Boost Your Science Knowledge with Enzyme Activity Worksheet

Unlock the Secrets of Life Science

The intricate processes of life sciences can be both fascinating and complex, and one of the crucial topics that often intrigues both students and enthusiasts is enzyme activity. Enzymes are the tiny workhorses in our cells, speeding up biochemical reactions that would otherwise take an extraordinarily long time to occur. By exploring enzyme activity through worksheets, one not only gains a deeper understanding of biology but also learns valuable skills in scientific observation and analysis.
Why Enzymes Matter

Enzymes are essential for life as we know it:
- Catalysis: Enzymes lower the activation energy of reactions, allowing chemical processes to happen at a pace suitable for living organisms.
- Specificity: Each enzyme has a particular substrate it binds to, like a key fitting into a lock, ensuring only specific reactions occur.
- Regulation: Enzyme activity can be controlled to adapt to the body’s needs, such as in response to changing environmental conditions or metabolic demands.
Enzyme Activity Worksheets: A Hands-On Approach

Enzyme activity worksheets provide a structured way to understand how these catalysts function. Here’s how you can use them to enhance your scientific knowledge:
Understanding Enzyme Kinetics
One key aspect of enzyme function is how they interact with their substrates over time:
- Learn about Michaelis-Menten kinetics, which describes the relationship between enzyme concentration and substrate concentration, providing insights into the rate of enzyme reactions.
- Experiment with conditions affecting enzyme velocity like pH, temperature, substrate concentration, and inhibitors or activators.
- Work through problems that help you understand enzyme inhibition, both competitive and non-competitive.
💡 Note: Always refer to real-life scenarios for better comprehension; for instance, how the enzyme lactase functions when you consume dairy products.
Experimental Design and Data Analysis
Through enzyme activity worksheets, you can simulate or study real experiments:
- Design experiments to test enzyme function under varying conditions.
- Collect and analyze data, which can be quantitative (enzyme reaction rates) or qualitative (observations of reaction progress).
| Enzyme | Optimal pH | Optimal Temperature (°C) | Substrate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salivary Amylase | 6.7 - 7.0 | 32 - 37 | Starch |
| Pepsin | 1.5 - 2.0 | 37 | Proteins |
| Trypsin | 7.5 - 8.5 | 37 | Proteins |

Enzyme Activity in Different Environments
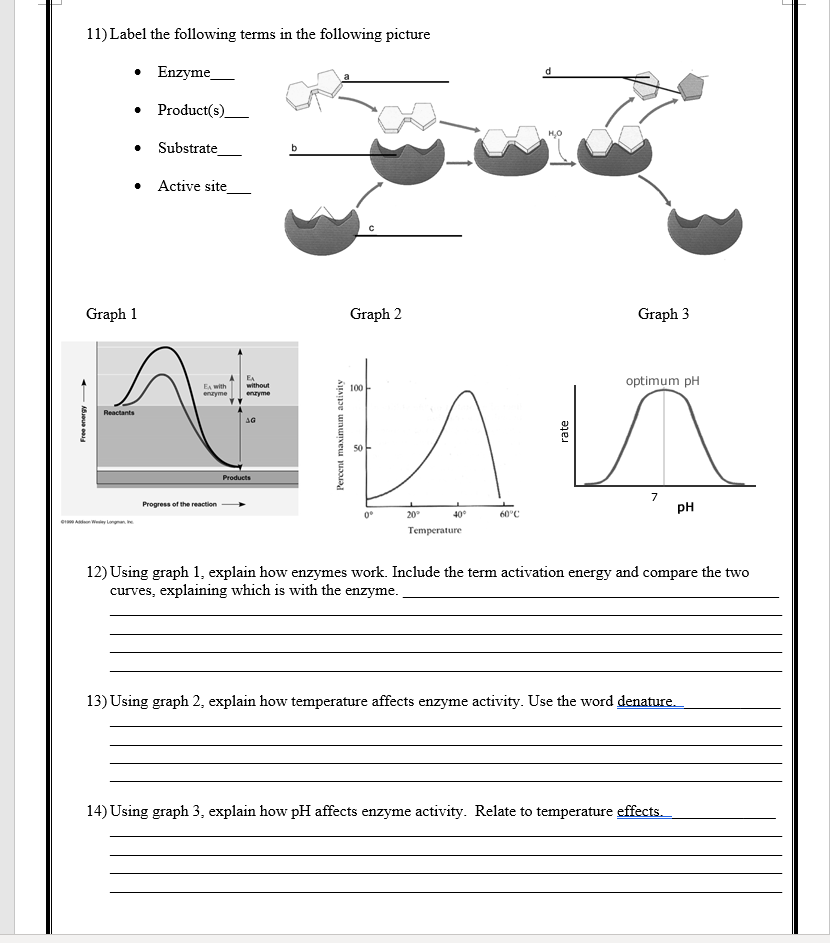
Understanding how environmental conditions affect enzymes helps in predicting and understanding:
- How and why certain enzymes are found in specific organs or biological conditions.
- The importance of maintaining a stable internal environment (homeostasis) for optimal enzyme function.
- Why certain biological processes can be disrupted by changes in environmental conditions.
Applications of Enzyme Activity

