5 Key Facts About Electrons in Atoms
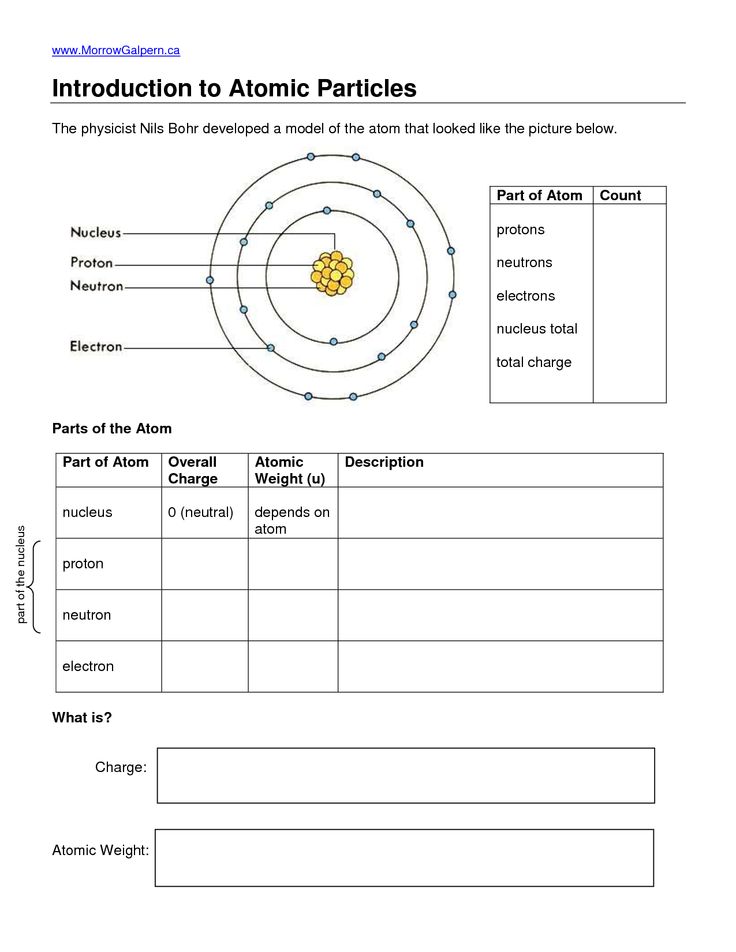
At the heart of modern chemistry and physics lies the concept of electrons, those tiny, negatively charged particles that play a significant role in the behavior and characteristics of atoms. Understanding electrons and their behavior within atoms is crucial not just for academic purposes but for practical applications in technology, material science, and beyond. Here are five essential facts about electrons in atoms that form the backbone of atomic theory.
The Structure and Existence of Electrons


Electrons, first theorized by J.J. Thomson in the late 19th century, are subatomic particles that exist in a sort of cloud around an atom’s nucleus. They have an incredibly small mass—about 1⁄1836 of that of a proton or neutron—and carry a charge of approximately -1.602 x 10-19 coulombs. Here are some key points:
- Electrons are not uniformly spread but exist in shells or energy levels, with the innermost shell closest to the nucleus.
- The energy of an electron determines its shell, with lower energy electrons closer to the nucleus.
- Electrons also have a wave-particle duality, behaving both as particles and waves, a phenomenon described by quantum mechanics.
Electrons in Energy Levels

