Explore the Wonders of the Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet

When you delve into the study of physics, understanding the electromagnetic spectrum becomes an essential part of your journey. It's not just the backbone of numerous technologies we rely on today—from Wi-Fi signals to medical imaging techniques like MRI—it's also fundamental to how we perceive the universe. This blog post will take you on an adventure through the electromagnetic spectrum, offering a comprehensive worksheet designed to enhance your learning experience.
What is the Electromagnetic Spectrum?

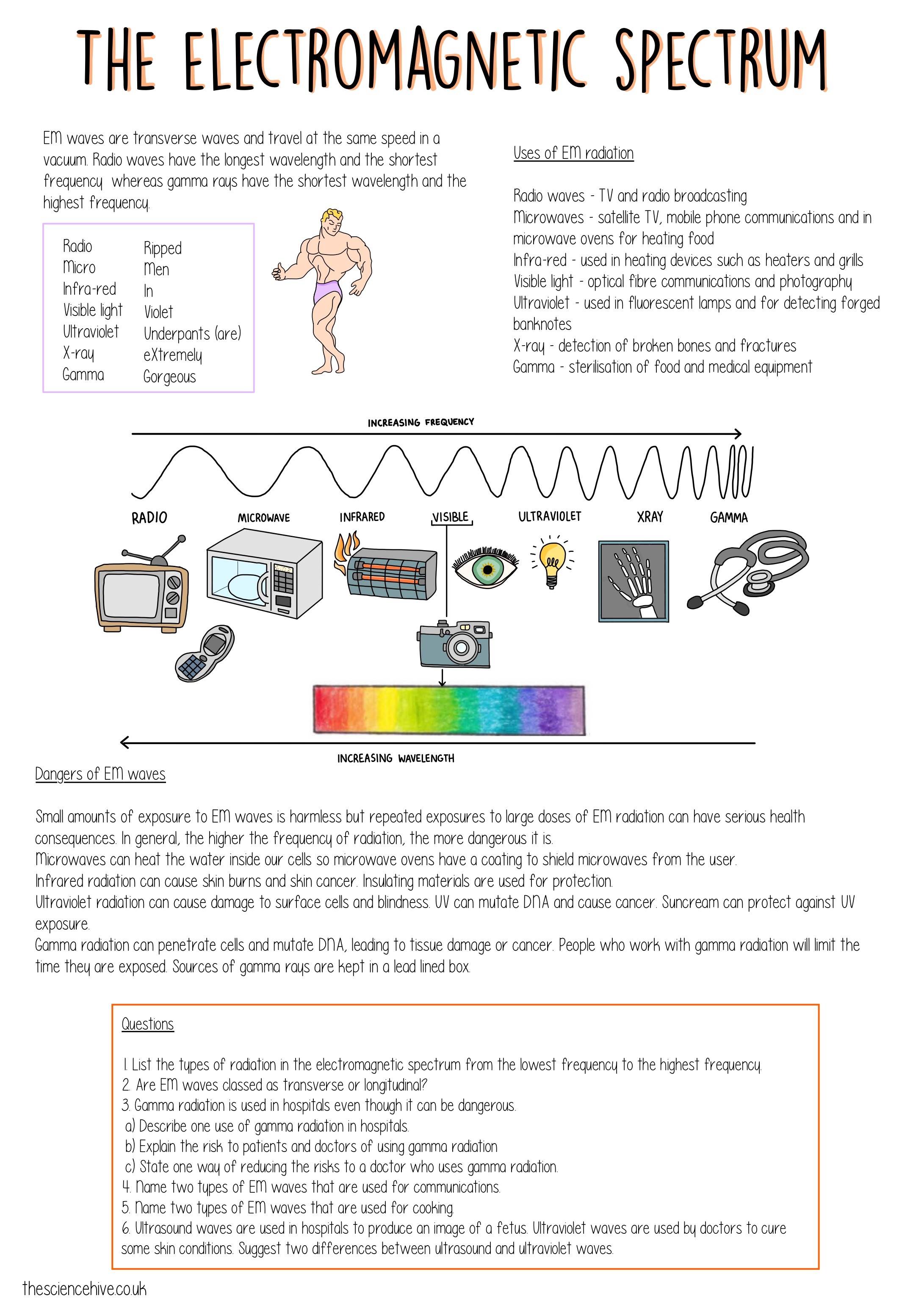
The electromagnetic spectrum is a range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation, and this energy travels through space at the speed of light. It encompasses everything from long-wavelength radio waves to gamma rays with the shortest wavelengths. Here’s a quick overview:
- Radio Waves: Used in broadcasting and communications.
- Microwaves: Utilized in satellite communications, radar, and cooking.
- Infrared: Heat and thermal imaging.
- Visible Light: What our eyes can see, divided into colors by wavelength.
- Ultraviolet (UV): Known for causing sunburn but essential for Vitamin D synthesis.
- X-Rays: Used in medical diagnostics.
- Gamma Rays: Emitted by radioactive materials, used in cancer treatment.
Exploring Each Segment of the Spectrum
Let’s dive deeper into each part of the electromagnetic spectrum:
Radio Waves