Enzyme activity is not just an academic exercise; it has real-world applications:
- Medicine: Enzymes as diagnostic tools, drug targets, and for enzyme replacement therapy.
- Industry: Enzymes in detergents, brewing, baking, and biotechnology for the production of biofuels and pharmaceuticals.
- Environmental Science: Enzymes in bioremediation to clean up pollutants.
🔬 Note: The complexity of enzyme function can be overwhelming, but understanding their basics is essential for many scientific disciplines.
Mastering Enzyme Activity through Worksheets

Worksheets can be invaluable tools for mastering enzyme activity:
- Reinforcing theoretical knowledge through practical application.
- Providing repetitive practice to solidify understanding of key concepts.
- Simulating experiments that might not be possible in a classroom setting due to time or equipment constraints.
Wrapping Up
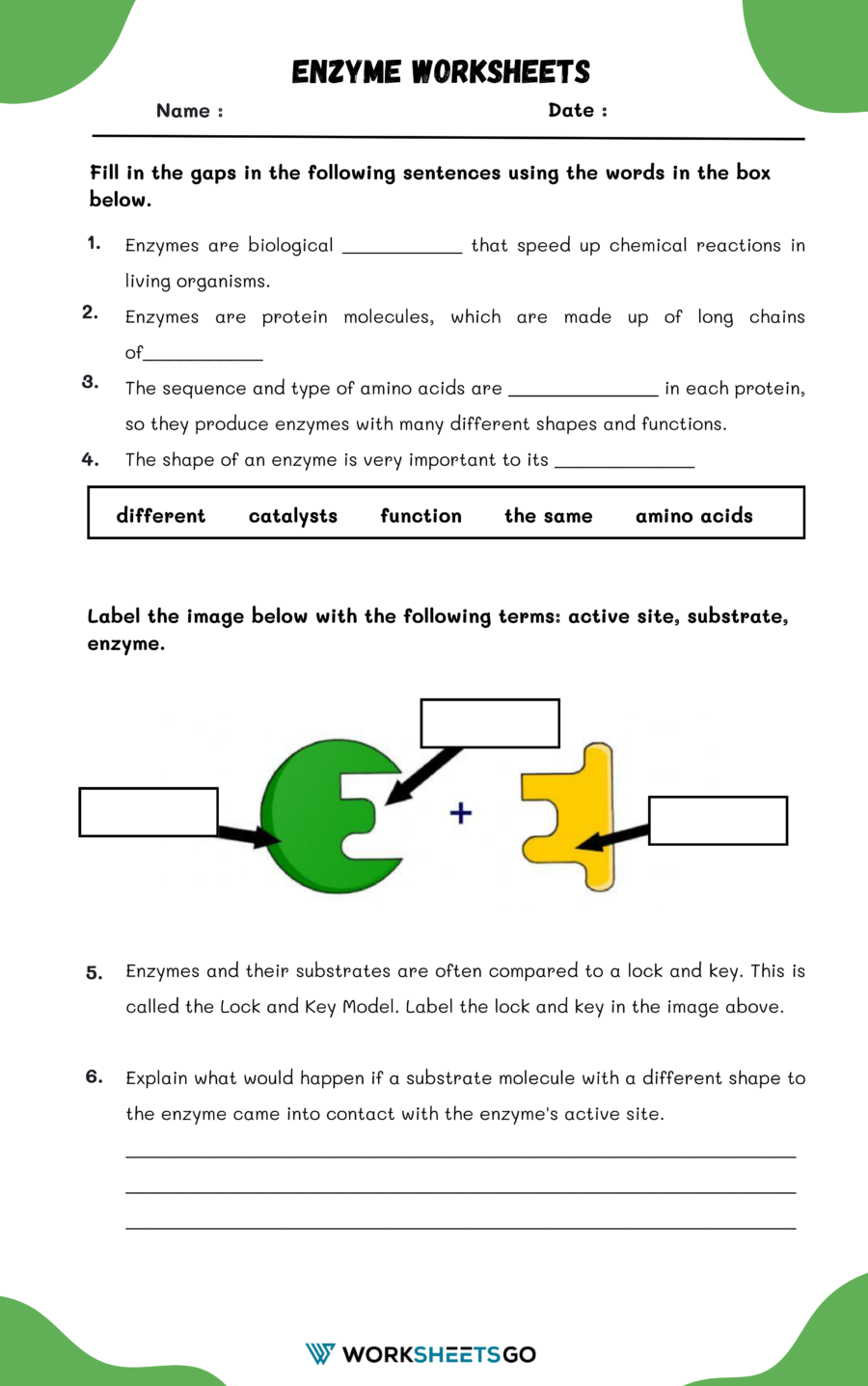
The study of enzyme activity through worksheets is a gateway to comprehending the delicate machinery of life. These exercises help to visualize how enzymes operate, enhance one’s ability to design experiments, and reinforce the importance of enzymes in everyday biological processes. By immersing oneself in such activities, not only do we understand the basics of biochemistry, but we also bridge the gap between theory and real-world application.
Why are enzymes critical for life?

+
