Enlisted Navy Rank Structure
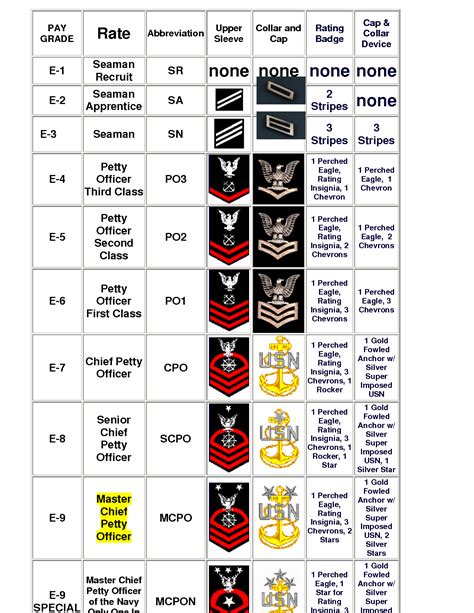
Understanding the Enlisted Navy Rank Structure

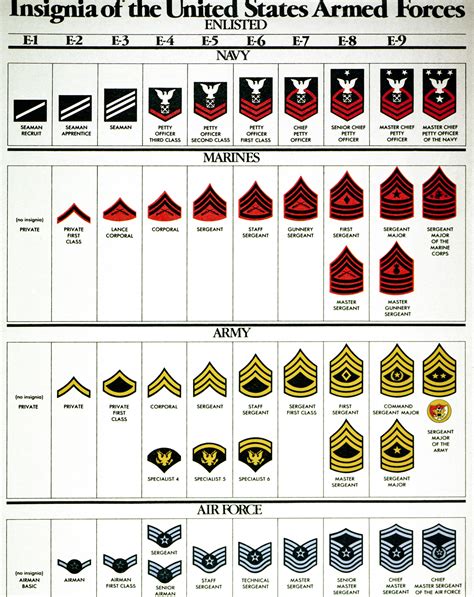
The United States Navy has a unique rank structure that is different from other branches of the military. The enlisted rank structure is divided into three main categories: junior enlisted, non-commissioned officers (NCOs), and senior enlisted. Each category has its own set of ranks, and each rank has its own set of responsibilities and requirements.
Junior Enlisted Ranks (E-1 to E-3)

