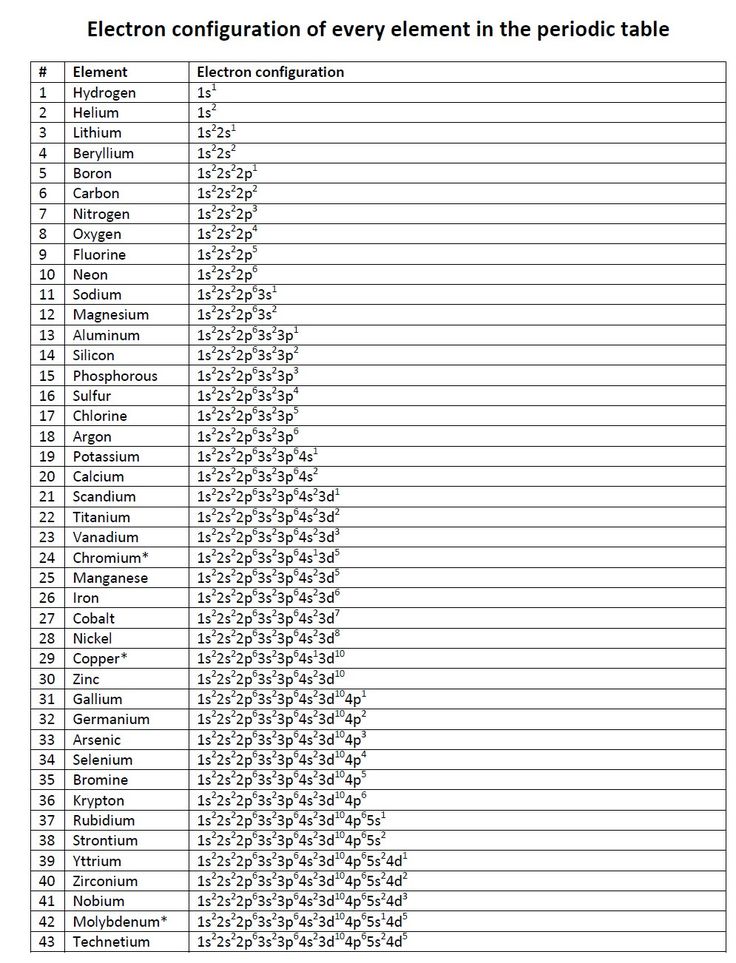
5 Essential Tips for Electron Configuration Practice

Understanding electron configuration is fundamental for anyone studying chemistry or related sciences. It's not just about memorizing patterns; it's about understanding the logical arrangement of electrons in atoms, which can open the doors to comprehending chemical reactions, bonding, and much more. Here, we delve into five essential tips that can help you master the art of electron configuration practice.
Tip 1: Learn the Periodic Table Structure

The periodic table is not just a display of elements; it’s a map for electron configuration. Each group (column) indicates the number of valence electrons, which directly relates to the electron configuration. Here’s how you can leverage this:
- Group 1: Elements have an electron configuration ending in s1 (excluding Helium).
- Group 2: Elements end in s2.
- Group 13-18: These groups show the filling of p orbitals, ending in pn where n is 1 through 6 for different groups.
- Transition metals: Here, d orbitals start filling. Each block (e.g., 3d, 4d) spans a row of transition metals.
Tip 2: Memorize Aufbau Principle, Pauli Exclusion Principle, and Hund’s Rule

Understanding the rules governing electron placement is crucial:
- Aufbau Principle: Electrons fill orbitals starting from the lowest energy level.
- Pauli Exclusion Principle: Only two electrons can occupy the same orbital, and they must have opposite spins.
- Hund’s Rule: Electrons will singly occupy orbitals within a subshell before pairing up.
These principles explain the electron configuration trend observed in the periodic table.

Tip 3: Practice Writing Electron Configurations

Consistent practice is the key to mastering electron configuration. Here are some steps:
- Write out the ground state electron configuration for simple elements.
- Move on to elements with exceptions like chromium and copper.
- Compare and contrast the electron configurations across a period and down a group.
✨ Note: Don’t be discouraged if you don’t get it right away; electron configuration practice builds on repetition and familiarity.
Tip 4: Use Visualization Techniques
Visual aids can significantly enhance your understanding:
- Draw orbitals diagrams to visually see how electrons are arranged.
- Use energy diagrams to show the relative energy levels of different subshells.
- Employ color-coding for different electron subshells or spin directions to make patterns easier to recognize.
| Subshell | Order of Filling | Max. Electrons |
|---|---|---|
| 1s | 1st | 2 |
| 2s | 2nd | 2 |
| 2p | 3rd | 6 |
| 3s | 4th | 2 |
| 3p | 5th | 6 |

Tip 5: Solve Electron Configuration Problems

Applying your knowledge through problem-solving solidifies your understanding:
- Practice with exceptions in electron configuration like transition metals.
- Determine the electron configuration from atomic numbers.
- Work on ions and excited states where electrons can be in higher energy levels than usual.
📋 Note: Practice problems can be found in textbooks, online resources, or through classroom exercises.
In this journey to mastering electron configuration, these five tips provide a structured approach to learning. By understanding the structure of the periodic table, memorizing fundamental principles, practicing configurations, visualizing electron arrangements, and solving problems, you will gain a deeper insight into the atomic world. Remember, electron configuration isn't just about memorization; it's about recognizing patterns, understanding logical sequences, and appreciating the complexity of atoms.
Why is electron configuration important?

