Enzyme Worksheet Answers: Quick Guide for Students
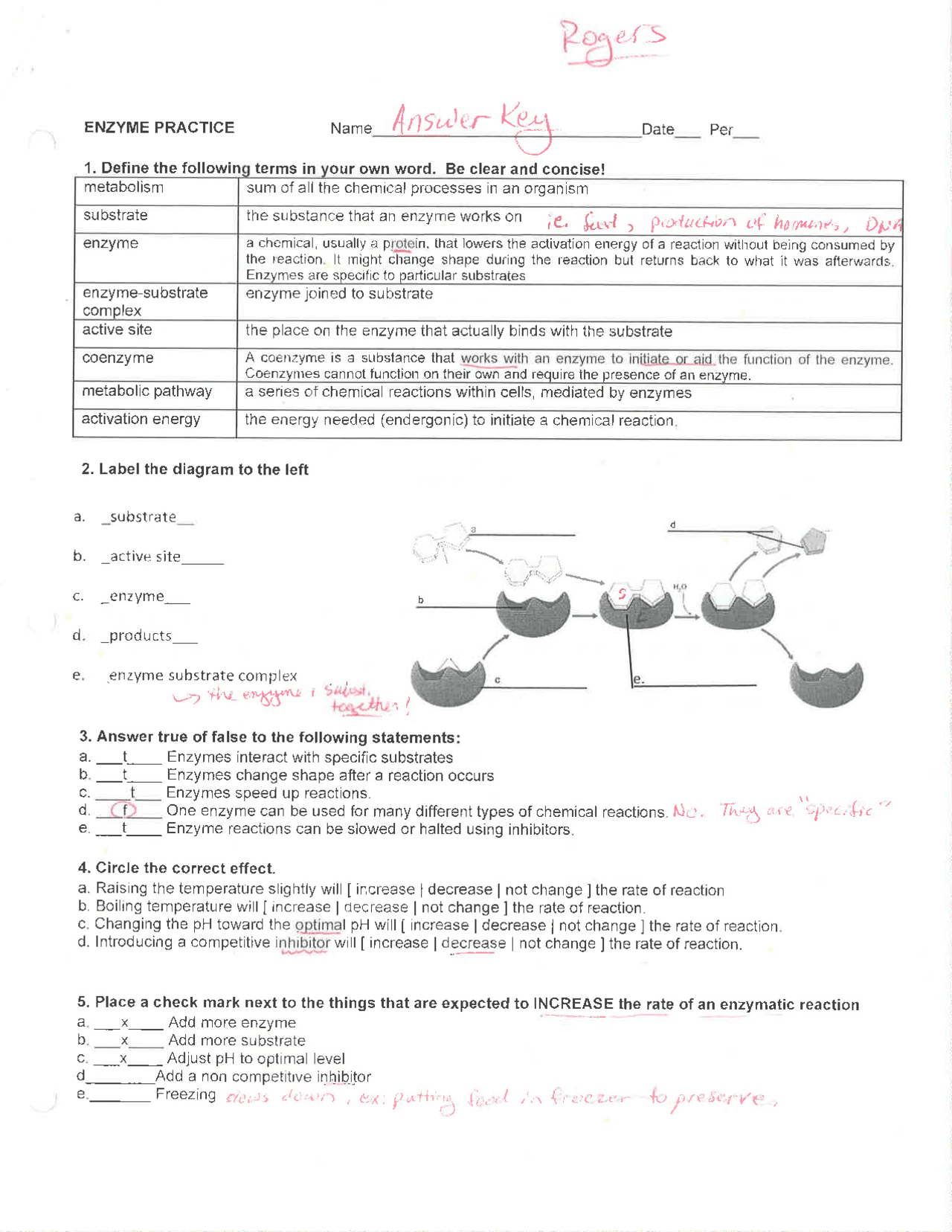
Understanding enzymes can seem like a daunting task for many students, but with the right resources and explanations, it can become much clearer. This guide aims to provide comprehensive answers to common enzyme-related questions found in worksheets, making it an essential tool for studying biology. Let's dive into the world of enzymes and unravel the mysteries together.
What are Enzymes?


