Unlocking Answers: Electromagnetic Worksheet Insights Revealed

Discovering the intricacies of electromagnetic principles isn't just academic; it's a gateway to understanding the world around us. From the electric current running through our devices to the Earth's natural magnetic fields, electromagnetic phenomena dictate much of the technology and natural phenomena we encounter daily. In this comprehensive exploration, we'll delve into the mysteries of electromagnetism, deciphering how magnetic fields, electricity, and waves interact to form the invisible forces that shape our reality. Whether you're a student, educator, or simply a curious mind, this post will guide you through an electromagnetic worksheet, revealing insights that make complex ideas accessible and exciting.
Understanding the Basics of Electromagnetism


Electromagnetism is not just another chapter in your physics textbook; it’s the foundation of modern civilization:
- Definition: Electromagnetism deals with the interactions between electric charges, magnetic fields, and the electromagnetic force, one of the four fundamental forces of nature.
- Key Components:
- Electromagnetic Force - Acts between charged particles.
- Electric Fields - Surrounds electrically charged particles.
- Magnetic Fields - Generated by moving charges or magnetic materials.
Here’s a basic table to help you remember how these components interact:
| Component | Interaction |
|---|---|
| Electric Charge | Produces Electric Field |
| Electric Field | Attracts or repels charges, Induces electric currents |
| Magnetic Field | Attracts or repels magnets, Influences charged particles’ movement |
| Moving Charge | Creates Magnetic Field |

⚡ Note: Understanding the interaction of electric and magnetic fields provides a framework for understanding many modern technologies, including MRI machines, electric motors, and wireless communication.
Dissecting Magnetic Field Concepts


Magnetic fields are central to electromagnetic phenomena:
- Field Lines: Imagine an invisible structure that guides magnetic forces, much like the Earth’s magnetic field guides compass needles.
- Flux Density (B): This is the strength of a magnetic field per unit area, measured in Tesla or Gauss.
- Earth’s Magnetic Field: It’s not just for navigation; it protects us from solar winds, creating the auroras.
Let’s delve into a practical example through our worksheet:
🌏 Note: Remember that magnetic field lines form closed loops, giving us insights into the behavior of magnetic forces.
Exploring Electric Fields and Potential