Radio waves have the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies of the electromagnetic spectrum. They are primarily used for:
- TV and radio broadcasting.
- Cell phone communication.
- Satellite communication.
Microwaves

Microwaves are known for:
- Operating at frequencies useful for radar and satellite TV.
- Heating food in microwave ovens due to the resonance of water molecules.
Infrared


This invisible radiation is felt as heat and is used in:
- Thermal imaging.
- Night vision equipment.
- Heating elements like infrared heaters.
🔥 Note: Infrared radiation is not visible but can be detected by specialized cameras.
Visible Light


Visible light is a small part of the spectrum that our eyes can perceive. It:
- Is responsible for color vision, where different wavelengths are interpreted as different colors.
- Enables photosynthesis, a critical process for life on Earth.
Ultraviolet (UV)


UV radiation has shorter wavelengths than visible light and is:
- Known for causing skin damage.
- Crucial for the production of Vitamin D in the skin.
- Used in UV lamps for sterilization purposes.
🌞 Note: UV light can be harmful to eyes and skin; always use appropriate protection when working with UV sources.
X-Rays


X-rays have:
- High enough energy to penetrate through tissues, making them invaluable in medical imaging.
- Various applications in research and security scanning.
Gamma Rays


The highest energy electromagnetic radiation, gamma rays:
- Are produced by nuclear reactions or processes in high-energy physics.
- Can treat and destroy cancer cells.
- Are used in industry to test the integrity of welds in pipes and other machinery.
⚛️ Note: Gamma rays are incredibly energetic and require careful handling to avoid harm.
EM Spectrum Worksheet

Here is a simple worksheet to test your understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum:
| EM Wave | Wavelength | Frequency | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radio Waves | 1 mm to 100 km | 3 kHz to 300 GHz | Communication, Broadcasting |
| Microwaves | 1 mm to 1 meter | 300 MHz to 300 GHz | Radar, Satellite Communication, Heating |
| Infrared | 700 nm to 1 mm | 430 THz to 300 GHz | Thermal Imaging, Night Vision |
| Visible Light | 400 nm to 700 nm | 400 THz to 790 THz | Vision, Photosynthesis |
| Ultraviolet | 10 nm to 400 nm | 750 THz to 30 PHz | Vitamin D Production, Sterilization |
| X-Rays | 0.01 nm to 10 nm | 30 PHz to 30 EHz | Medical Imaging, Security Scanning |
| Gamma Rays | < 1 pm to 10 pm | 30 EHz to 300 EHz | Cancer Treatment, Industry |

As you've explored this vibrant world of electromagnetic waves, it's clear how they shape our existence, technology, and understanding of the universe. From the warmth of a sunny day to the high-energy radiation used in cancer treatment, these invisible forces are all around us, silently at work.
The electromagnetic spectrum is not just a physics concept but a multifaceted marvel that influences daily life in numerous ways. Its study opens doors to understanding fundamental science, technology, health, and even the cosmos beyond our planet. We've covered the spectrum's main components, their applications, and how they interact with the world. Armed with this knowledge, you're better equipped to appreciate and potentially contribute to the technological innovations of tomorrow.
What are the primary applications of microwaves?

+
Applications include satellite communication, radar, and heating food in microwave ovens.
Can ultraviolet radiation be beneficial?

+
Yes, UV light is essential for the production of Vitamin D in the skin, although excessive exposure can lead to harm.
How does gamma radiation differ from X-rays?

+
While both are high-energy electromagnetic waves, gamma rays originate from the nucleus of atoms due to radioactive decay, while X-rays are generally produced by processes outside the nucleus, like fast-moving electrons hitting metal.