5 Key Insights on Energy Pyramids Worksheet Answers

Energy pyramids are essential tools used by ecologists and educators to illustrate the flow of energy through an ecosystem, often showing a decrease in available energy at each trophic level. Here are 5 key insights into energy pyramids worksheet answers:
The Concept of Energy Transfer


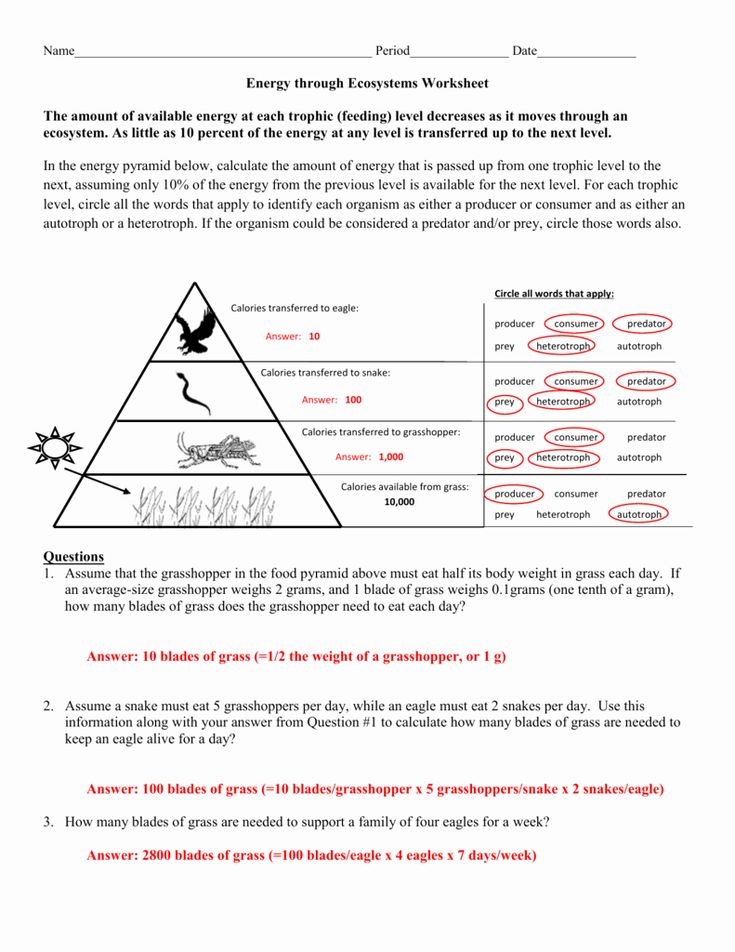
- Energy transfer in ecosystems follows the Lindeman’s 10% rule, which states that only about 10% of the energy at one trophic level is transferred to the next. This inefficiency is due to various factors like metabolic processes, heat loss, and non-digestible parts of food.
- The energy pyramid worksheet answers often highlight this efficiency, making it clear why organisms at higher trophic levels require larger quantities of lower level organisms for sustenance. This pyramid shape demonstrates the disproportionate energy availability from the bottom to the top.
Primary Production and Pyramid Shape

| Trophic Level | Organisms | Energy Transfer Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Producers (Trophic level 1) | Plants, algae, phytoplankton | 100% |
| Primary Consumers (Trophic level 2) | Herbivores | 10% |
| Secondary Consumers (Trophic level 3) | Carnivores or Omnivores | 1% |
| Tertiary Consumers (Trophic level 4) | Top carnivores | 0.1% |

🌱 Note: Understanding the proportion of energy transfer is crucial for grasping the ecological food web dynamics.
Energy Loss Through Decomposition

- Decomposers play a significant role in energy pyramids, breaking down dead organisms and waste material, releasing nutrients back into the environment. However, the energy released is in a form not directly usable by higher trophic levels.
- In most worksheets, answers to questions about decomposers’ roles highlight this point, showing how these organisms contribute to nutrient cycling rather than directly to energy flow through the pyramid.
Human Impact and Energy Pyramids
- Human activities like pollution, deforestation, and hunting can disrupt the balance of energy pyramids by altering population numbers at various trophic levels. Students often analyze these effects through hypothetical or real scenarios in their worksheet answers.
- Education on human impacts often involves discussing how energy pyramids can shift due to changes in primary productivity or changes in higher trophic levels due to human consumption or conservation efforts.
The Importance of Energy Pyramids in Conservation

- Understanding energy pyramids helps in conservation efforts by showing how removing or overpopulating a single species can affect the entire ecosystem.
- Worksheet answers might focus on case studies or theoretical problems that illustrate how conservation practices like creating protected areas or managing invasive species can be informed by energy pyramid principles.
Recognizing the dynamics of energy transfer through an ecosystem through the lens of an energy pyramid provides not only fascinating insights into ecological sustainability but also into how we, as humans, interact with and influence these systems. By grasping these concepts, we're better equipped to make informed decisions about environmental conservation and how our daily actions impact the natural world. From understanding the inefficiency of energy transfer to acknowledging our role in altering ecosystems, energy pyramids serve as a pivotal educational tool.
Why do most energy pyramid worksheets emphasize the 10% rule?

+
The 10% rule is a simplified but effective way to explain the energy inefficiency in ecosystems, making it a cornerstone for understanding ecological energy transfer.
How does human impact affect energy pyramids?

+
Human activities can disrupt the natural balance of energy pyramids by altering energy flow at different trophic levels, often causing instability or shifts in species populations.
What are decomposers’ roles in the energy pyramid?

+
Decomposers release energy from dead organisms back into the ecosystem, but this energy is not transferred to higher trophic levels; instead, it returns to the nutrient cycle, aiding in new primary production.