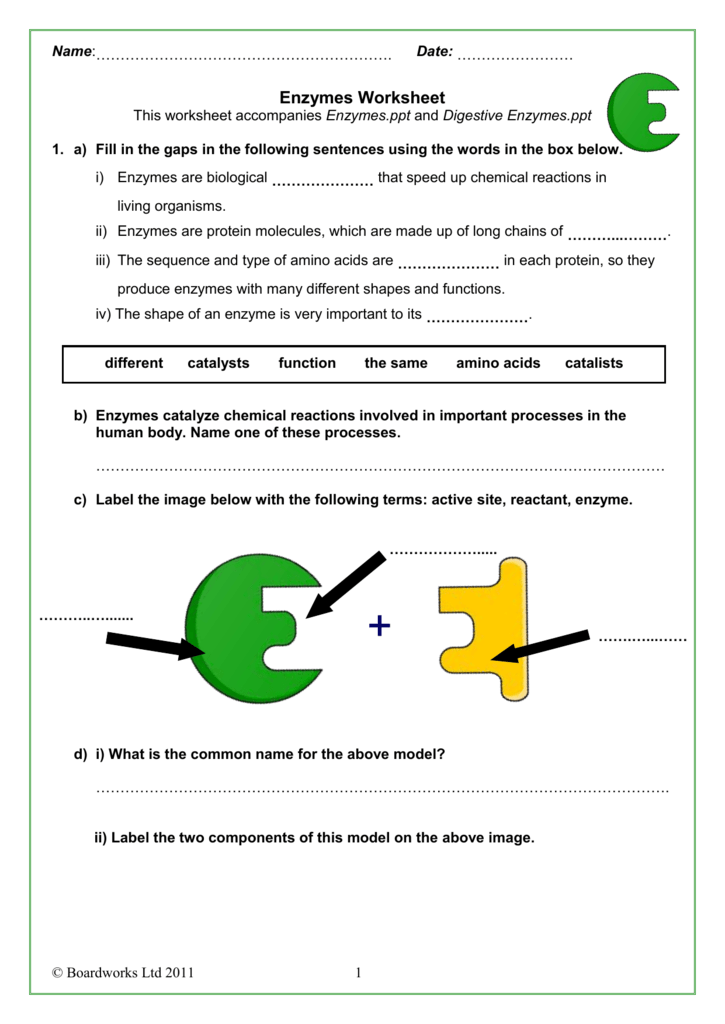
Enzymes are biological molecules (proteins) that act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions in the body. They are not consumed in the reactions they catalyze, allowing them to work repeatedly. Here’s what you should know:
- Nature: Proteins or RNA enzymes (ribozymes).
- Function: Lower the activation energy for reactions to occur, thereby accelerating reaction rates without altering the equilibrium between reactants and products.
- Specificity: Each enzyme has a specific substrate (the molecule upon which the enzyme acts).
How Do Enzymes Work?

