5 Essential Tips for Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheets

Understanding the electromagnetic spectrum is fundamental for students in physics, engineering, and various related scientific fields. This spectrum encompasses all types of electromagnetic radiation, from the lowest energy (radio waves) to the highest (gamma rays). Mastering this concept can be challenging, but with the right tools and strategies, it can become an engaging and enriching part of any educational journey. Here are five essential tips for effectively working with electromagnetic spectrum worksheets.
1. Know the Basics of the Electromagnetic Spectrum

The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuous range of wavelengths and frequencies of electromagnetic waves. To effectively work with it:
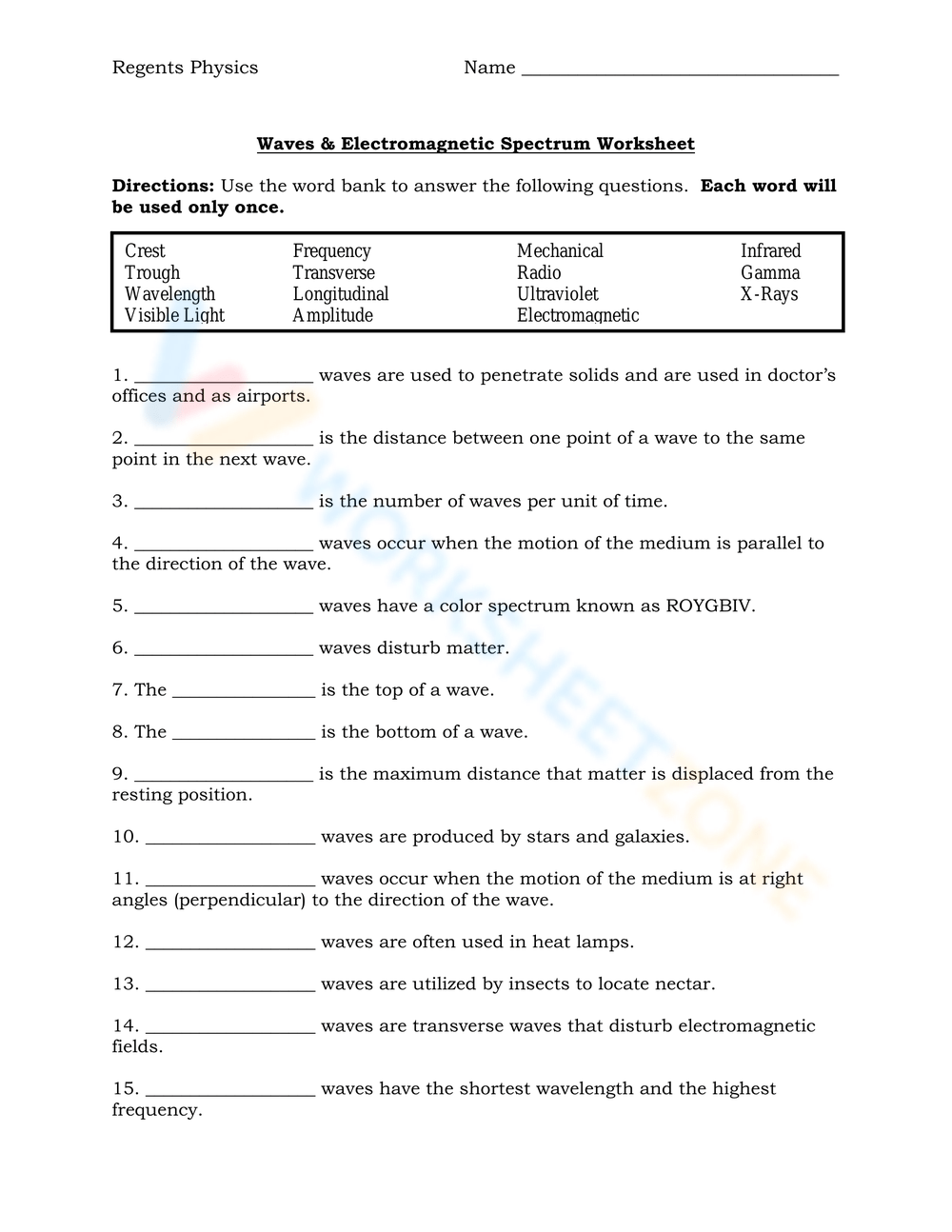
- Understand the Wave Properties: Recognize that all electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light (c = 3 x 10^8 m/s) and that they differ only in wavelength and frequency.
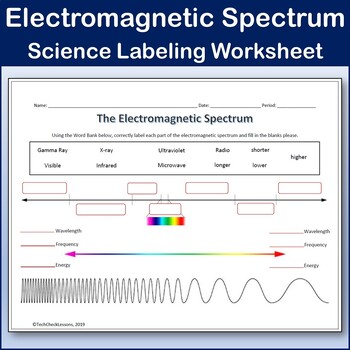
- Learn the Categories: Familiarize yourself with the different types of waves - Radio Waves, Microwaves, Infrared, Visible Light, Ultraviolet, X-rays, and Gamma Rays.
- Study the Interactions: How these waves interact with matter varies significantly across the spectrum; understanding these interactions can help in visualizing the spectrum's properties.
🧠 Note: Remember, the electromagnetic spectrum is not just about listing types of radiation but understanding how each type interacts differently with matter and devices.
2. Use Interactive Tools and Visual Aids