Enzymes catalyze biochemical reactions, which are essential for cellular metabolism, growth, repair, and various physiological processes. Without enzymes, life as we know it would not be possible because these reactions would occur too slowly to sustain life.
How does pH affect enzyme activity?

+
The activity of enzymes can be greatly influenced by pH due to changes in the enzyme’s shape at extreme pH levels. Each enzyme has an optimal pH range where it functions most efficiently. Deviations from this range can denature the enzyme, rendering it less or completely inactive.
Can enzymes be reused in reactions?

+
Yes, enzymes are not consumed during the reaction they catalyze. After the product is formed, the enzyme is released unchanged and can bind with another substrate molecule, allowing for multiple reactions to be facilitated by the same enzyme molecule.
What are enzyme inhibitors?

+
Enzyme inhibitors are molecules that decrease or block enzyme activity. They can bind to the enzyme, either at the active site (competitive inhibition) or at another location that affects the enzyme’s shape (non-competitive inhibition), thus reducing its catalytic efficiency.
How can understanding enzymes benefit research and industry?
+Understanding enzyme function has numerous applications:
- Developing more effective drugs by targeting enzyme pathways.
- Biotechnological processes where enzymes speed up industrial reactions.
- Designing enzyme-based biosensors for environmental monitoring.
- Creating enzyme-modified foods or improving food processing techniques.