Electric fields are invisible yet powerful, and they:
- Guide the motion of charged particles.
- Are fundamental in the operation of electrical devices.
- Can be represented mathematically and visually to predict particle behavior.
By working through the worksheet, students can:
- Learn to calculate the electric field’s strength around a point charge or between charges.
- Understand the concept of electric potential and how it relates to energy and work.
⚡ Note: Visualizing electric fields can help in solving complex problems in electromagnetism.
Navigating through Electromagnetic Waves
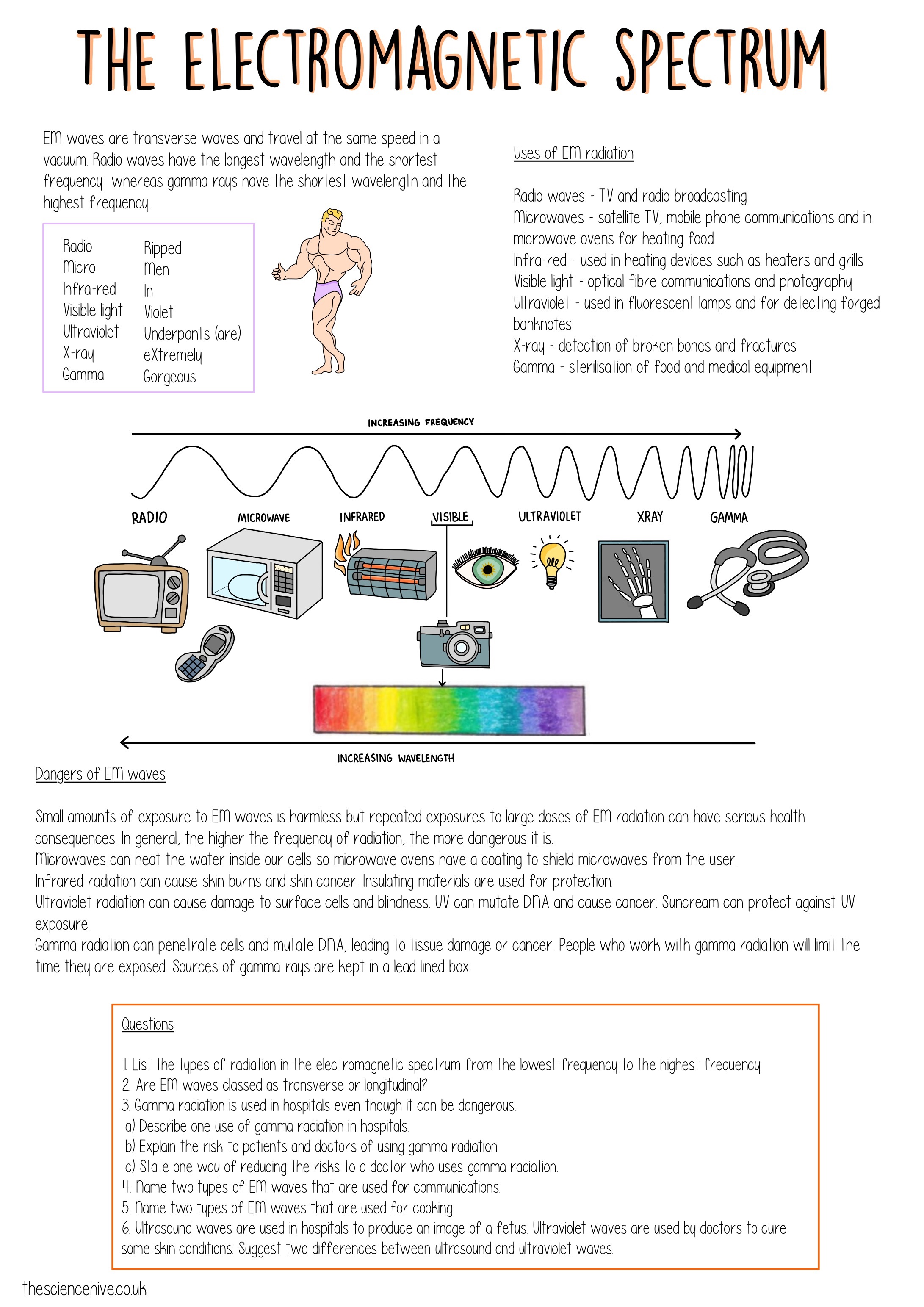

The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses waves that propagate through space, encompassing:
- Radio Waves to Gamma Rays - Each with unique properties and applications.
- Wavelength and Frequency - Understand their inverse relationship.
- Applications - From communication (radio, Wi-Fi) to medical imaging (X-rays).
The worksheet can demonstrate how electromagnetic waves:
- Transmit energy and information.
- Have both electric and magnetic field components oscillating perpendicularly.
Solving Electromagnetic Problems

Practical problems can be daunting, but here are key steps to navigate them:
- Identify Key Parameters: Determine what you need to solve for, whether it’s force, field strength, or energy.
- Use Formulas: Apply the appropriate equations from Coulomb’s Law, Faraday’s Law, or Ampere’s Law.
- Unit Consistency: Ensure all values are in SI units before calculating.
- Understand Context: Know if you’re dealing with static or dynamic fields, as the approach can differ.
The worksheet often provides scenarios where you can practice these steps in action, offering real-world context to theoretical knowledge.
The journey through this electromagnetic worksheet has been enlightening, offering a clear path through the foundational concepts of electromagnetism. From understanding the interaction of electric and magnetic fields to visualizing complex wave patterns, we've deciphered the invisible forces that influence our world. This knowledge not only fuels our curiosity but also empowers us to comprehend and innovate in the realm of technology and beyond. So whether you're designing new devices, navigating through cosmic phenomena, or simply grasping how your smartphone works, the principles of electromagnetism form the core of our understanding, connecting the abstract to the tangible in a seamless dance of science and discovery.
What is the difference between an electric field and a magnetic field?
+
An electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and exerts force on other charges. Conversely, a magnetic field is generated by moving charges or magnetic materials, influencing the movement of charges or other magnets.
How does the Earth’s magnetic field protect us?

+
The Earth’s magnetic field deflects charged particles coming from the sun (solar wind) away from our planet, preventing the atmosphere from being eroded and creating phenomena like auroras.
What are some real-world applications of electromagnetic waves?

+
Electromagnetic waves have diverse applications including radio and television broadcasting, Wi-Fi, cellular communication, radar, microwave cooking, medical imaging (X-rays, MRI), and even the heating of our planet by solar radiation.