Enzymes work through several mechanisms:
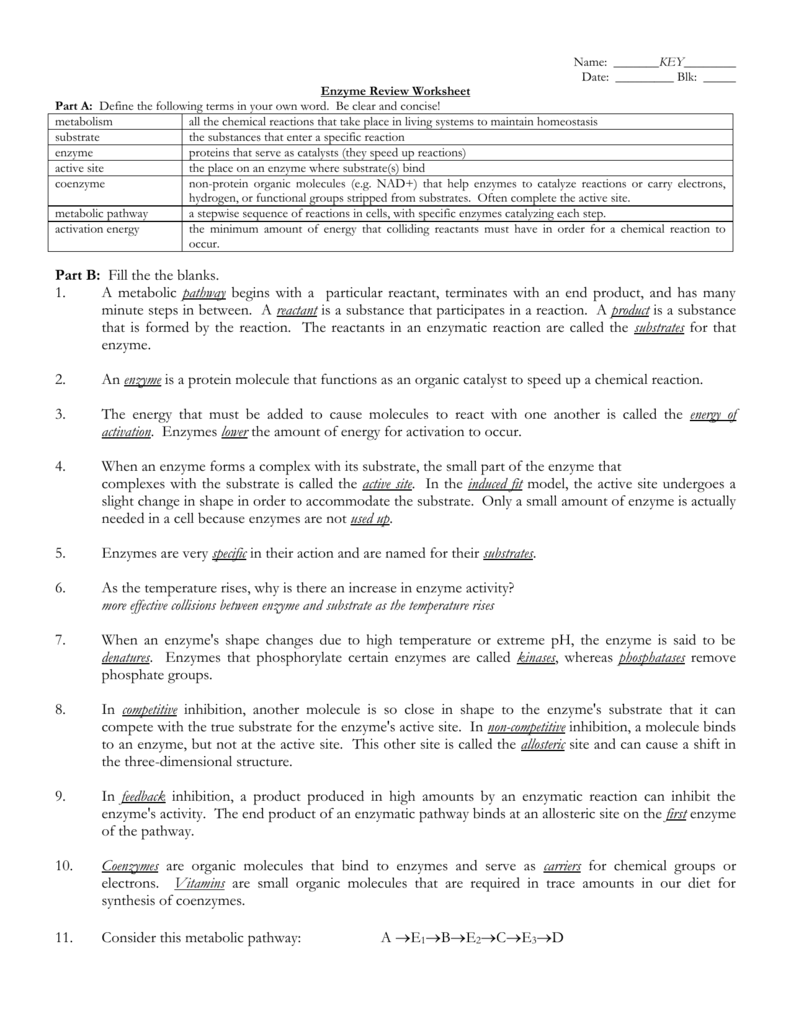
- Active Site: The region of the enzyme where the substrate binds, forming an enzyme-substrate complex.
- Lock and Key Model: This model suggests enzymes and substrates have complementary shapes, like a lock and key.
- Induced Fit Model: Upon binding, the enzyme’s active site changes slightly to fit the substrate more snugly, optimizing the reaction.
Enzyme Catalysis Steps:
- Enzyme and substrate come together.
- Binding of substrate to the active site.
- Enzyme undergoes a conformational change (induced fit).
- Chemical reaction occurs, converting substrate into product.
- Product is released, and the enzyme is ready for another cycle.
🔍 Note: Remember that the rate of enzymatic reactions can be influenced by several factors like temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and enzyme concentration.
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity

Enzyme activity is not static; it can be influenced by:
- Temperature: Optimal temperature allows enzymes to function at their peak. However, extreme temperatures denature enzymes.
- pH: Enzymes have an optimal pH range where they are most active.
- Substrate Concentration: Reaction rate increases with substrate concentration until the enzyme is saturated.
- Enzyme Concentration: More enzyme means more catalytic sites for substrate binding, increasing the reaction rate.
Common Enzyme Worksheet Questions and Answers
Here are some common questions you might encounter in enzyme worksheets:
1. What happens if the active site of an enzyme is altered?

An alteration in the active site can either reduce or completely inhibit the enzyme’s ability to bind with its substrate, effectively stopping or slowing down the reaction it catalyzes.
2. Why do enzymes show a bell curve when plotted against pH or temperature?

Enzymes are most active at their optimum conditions. Deviations from these conditions either denature the enzyme (making it less effective or inactive) or change its structure enough to reduce efficiency. This results in a peak at the optimum conditions on a graph.
3. How do competitive and non-competitive inhibitors affect enzymes?

- Competitive Inhibitors: Bind to the enzyme’s active site, competing with the substrate.
- Non-competitive Inhibitors: Bind to another site (allosteric site) and change the enzyme’s shape, reducing its catalytic activity.
4. What’s the role of cofactors and coenzymes?

Cofactors and coenzymes are non-protein chemical compounds that assist enzymes:
- Cofactors: Often metal ions like Zn²⁺ or Mg²⁺ that help stabilize the enzyme-substrate complex.
- Coenzymes: Organic molecules, usually vitamins or their derivatives, that participate in enzyme reactions.
By understanding these key aspects of enzymes, students can appreciate how life processes are regulated at the molecular level. Whether you're preparing for an exam or just seeking to understand biology better, these answers provide a foundation for deeper exploration into the fascinating world of biochemistry.
What is the difference between an enzyme and a catalyst?

+
An enzyme is a specific type of catalyst that is a biological molecule, most often proteins, used to speed up chemical reactions within the body. Catalysts, in general, can be any substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process, but they are not necessarily biological.
Can enzymes be reused?

+
Yes, one of the defining characteristics of enzymes is that they can catalyze reactions repeatedly. After the product is released, the enzyme returns to its original shape, ready to bind with another substrate molecule.
How do enzymes interact with substrates?

+
Enzymes bind to their substrates at specific sites called active sites. This interaction is usually highly specific due to the complementary shapes of the enzyme and substrate, which allows for precise molecular recognition and catalysis.