Master the Basics: Empirical and Molecular Formula Practice

Understanding the fundamentals of chemistry is essential not just for chemists and chemical engineers but for anyone curious about the natural world. Among these fundamentals, the concepts of empirical and molecular formulas stand out as keystones in understanding the composition of chemical compounds. Whether you're a student tackling chemistry courses, or a professional seeking to brush up on your knowledge, mastering these basics can greatly enhance your grasp of material science, biochemistry, environmental science, and many other fields. Let's dive into the intricacies of empirical and molecular formulas and practice their calculation.
What are Empirical and Molecular Formulas?

An empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms present in a compound. It does not necessarily reflect the actual number of atoms in each molecule of the compound. Instead, it gives the proportions of elements in their simplest form. For example, the empirical formula for hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is HO, showing a 1:1 ratio of hydrogen to oxygen.
The molecular formula, on the other hand, shows the actual number of each type of atom in a single molecule of a compound. This formula can be derived from the empirical formula by multiplying the subscripts by a whole number. Using the previous example, the molecular formula for hydrogen peroxide is H2O2, indicating two hydrogen atoms for every two oxygen atoms.
Calculating the Empirical Formula
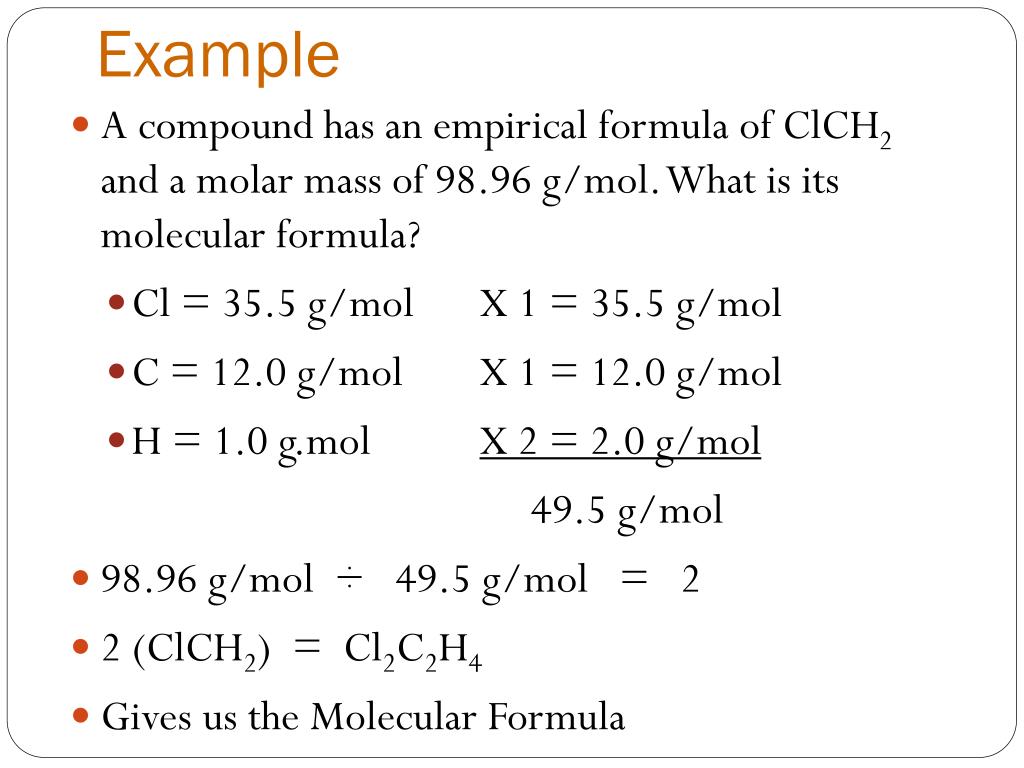
To calculate the empirical formula, follow these steps:
- Determine the mass or percent composition of each element in the compound.
- Convert the mass or percent composition into moles by dividing by the element’s atomic mass.
- Divide the moles of each element by the smallest number of moles to get the simplest ratio. If necessary, multiply by the smallest whole number to make all ratios whole numbers.
- The ratios now give you the subscripts for the empirical formula.
| Element | Mass (g) | Moles | Ratio | Whole Number Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 4.0 | 3.97 (4.0 / 1.01) | 1 | 1 |
| Oxygen | 32.0 | 2.0 (32.0 / 16.0) | 0.5 | 1 |
💡 Note: When calculating the empirical formula, if your ratio yields a non-whole number like 1.5 or 2.5, multiply all ratios by a whole number (usually 2 or 3) to obtain whole numbers.
Calculating the Molecular Formula

