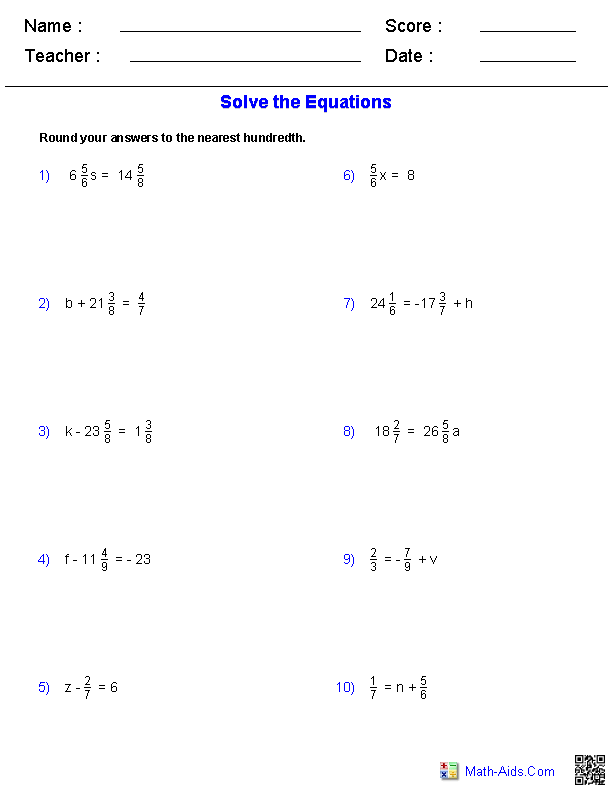Boost Your Chemistry Skills with Energy Worksheet #1

Chemistry is a fascinating field that intertwines with numerous aspects of daily life, from the food we eat to the technology we use. A robust understanding of chemistry can open up diverse career pathways and enhance one's ability to understand and innovate within scientific contexts. For those looking to strengthen their grasp on this subject, energy-related concepts are pivotal. Energy is at the core of chemical reactions and processes. This post delves into the Energy Worksheet #1 – an excellent resource to boost your chemistry skills, particularly in understanding energy concepts within chemical contexts.
Why Energy Matters in Chemistry

Before diving into the worksheet itself, let's appreciate why energy is fundamental in chemistry:
- Chemical Bonding: The formation, breaking, and rearrangement of chemical bonds all involve energy.
- Chemical Reactions: Energy changes occur when reactions proceed, affecting their feasibility, rate, and equilibrium.
- Heat of Reaction: Exothermic and endothermic reactions showcase how energy is released or absorbed.
Overview of Energy Worksheet #1

Energy Worksheet #1 is designed to help students:
- Understand concepts like potential energy, kinetic energy, and internal energy.
- Learn how to calculate and interpret energy changes in reactions.
- Practice solving problems related to heat capacity, calorimetry, and enthalpy.
This worksheet typically includes a variety of problem types, from simple calculations to more complex scenarios requiring a deep understanding of energy principles. Let's explore these components in detail.
Key Concepts Covered in the Worksheet

Potential Energy

Potential energy (PE) refers to the stored energy in an object due to its position or configuration. In a chemical context, this includes:
- Bond Energy: Energy associated with the formation of chemical bonds.
- Intermolecular Forces: Forces that bind molecules together, influencing their PE.
Kinetic Energy

Kinetic energy (KE) is the energy of motion. In chemistry:
- Translational KE: Movement of molecules or particles through space.
- Vibrational KE: Oscillations or vibrations within molecular structures.
Internal Energy

Internal energy (U) sums up all forms of energy within a system, including:
- Kinetic and Potential Energies: The sum of KE and PE for all particles within the system.
- Energy of Bonds: Energy held in the chemical bonds of a substance.
Energy Worksheet #1 – Problems and Solutions

Here’s a brief overview of some typical questions you might find in Energy Worksheet #1:
Question 1: Heat Capacity Calculations

| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| A 100-gram sample of water is heated from 25°C to 75°C. What is the change in internal energy if the specific heat capacity of water is 4.18 J/g°C? |
Using q = mc∆T: q = 100g * 4.18 J/g°C * (75°C - 25°C) q = 20,900 J or 20.9 kJ |

Question 2: Enthalpy of Reaction

Consider the reaction:
C₂H₄(g) + 3O₂(g) → 2CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(g)
Given the standard enthalpies of formation:
- C₂H₄: -393.5 kJ/mol
- O₂: 0 kJ/mol
- CO₂: -393.5 kJ/mol
- H₂O(g): -241.8 kJ/mol
Calculate the enthalpy change for this reaction.
🔍 Note: Enthalpy of formation provides a direct path to compute reaction enthalpy.
Question 3: Heat Transfer and Work

