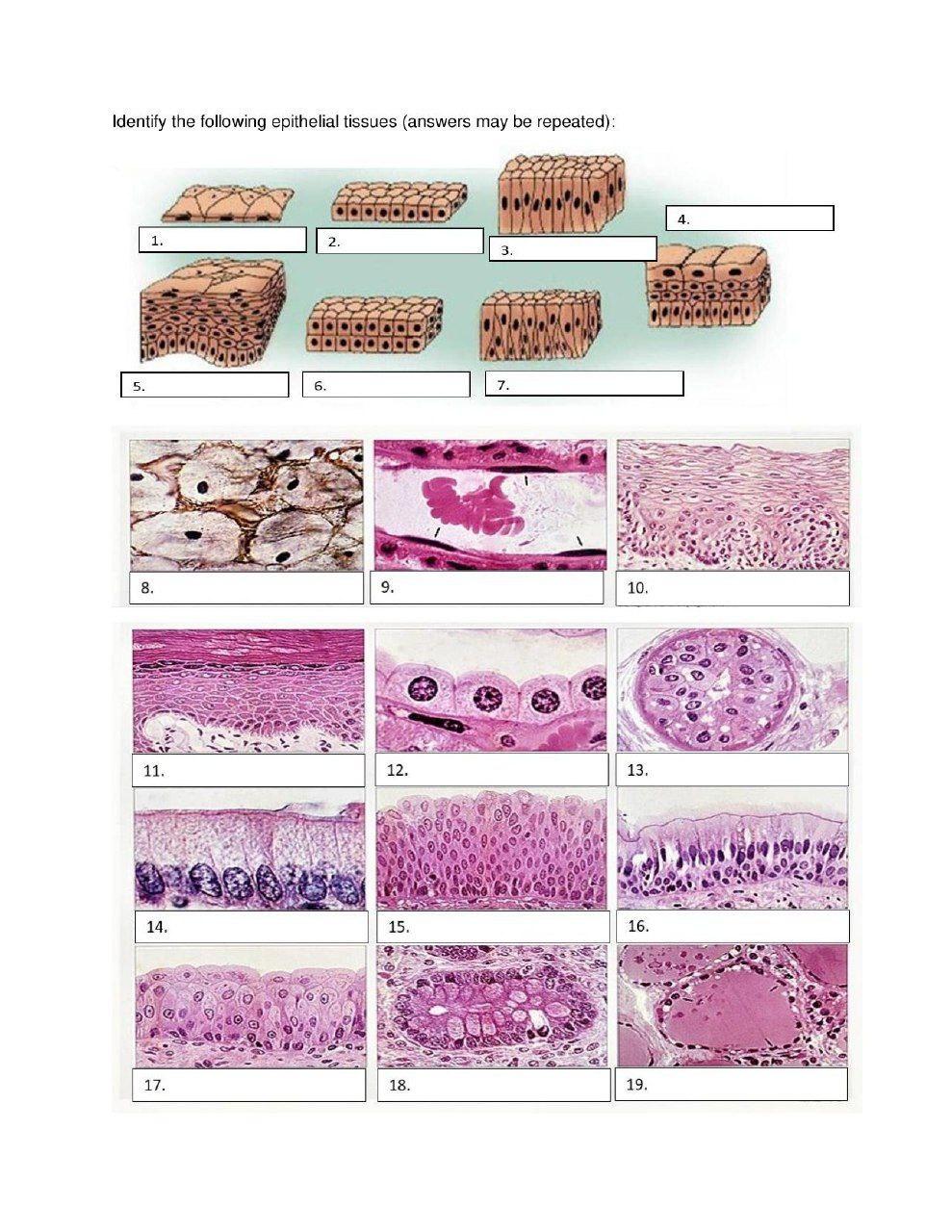
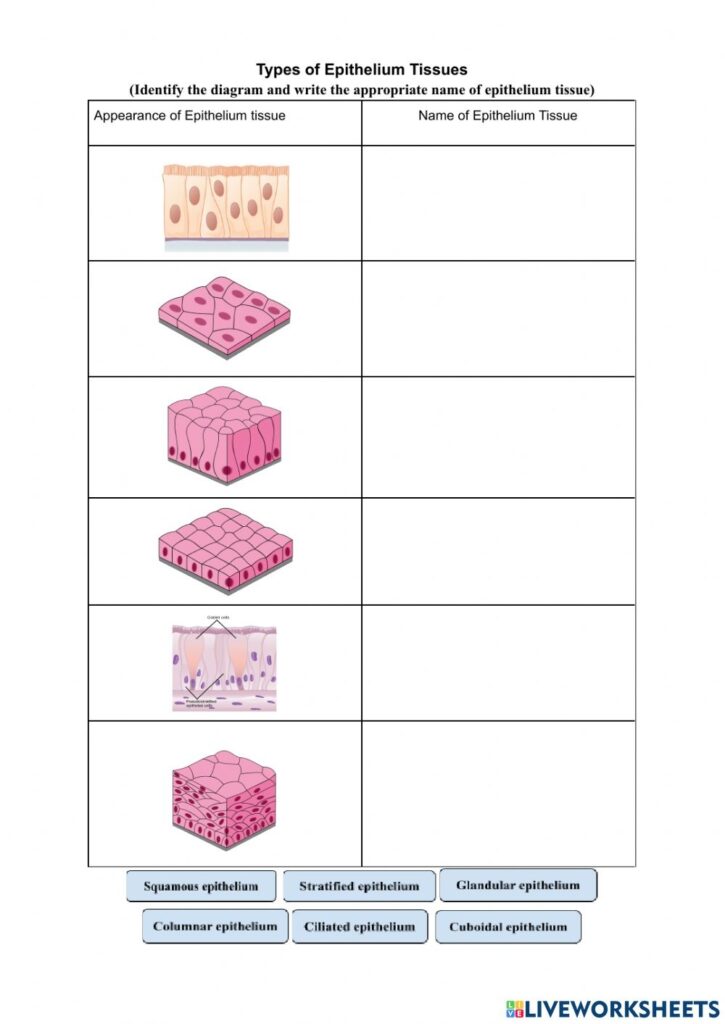
Types of Epithelial Tissue
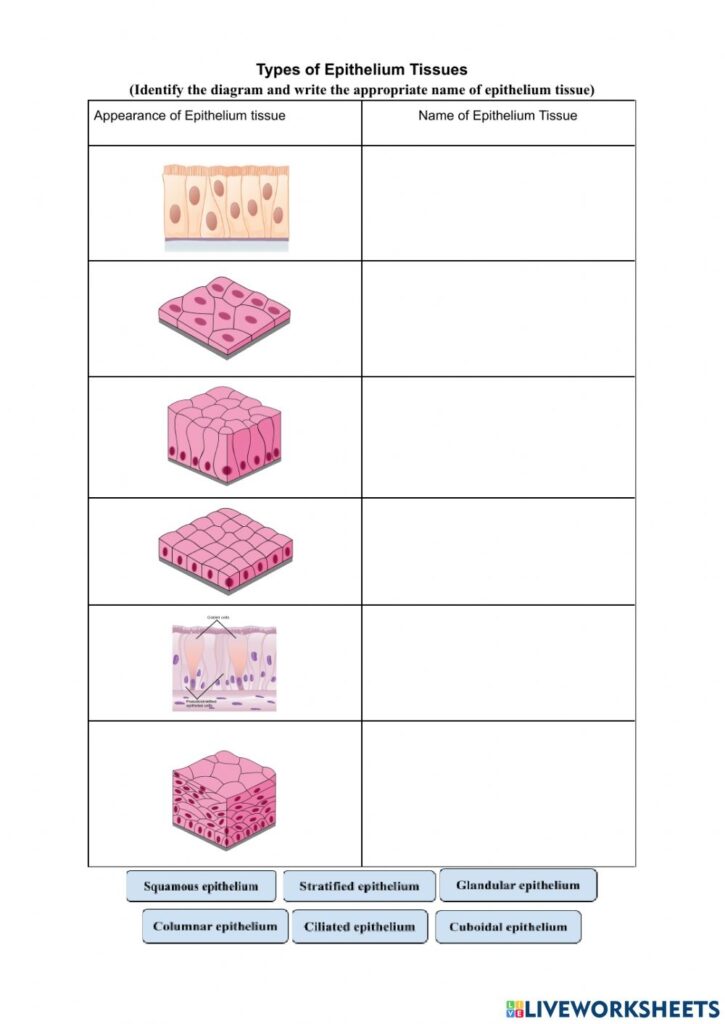
| Type | Description | Example Location |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Squamous Epithelium | Thin, flat cells for diffusion | Alveoli in lungs, lining of blood vessels |
| Simple Cuboidal Epithelium | Cube-shaped cells for secretion or absorption | Kidney tubules, glands |
| Simple Columnar Epithelium | Tall cells for secretion or absorption | Stomach lining, intestines |
| Stratified Squamous Epithelium | Layered cells for protection | Skin, esophagus, vagina |
| Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium | Appears layered but isn’t; for secretion and movement of mucus | Respiratory tract |