+
Electron configuration is crucial for understanding how atoms interact, bond, and form compounds. It helps predict an atom’s chemical behavior, reactivity, and how electrons will be involved in chemical reactions.
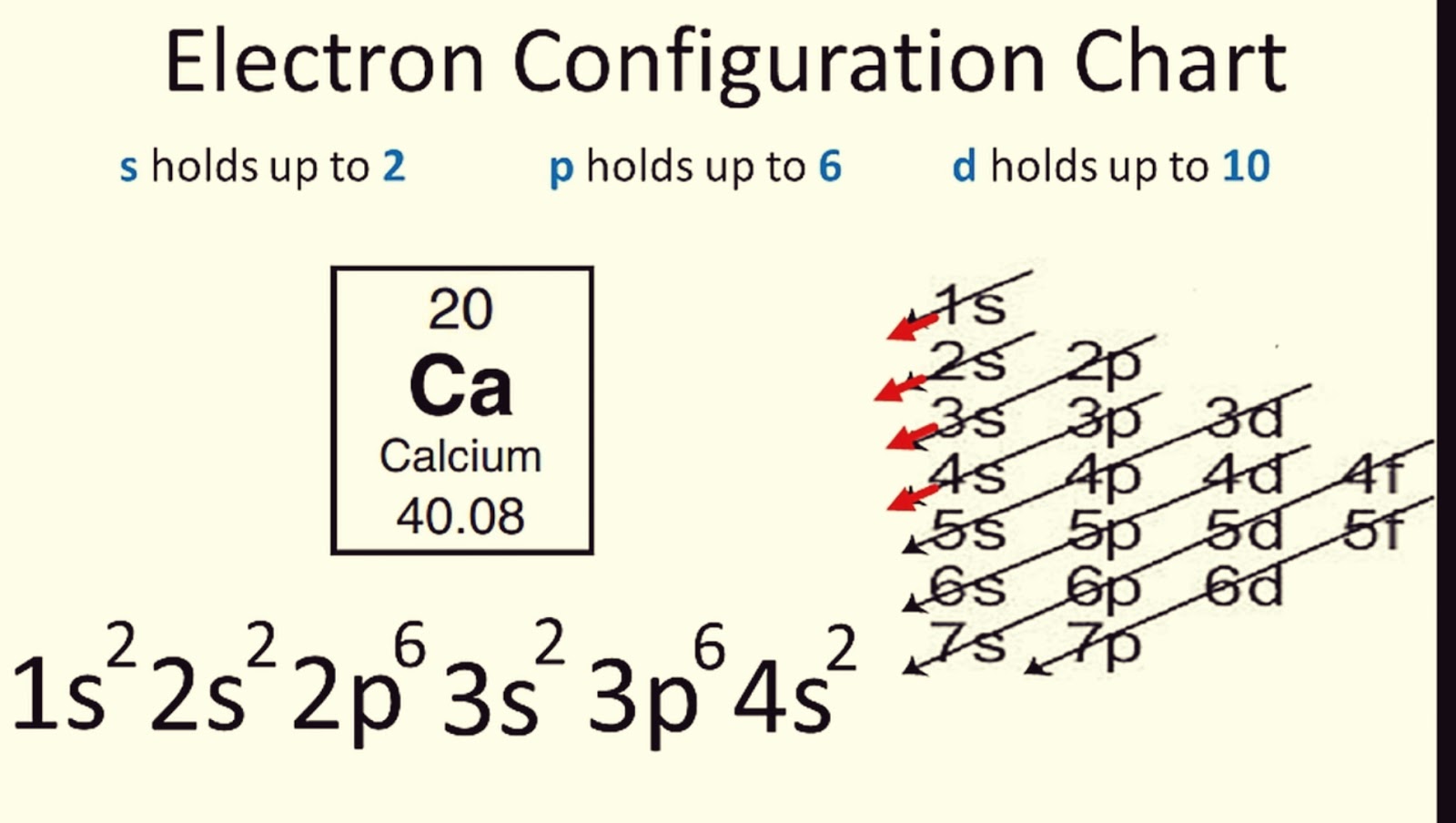
How can one remember the order of filling orbitals?
+
Using the periodic table as a guide, or mnemonic devices like the Diagonal Rule, helps recall the order. You can also remember a short poem or acronym that outlines the filling sequence.
What are some common pitfalls when learning electron configuration?

+
Students often forget exceptions in electron configuration like those for chromium and copper. Overlooking Hund’s Rule or ignoring the spin of electrons can also lead to mistakes. Moreover, confusing the sequence in which orbitals are filled is another common error.