Energy Transformation Worksheet Answers: Simplified Solutions

Energy transformation is a fundamental concept that not only dictates the efficiency of energy systems but also shapes our daily experiences with technology and nature. In this detailed guide, we will delve into the essential principles of energy transformations, covering how energy changes from one form to another through various processes and systems. This blog post serves as an in-depth worksheet answer guide, providing clear explanations and solutions to understanding the myriad ways energy is transformed in our environment.
What is Energy Transformation?

Energy transformation refers to the process by which energy changes from one form to another. This can occur in a myriad of settings, from the basic functioning of an electric circuit to the complex biochemical processes within living organisms. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, as stated by the Law of Conservation of Energy, but it can change its form:
- Kinetic to potential, and vice versa
- Chemical to thermal or electrical
- Light to electrical in solar cells

Key Concepts of Energy Transformation

Understanding the following key concepts will help in comprehending the intricacies of energy transformation:
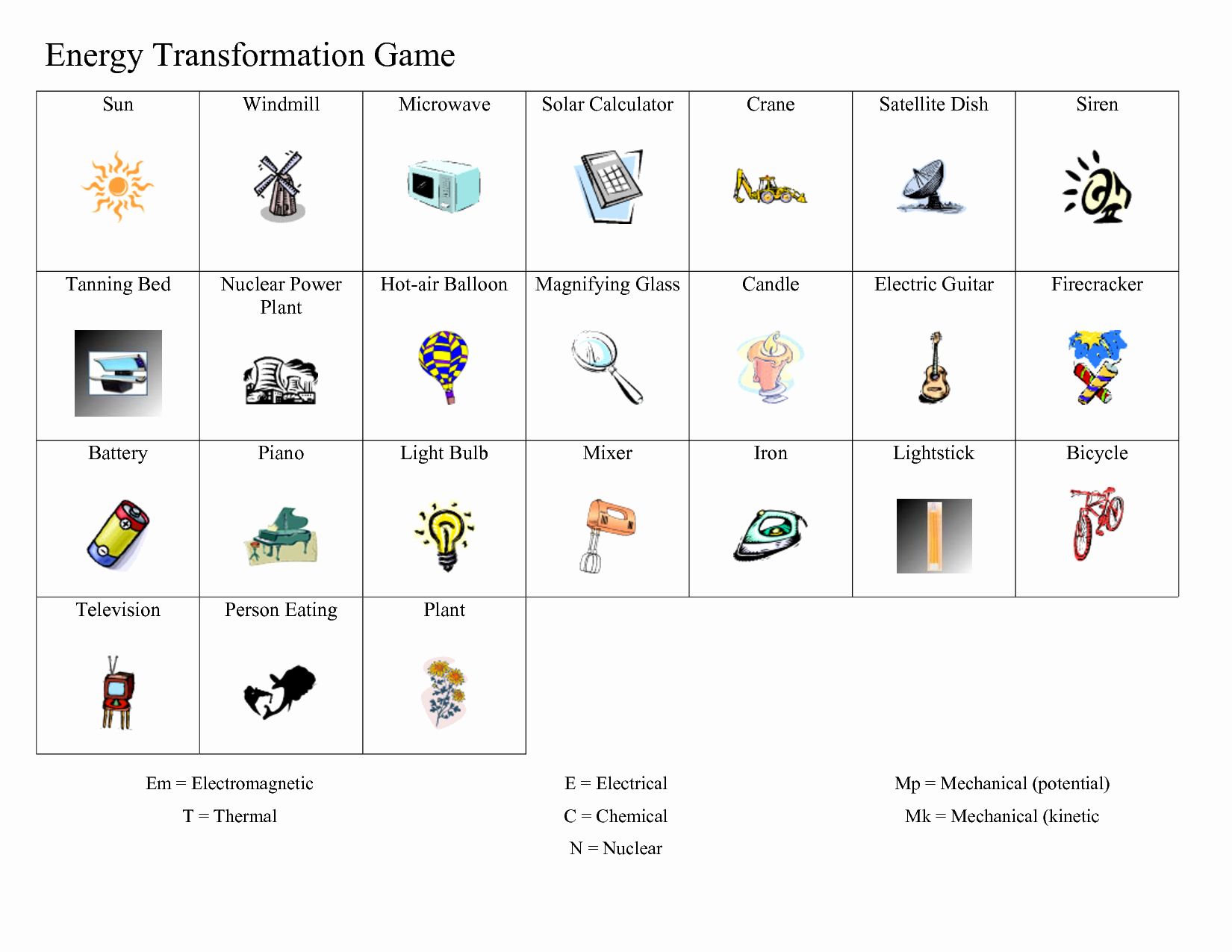
- Forms of Energy: There are numerous forms energy can take, such as kinetic, potential, thermal, chemical, electrical, nuclear, elastic, gravitational, and light energy.
- Conservation of Energy: While energy transforms, the total amount remains constant.
- Energy Efficiency: During transformation, some energy is often lost as unusable heat, reducing overall efficiency.
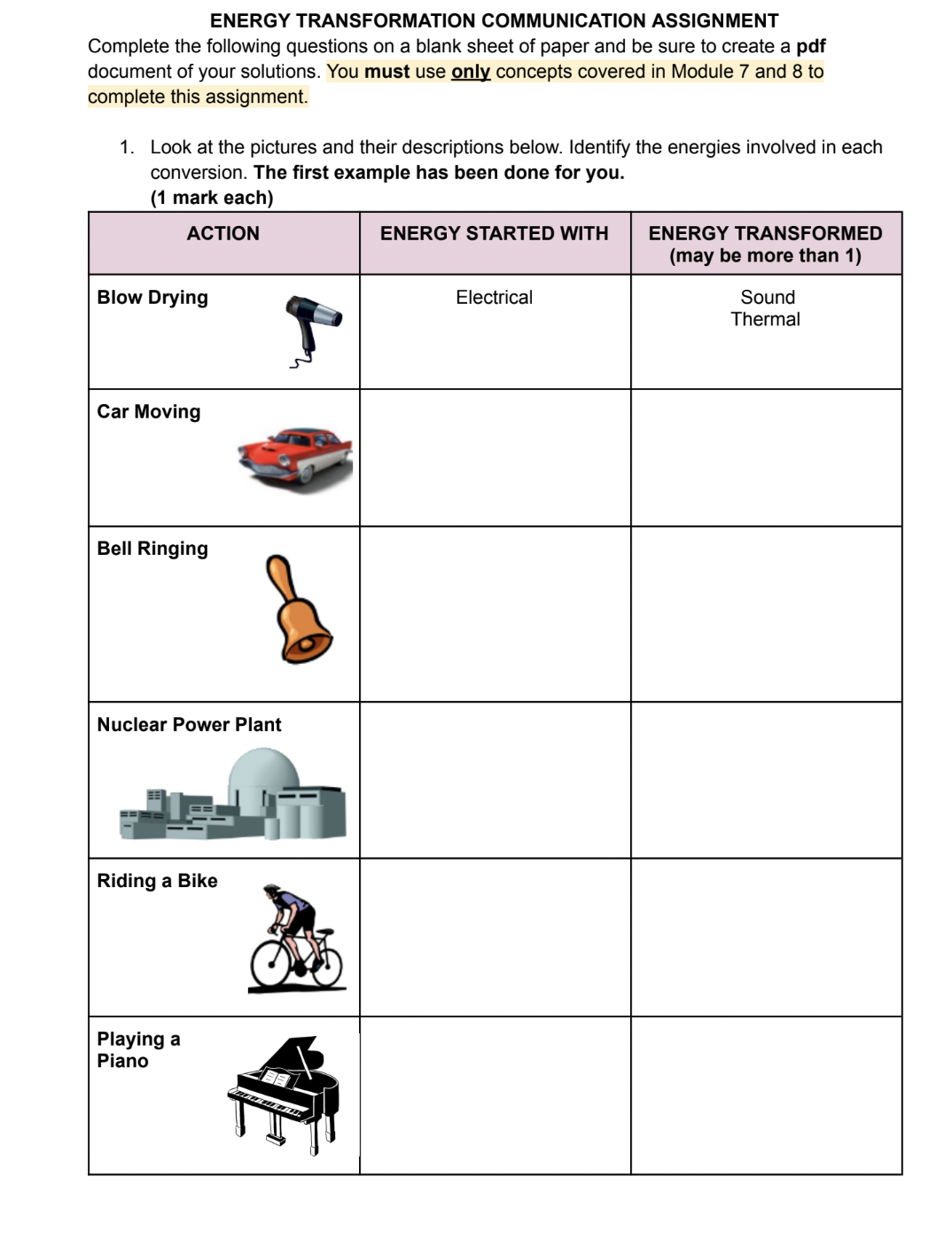
Common Energy Transformation Processes

Let’s explore some everyday examples of energy transformations:
Electrical to Thermal
This is seen in devices like heaters or toasters:
- Electricity flows through a resistor, generating heat.
- Heat is then transferred to the surroundings or used to cook food.
Chemical to Electrical

In batteries, chemical reactions release electrons, converting chemical energy into electrical:
- Electrons move from anode to cathode, creating a flow of electricity.
Mechanical to Electrical
A typical example is an electric generator:
- Mechanical work is done on a coil to induce an electric current through electromagnetic induction.
Light to Chemical