👀 Note: Stratified epithelium implies protection, whereas simple types are generally for secretion or absorption.
Educational Value of Epithelial Tissue Worksheets

- Visual Learning: Worksheets help students visualize and recognize the various structures and functions.
- Practical Application: Identifying cells under a microscope, reinforcing theoretical knowledge.
- Comprehension: Exercises aid in understanding the complexities of epithelial tissue through problem-solving.
- Memory Retention: Regular practice through worksheets enhances long-term memory of anatomy.
Common Questions and Answers on Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue worksheets often provide sample questions to test knowledge:
- Q: Why does the skin contain stratified squamous epithelium?
A: For its protective role; the multiple layers offer resistance to mechanical and chemical stress. - Q: What type of epithelial tissue would you find in the kidney nephron?
A: Simple cuboidal epithelium; these cells are efficient for secretion and absorption of filtrate. - Q: How do glands develop from epithelial tissue?
A: Through invagination or infolding of epithelial cells, which can then specialize into secretory units.
In wrapping up, epithelial tissue is an essential component of the human body, providing both structural integrity and functional capabilities. Understanding its types, functions, and the educational tools like worksheets designed to teach these concepts is crucial for students in biology, medicine, and related fields. Epithelial tissue is not just a layer of cells; it’s the frontline of defense, the gatekeeper for absorption, and the dynamic workhorse of our organs. Through worksheets and practical learning, one can appreciate the complexity and beauty of epithelial tissue, making it an integral part of the biological sciences curriculum.
What is the primary function of epithelial tissue?
+
The primary function of epithelial tissue includes protection, absorption, secretion, excretion, filtration, and sensation.
Why is the basement membrane important?
+
The basement membrane provides a layer for epithelial tissue to adhere to, offering support and acting as a selective barrier.
Can epithelial tissue regenerate?

+
Yes, epithelial tissue has a high capacity for regeneration due to its role in body coverage and organ lining.