When a gas expands against a constant pressure of 2 atm from 5.0 liters to 7.0 liters at a constant temperature, calculate the work done by the gas.
🔍 Note: Work done by or on a system is another way energy changes manifest in chemistry.
Using Energy Worksheet #1 for Effective Learning

To make the most out of Energy Worksheet #1, consider these strategies:
- Systematically Solve Problems: Start with basic calculations and gradually tackle more complex scenarios.
- Understand Concepts: Link the mathematical solutions to the underlying chemical principles. Understand why these calculations make sense.
- Review and Reflect: After solving problems, review your work to consolidate learning and to identify areas for improvement.
Strategies for Difficult Energy Concepts
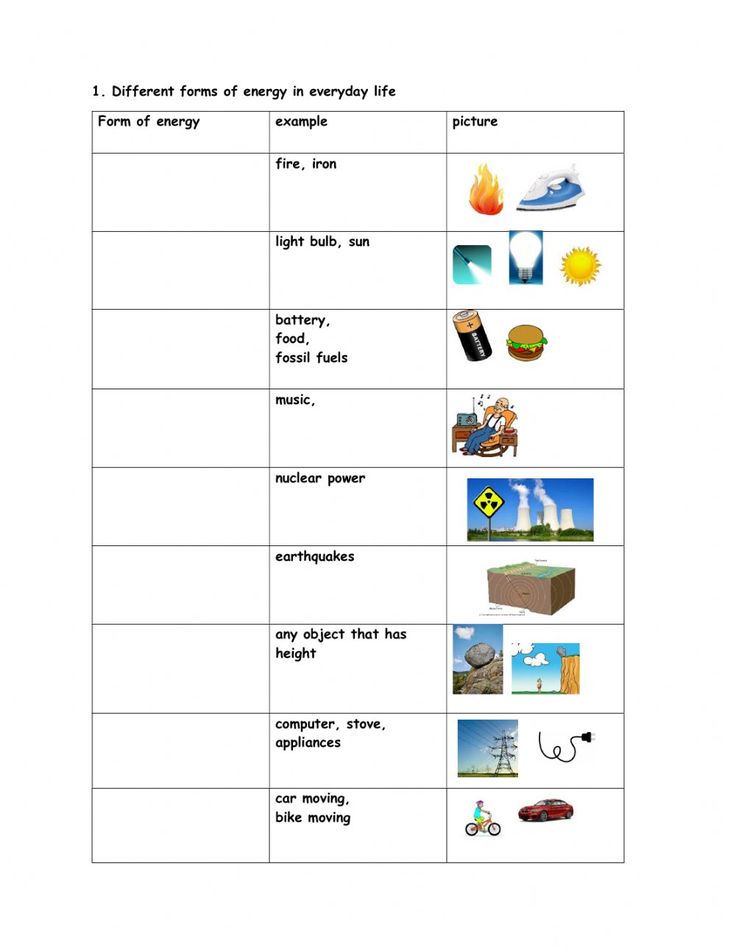
Energy in chemistry can be tricky. Here are some tips to master complex concepts:
- Visualization: Use diagrams to visualize energy changes, molecular structures, and energy landscapes.
- Analogies: Analogies can help connect abstract chemical principles with everyday experiences, making learning more intuitive.
- Real-World Applications: Relate concepts to real-life scenarios, like fuel efficiency or metabolism, to ground the learning in practical contexts.
In wrapping up this exploration of Energy Worksheet #1, let's consolidate the key takeaways. This worksheet serves as an invaluable tool for developing a solid grasp of energy concepts in chemistry. It spans fundamental ideas like potential, kinetic, and internal energy, and delves into practical applications through problem-solving. By mastering the principles outlined, you equip yourself not just with knowledge but with problem-solving skills applicable across various chemical contexts. Remember, energy is not just a mathematical abstraction; it's the driving force behind all chemical processes, making its understanding essential for anyone looking to excel in chemistry.
Why is energy conservation important in chemistry?
+
Energy conservation is crucial because it dictates the balance and feasibility of chemical reactions. Understanding it allows us to predict reactions, optimize processes, and design efficient energy storage systems.
How do you calculate energy changes in reactions?

+
Energy changes in reactions can be calculated using various methods like Hess’s Law, bomb calorimetry, or through the study of standard enthalpies of formation.
What’s the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions?

+
Endothermic reactions absorb energy from their surroundings, making it colder, while exothermic reactions release energy, heating their surroundings. This energy exchange is reflected in the enthalpy change (∆H) of a reaction.