5 Advantages of Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch Systems

Revolutionizing Aircraft Launch: The Electromagnetic Advantage

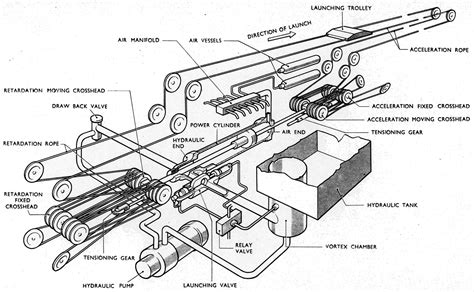
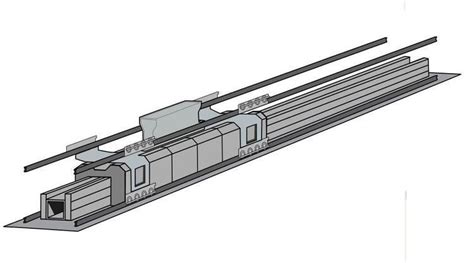
The electromagnetic aircraft launch system (EMALS) is a game-changing technology that has been gaining attention in recent years. This innovative system uses electromagnetic forces to launch aircraft from naval vessels, replacing traditional steam-powered catapults. As the world’s navies continue to evolve and modernize, the advantages of EMALS are becoming increasingly clear.
Advantage 1: Increased Efficiency

One of the primary benefits of EMALS is its increased efficiency compared to traditional steam catapults. EMALS uses electromagnetic forces to accelerate aircraft to takeoff speed, which results in a more efficient use of energy. This is because EMALS only uses energy when an aircraft is being launched, whereas steam catapults require a constant supply of steam to maintain pressure. This reduction in energy consumption leads to significant cost savings and reduced maintenance requirements.
Advantage 2: Improved Reliability
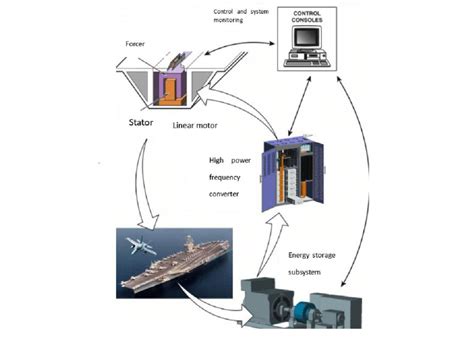
EMALS is a more reliable system than traditional steam catapults. The electromagnetic forces used in EMALS are more consistent and predictable, resulting in fewer errors and malfunctions. Additionally, EMALS has fewer moving parts than steam catapults, which reduces the risk of mechanical failure. This increased reliability translates to fewer delays and cancellations, ensuring that naval operations can proceed with minimal interruption.
Advantage 3: Greater Flexibility

EMALS offers greater flexibility than traditional steam catapults. The system can be easily adjusted to accommodate different types of aircraft, including smaller unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). This flexibility is essential for modern naval operations, where a variety of aircraft are often deployed on a single vessel. EMALS can also be integrated with other systems, such as arresting gear and aircraft handling systems, to create a seamless and efficient aircraft launch and recovery process.
Advantage 4: Reduced Maintenance

EMALS requires significantly less maintenance than traditional steam catapults. The system’s electromagnetic forces eliminate the need for steam, which reduces the risk of corrosion and wear on moving parts. Additionally, EMALS has fewer components than steam catapults, which reduces the number of parts that need to be replaced or maintained. This reduced maintenance requirement leads to significant cost savings and increased availability of naval vessels.
Advantage 5: Enhanced Safety

EMALS is a safer system than traditional steam catapults. The electromagnetic forces used in EMALS are more controlled and predictable, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries. Additionally, EMALS eliminates the risk of steam-related injuries and fatalities, which are a significant concern with traditional steam catapults. This enhanced safety feature is essential for naval operations, where the safety of personnel is paramount.
📝 Note: The advantages of EMALS are not limited to naval vessels. The technology has potential applications in commercial aviation and other industries where efficient and reliable launch systems are required.
In conclusion, the electromagnetic aircraft launch system offers numerous advantages over traditional steam catapults. Its increased efficiency, improved reliability, greater flexibility, reduced maintenance requirements, and enhanced safety features make it an attractive option for modern naval vessels. As the world’s navies continue to evolve and modernize, the adoption of EMALS is likely to become more widespread.
What is the primary benefit of EMALS?
+
The primary benefit of EMALS is its increased efficiency compared to traditional steam catapults.
How does EMALS improve reliability?

+
EMALS improves reliability by using electromagnetic forces that are more consistent and predictable, resulting in fewer errors and malfunctions.
Can EMALS be used with smaller aircraft?
+
Yes, EMALS can be easily adjusted to accommodate smaller aircraft, including unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).