5 Emergency Medical Specialists

Introduction to Emergency Medical Specialists

Emergency medical specialists are highly trained professionals who play a crucial role in the healthcare system. They are responsible for providing immediate medical attention to patients who are critically ill or injured. These specialists work in emergency departments, intensive care units, and other high-pressure environments, where they must make quick and accurate decisions to save lives. In this article, we will explore five different types of emergency medical specialists and their roles in the medical field.
1. Emergency Medicine Physicians

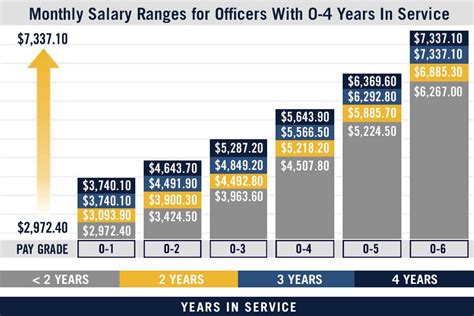
Emergency medicine physicians, also known as emergency room (ER) doctors, are medical specialists who diagnose and treat patients with acute illnesses or injuries. They work in emergency departments, where they assess patients, order diagnostic tests, and develop treatment plans. Emergency medicine physicians must be able to think critically and make quick decisions in high-pressure situations. They often work long hours, including night shifts, weekends, and holidays. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment of physicians and surgeons, including emergency medicine physicians, is projected to grow 7% from 2020 to 2030.
2. Paramedics

Paramedics are emergency medical technicians (EMTs) who provide advanced life support to patients in emergency situations. They work on ambulances, in emergency rooms, and in other healthcare settings, where they administer medications, perform medical procedures, and use specialized equipment to stabilize patients. Paramedics must be able to work well under pressure and make quick decisions in emergency situations. They often work long hours, including night shifts, weekends, and holidays. Paramedics must complete a paramedic training program and obtain certification or licensure to practice in their state.
3. Emergency Nurse Practitioners

Emergency nurse practitioners (ENPs) are advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs) who specialize in emergency nursing. They work in emergency departments, where they assess patients, diagnose illnesses, and develop treatment plans. ENPs often work independently, but they may also collaborate with physicians and other healthcare professionals to provide patient care. ENPs must complete a master’s degree program in nursing and obtain certification as a family nurse practitioner (FNP) or an acute care nurse practitioner (ACNP).
4. Anesthesiologists

Anesthesiologists are medical specialists who administer anesthetics to patients undergoing surgery, as well as provide pain management and critical care services. They work in operating rooms, intensive care units, and other healthcare settings, where they use their expertise to ensure patient safety and comfort. Anesthesiologists must be able to think critically and make quick decisions in high-pressure situations. They often work long hours, including night shifts, weekends, and holidays. Anesthesiologists must complete a residency program in anesthesiology and obtain board certification to practice in their state.
5. Critical Care Specialists

Critical care specialists, also known as intensivists, are medical specialists who care for patients who are critically ill or injured. They work in intensive care units (ICUs), where they use their expertise to manage life-supporting therapies, such as mechanical ventilation and dialysis. Critical care specialists must be able to think critically and make quick decisions in high-pressure situations. They often work long hours, including night shifts, weekends, and holidays. Critical care specialists must complete a fellowship program in critical care medicine and obtain board certification to practice in their state.
💡 Note: These medical specialists often work together as a team to provide comprehensive care to patients in emergency situations.
| Specialist | Education | Certification | Work Environment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emergency Medicine Physician | Medical degree (MD or DO) | Board certification in emergency medicine | Emergency department |
| Paramedic | Paramedic training program | Certification or licensure as a paramedic | Ambulance, emergency room |
| Emergency Nurse Practitioner | Master's degree in nursing | Certification as a family nurse practitioner (FNP) or acute care nurse practitioner (ACNP) | Emergency department |
| Anesthesiologist | Medical degree (MD or DO) | Board certification in anesthesiology | Operating room, intensive care unit |
| Critical Care Specialist | Medical degree (MD or DO) | Board certification in critical care medicine | Intensive care unit |

In summary, emergency medical specialists play a vital role in the healthcare system, providing immediate medical attention to patients who are critically ill or injured. These specialists, including emergency medicine physicians, paramedics, emergency nurse practitioners, anesthesiologists, and critical care specialists, work together as a team to provide comprehensive care to patients in emergency situations. Their education, certification, and work environment vary, but they all require strong critical thinking and decision-making skills to succeed in their roles.
What is the role of an emergency medicine physician?

+
Emergency medicine physicians diagnose and treat patients with acute illnesses or injuries in emergency departments.
What is the difference between a paramedic and an emergency nurse practitioner?

+
Paramedics provide advanced life support to patients in emergency situations, while emergency nurse practitioners assess patients, diagnose illnesses, and develop treatment plans in emergency departments.
What is the education and certification required to become an anesthesiologist?
+
Anesthesiologists must complete a medical degree program and a residency program in anesthesiology, and obtain board certification to practice in their state.