Photosynthesis in plants:
- Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll, converting it into chemical energy stored in glucose.
Real-life Applications of Energy Transformation

Here are some real-life applications where energy transformation plays a pivotal role:
Automobiles

An engine transforms chemical energy in gasoline into kinetic energy:
- Gasoline burns, releasing stored chemical energy.
- Expanding gases push pistons, converting chemical energy to mechanical.
- The mechanical motion then powers the car’s motion.
Wind Turbines

Wind energy is converted into electrical energy:
- Wind turns the blades.
- Blade motion rotates a generator, producing electricity.
💡 Note: The efficiency of wind turbines depends on various factors like wind speed and turbine design.
Solar Panels
Solar cells transform sunlight directly into electricity:
- Photons from the sun strike solar cells, generating electron-hole pairs.
- These pairs move, creating an electric current.
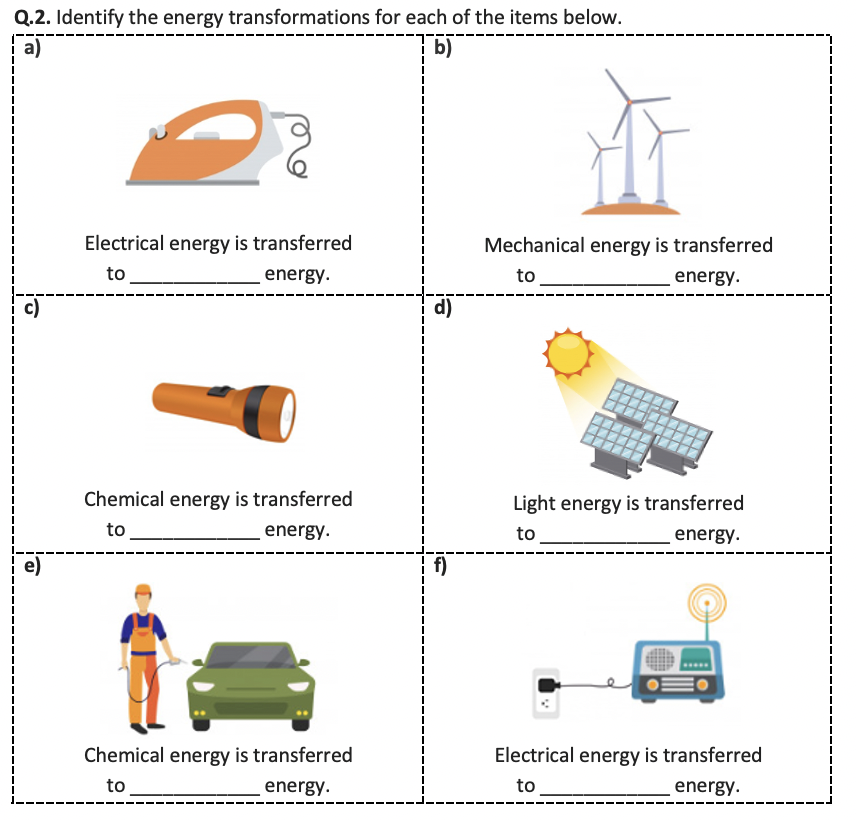
Worksheet Answers

To illustrate how these principles apply to specific questions, here are answers to common worksheet problems:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| How does a hydroelectric dam generate electricity? | The dam stores water at height, creating potential energy. When released, water flows, converting this energy into kinetic energy, which turns a turbine. The turbine then rotates a generator, converting kinetic energy to electrical energy. |
| Why do batteries eventually run out? |

The chemical reactions that produce electricity reach equilibrium or exhaust the reactants, stopping the flow of electrons. Thus, chemical energy is depleted.
In conclusion, energy transformation is a cornerstone of both natural and technological processes, allowing energy to be utilized in the most beneficial ways. Understanding how energy changes from one form to another enables us to create more efficient systems, reduce waste, and harness renewable sources to mitigate environmental impacts. Whether it’s through photosynthesis, the operation of your car’s engine, or the charging of your smartphone, energy transformation is always at work, shaping our world in subtle yet profound ways.
What is the most common type of energy transformation?

+
The most common is probably the conversion of chemical energy to thermal energy in processes like burning fossil fuels or during metabolic reactions in the human body.
Can energy transformation be 100% efficient?

+
No, no real-world energy transformation is 100% efficient; some energy always escapes as unusable heat due to the Second Law of Thermodynamics.
Why is solar energy considered a renewable resource?

+
Solar energy is renewable because it uses sunlight, which is available in virtually unlimited quantities, and the energy can be converted into electricity or heat without depleting its source.