The junior enlisted ranks are the entry-level ranks for new recruits. These ranks are:
- Seaman Recruit (E-1): This is the lowest rank in the Navy, and it is the rank that new recruits receive when they first enlist.
- Seaman Apprentice (E-2): This rank is given to sailors who have completed their initial training and are beginning their career in the Navy.
- Seaman (E-3): This rank is given to sailors who have completed their first year of service and have demonstrated a level of competence in their job.
Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks (E-4 to E-6)
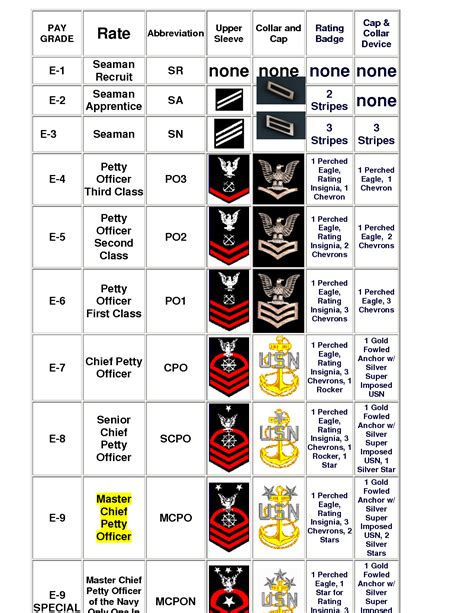
The NCO ranks are the backbone of the Navy’s enlisted leadership. These ranks are:
- Petty Officer Third Class (E-4): This rank is given to sailors who have demonstrated a level of leadership and expertise in their job.
- Petty Officer Second Class (E-5): This rank is given to sailors who have completed advanced training and have demonstrated a high level of competence in their job.
- Petty Officer First Class (E-6): This rank is given to sailors who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and expertise in their job.
Senior Enlisted Ranks (E-7 to E-9)
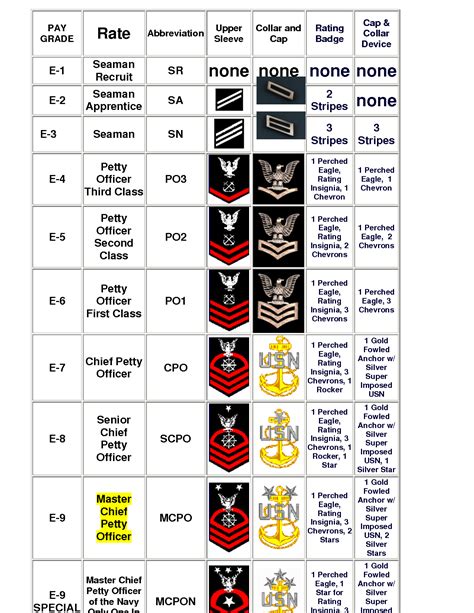
The senior enlisted ranks are the highest ranks in the Navy’s enlisted structure. These ranks are:
- Chief Petty Officer (E-7): This rank is given to sailors who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and expertise in their job.
- Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8): This rank is given to sailors who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and expertise in their job, and have also completed advanced training.
- Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9): This is the highest rank in the Navy’s enlisted structure, and it is given to sailors who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and expertise in their job.
📝 Note: The Navy also has a number of special ranks, such as the Navy Diver and the Navy SEAL, which are not part of the standard rank structure.
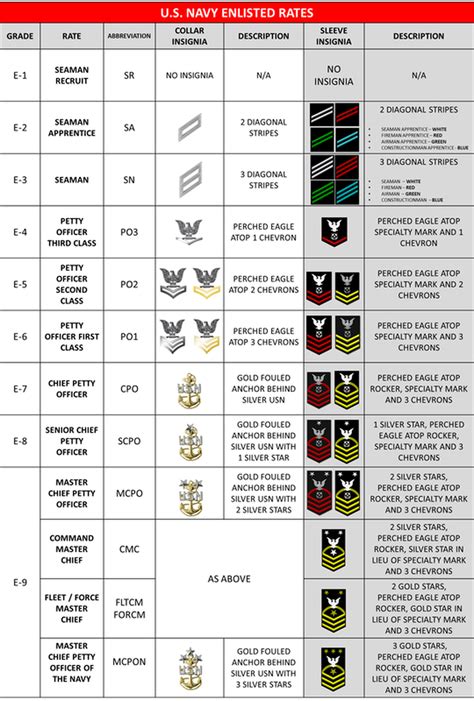
Rank Insignia
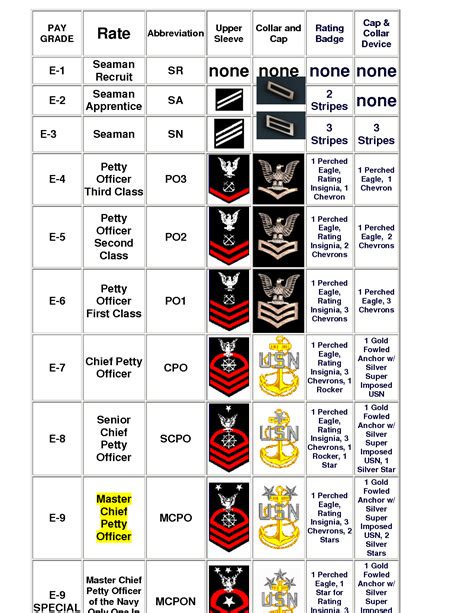
Each rank in the Navy has its own unique insignia, which is worn on the sleeve of the uniform. The insignia are as follows:
| Rank | Insignia |
|---|---|
| Seaman Recruit (E-1) | No insignia |
| Seaman Apprentice (E-2) | One diagonal stripe |
| Seaman (E-3) | Two diagonal stripes |
| Petty Officer Third Class (E-4) | One anchor |
| Petty Officer Second Class (E-5) | One anchor with one diagonal stripe |
| Petty Officer First Class (E-6) | One anchor with two diagonal stripes |
| Chief Petty Officer (E-7) | One anchor with three diagonal stripes |
| Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8) | One anchor with four diagonal stripes |
| Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9) | One anchor with five diagonal stripes |

Conclusion

The enlisted Navy rank structure is a complex system that is designed to recognize the achievements and leadership abilities of sailors. Each rank has its own unique insignia and set of responsibilities, and advancing through the ranks requires a combination of hard work, dedication, and leadership.
What is the lowest rank in the Navy?
+
The lowest rank in the Navy is Seaman Recruit (E-1).
What is the highest rank in the Navy’s enlisted structure?
+
The highest rank in the Navy’s enlisted structure is Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9).
How do sailors advance through the ranks in the Navy?

+
Sailors advance through the ranks in the Navy by completing training and demonstrating leadership and expertise in their job.