The molecular formula can be determined from the empirical formula if you know the molar mass of the compound:
- Find the empirical formula’s molar mass.
- Divide the compound’s given molar mass by the empirical formula’s molar mass. This gives you a whole number, which we’ll call ‘n’.
- Multiply each subscript in the empirical formula by ‘n’ to get the molecular formula.
Example: Suppose the empirical formula is CH and the molar mass is 78 g/mol. The molar mass of CH is 12 + 1 = 13 g/mol. Dividing 78 by 13 gives 'n' = 6. Therefore, the molecular formula is C6H6.
Empirical and Molecular Formula Practice Problems

Let’s apply what we’ve learned with some practice problems:
Problem 1:

A compound contains 24.75% magnesium, 12.84% carbon, and 62.41% oxygen by mass. Calculate the empirical formula.
- Convert percentages to grams (assuming 100g of the compound): Magnesium: 24.75g, Carbon: 12.84g, Oxygen: 62.41g
- Convert grams to moles:
- Mg: 24.75g / 24.31g/mol = 1.018 mol
- C: 12.84g / 12.01g/mol = 1.068 mol
- O: 62.41g / 16.00g/mol = 3.901 mol
- Divide by smallest moles to get the ratio:
- Mg: 1.018/1.018 = 1
- C: 1.068/1.018 = 1.05 ≈ 1 (for simplicity)
- O: 3.901⁄1.018 = 3.83 ≈ 4
- The empirical formula is MgCO4.
Problem 2:

The empirical formula of a compound is NO2, and its molar mass is 92.0 g/mol. Determine the molecular formula.
- Empirical formula weight = 14.01 + (2 * 16.00) = 46.01 g/mol
- ‘n’ = 92.0/46.01 ≈ 2
- Thus, the molecular formula is N2O4.
Understanding the Significance

Empirical and molecular formulas are not just academic exercises; they have real-world implications:
- They help in identifying compounds through their composition.
- They are crucial in drug synthesis for pharmaceuticals.
- They assist in determining the stoichiometry for reactions in industry and research.
💡 Note: The difference between empirical and molecular formulas can provide insights into the bonding structure of molecules, particularly in polymers where the empirical formula might represent the repeat unit.
In recapitulating our exploration, understanding and calculating empirical and molecular formulas unlocks a deeper comprehension of chemical substances. These skills are foundational for advancing in chemistry, biochemistry, or any science-related discipline. By practicing these calculations, you not only grasp the structural aspects of chemistry but also the quantitative analysis that underpins so much of scientific inquiry. Remember, the next time you encounter a new compound, you now have the tools to deduce its simplest form and potentially its actual molecular structure, enriching your understanding of the material world around you.
What’s the difference between an empirical and a molecular formula?

+
An empirical formula provides the simplest ratio of atoms in a compound, whereas a molecular formula shows the actual number of each atom in one molecule of the compound.
Why can’t the empirical formula always give the molecular formula?

+
The empirical formula simplifies the ratios of atoms. In some cases, like water (H2O) or carbon dioxide (CO2), the empirical and molecular formulas are the same because the atoms are already in their simplest whole-number ratio. In other cases, the empirical formula is a fraction of the molecular formula, and additional data (like molar mass) is needed to determine the actual molecular formula.
How can knowing the empirical formula help in the lab?

+
In the lab, knowing the empirical formula can help chemists:
- Identify unknown substances through their composition.
- Develop new compounds with specific ratios of elements.
- Understand reaction mechanisms by knowing which atoms are involved in a reaction.