Visual learning can drastically improve understanding:
- Diagrams and Charts: Use spectrum charts to visually see where different types of radiation fall. Color-code these charts for easier memorization.
- Interactive Simulations: Many online resources offer interactive simulations where you can manipulate wavelengths and observe the effects.
- Physical Models: Sometimes, having tangible models or even building your own can solidify understanding. For instance, a simple setup of a prism splitting light into its colors can be insightful.

🌐 Note: Interactive tools are especially useful for grasping the abstract nature of electromagnetic waves which can't be directly observed.
3. Apply Mathematical Concepts

Mathematics is a key tool in understanding electromagnetic waves:
- Wave Equations: Know how to use equations like λ = c/f (where λ is wavelength, c is the speed of light, and f is frequency).
- Units and Conversions: Be comfortable converting between different units of measurement like Hz to eV or meters to nanometers.
- Practice with Worksheets: Engage with worksheets that involve solving equations related to electromagnetic waves. This practice will reinforce your mathematical skills.
| Type of Radiation | Wavelength (m) | Frequency (Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| Radio Waves | 103 - 10-1 | 103 - 109 |
| Microwaves | 10-1 - 10-3 | 109 - 1011 |

4. Understand Practical Applications

Linking theory with practical uses can enhance learning:
- Everyday Examples: Discuss how electromagnetic waves are used in everyday technology like WiFi, Bluetooth, satellite communication, and medical imaging.
- Case Studies: Explore real-world applications in different fields, from astronomy (gamma-ray bursts) to cooking (microwave ovens).
- Project Work: Consider projects where students must design something using electromagnetic principles, like a simple radio or antenna system.
📡 Note: Application-based learning not only reinforces knowledge but also ignites curiosity and creativity in understanding abstract concepts.
5. Participate in Group Activities and Discussions
Learning in a group can provide diverse perspectives:
- Group Problem Solving: Work through electromagnetic problems in groups to understand different approaches to solving issues.
- Debates and Discussions: Hold sessions where the implications of different spectrum parts can be debated, like the use of X-rays versus MRI in medical diagnostics.
- Peer Teaching: Explain concepts to peers. Teaching is an excellent way to consolidate your own understanding.
To sum up our journey through the electromagnetic spectrum, we've explored essential tips for mastering this complex subject. From understanding the basic wave properties to applying mathematical equations, using visual aids, recognizing real-world applications, and engaging in group activities, we've covered various strategies that can enhance the learning experience. Each method not only aids in grasping the theoretical aspects but also in appreciating how these concepts manifest in everyday life and technology.
What are the practical uses of the electromagnetic spectrum?

+
The electromagnetic spectrum has numerous applications in various fields:
- Communications: Radio waves, microwaves, and infrared are used for broadcasting, Wi-Fi, cell phones, and satellite communications.
- Medical Imaging: X-rays for diagnostics, MRI using radio waves, and thermography with infrared.
- Cooking: Microwaves for heating food.
- Astronomy: Observations across the entire spectrum to study celestial bodies.
- Safety: UV light in tanning and sterilization, gamma rays in cancer treatment.
How can understanding the electromagnetic spectrum benefit a career?

+
Knowledge of the electromagnetic spectrum can be vital in:
- Engineering: For designing antennas, radar systems, and communication technology.
- Medicine: In diagnostic imaging, radiation therapy, and research.
- Physics and Astronomy: To understand and study light, radiation, and cosmic phenomena.
- Environmental Science: For studying Earth’s atmosphere and climate.
Why is visual learning important for the electromagnetic spectrum?
+
Visual learning is crucial because:
- Abstract Concepts: It helps make abstract concepts more tangible and easier to understand.
- Memory Aid: Visual aids can significantly improve retention and recall of information.
- Engagement: Interactive tools can engage learners more deeply, making complex information more relatable.