The arrangement of electrons in energy levels around an atom’s nucleus is fundamental to understanding atomic structure:
- Each energy level or shell can hold a maximum number of electrons, commonly calculated as 2n2 where n is the shell number.
- The lowest energy level (n=1) can hold two electrons, while the next level (n=2) can accommodate eight.
- The filling of these levels follows the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons occupy the lowest energy levels available.
- Shells are further divided into subshells (s, p, d, f) with different shapes and energy values, adding complexity to the electron’s behavior.
🔍 Note: Understanding the energy levels of electrons is vital for grasping atomic bonding and the periodic table’s structure.
Valence Electrons
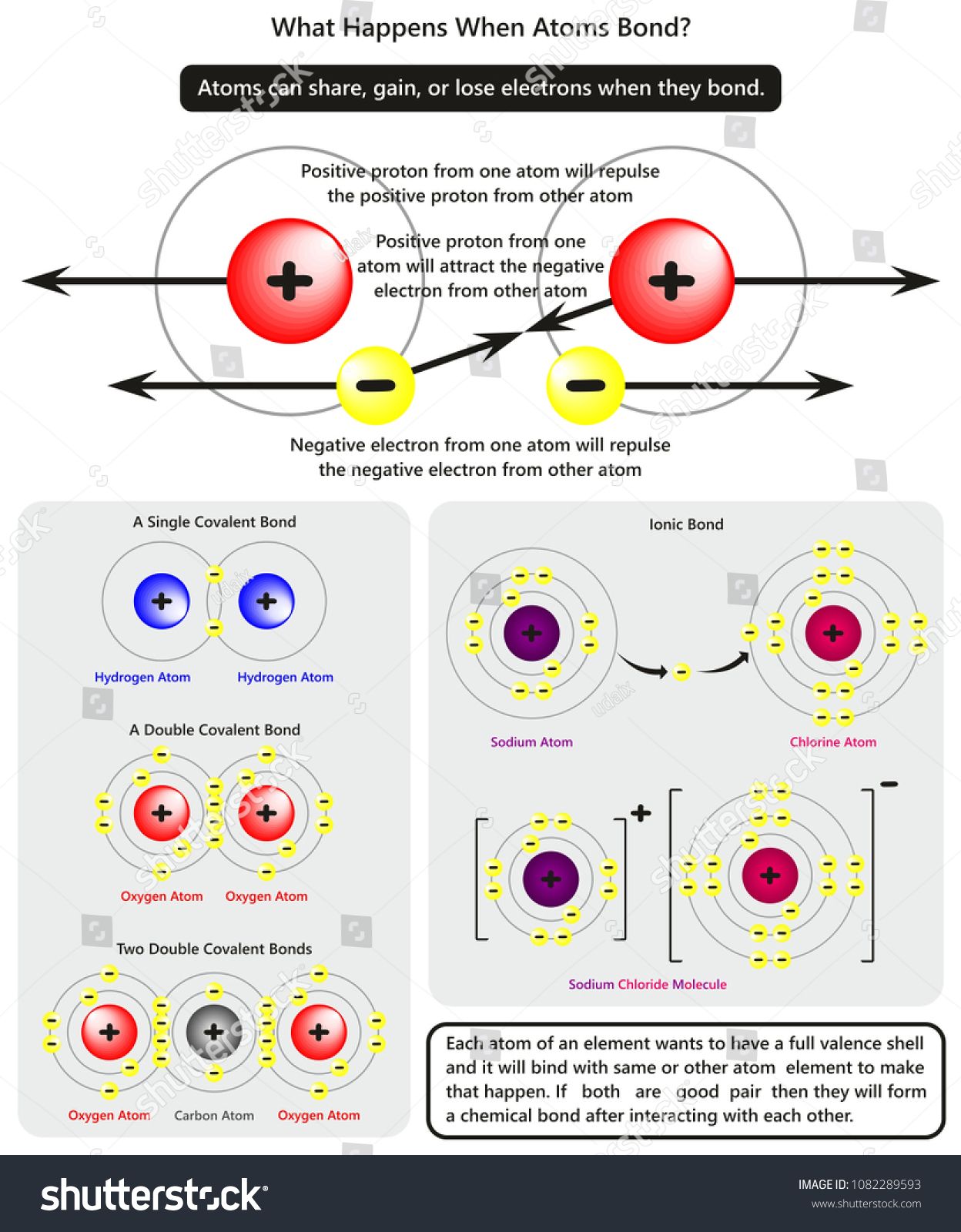

The outermost electrons in an atom are called valence electrons. They are:
- Responsible for the atom’s chemical behavior, reactivity, and bonding capabilities.
- Key to understanding why elements in the same group (column) of the periodic table have similar properties.
- Directly involved in forming bonds when atoms come together to share, gain, or lose electrons.
Electron Configurations

Each element has a unique electron configuration, which denotes how electrons are distributed among the shells and subshells. For example:
- Hydrogen (H) has one electron in its first shell: 1s1.
- Oxygen (O) has eight electrons with the configuration 1s2 2s2 2p4.
Understanding electron configurations helps in:
- Predicting chemical behavior and ion formation.
- Explaining the color of ions in coordination compounds.
- Analyzing the electronic spectra of atoms and molecules.
| Element | Atomic Number | Electron Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | 1s1 |
| Helium | 2 | 1s2 |
| Carbon | 6 | 1s2 2s2 2p2 |

Behavior of Electrons and Quantum Mechanics


The behavior of electrons in atoms is governed by the principles of quantum mechanics, including:
- Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle: You cannot precisely know both the position and momentum of an electron simultaneously.
- Pauli Exclusion Principle: No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers, leading to electron spin, a magnetic property.
- Wavefunctions and Orbitals: Electrons exist in atomic orbitals, probability distributions of finding an electron in a given region around the nucleus.
⚛️ Note: Quantum mechanics provides the foundation for our current understanding of atoms and how they interact chemically and physically.
To sum up, the behavior of electrons within atoms encompasses fundamental concepts that explain much of the world we observe at both the macroscopic and microscopic levels. From the simple structure of hydrogen to the complex configurations of heavy elements, the movement, energy, and interactions of electrons dictate the formation of bonds, the properties of substances, and the very nature of matter itself.
Why do valence electrons matter in chemical reactions?

+
Valence electrons determine how an atom will interact with other atoms to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, which drives chemical reactions.
How do electrons contribute to an atom’s magnetism?

+
Electrons possess an intrinsic property called spin, which can be thought of as either “up” or “down”. When electrons in an atom or molecule are unpaired, their spins contribute to the atom’s magnetic moment, leading to paramagnetism or magnetism.
What is electron affinity?
+
Electron affinity is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a neutral atom to form a negative ion. It reflects how much an atom wants to gain an extra electron, which is particularly important for non-metals.