Ecology Energy Pyramid Worksheet Explained

Understanding the flow of energy within an ecosystem is crucial for appreciating how organisms interact and survive. An excellent tool for this understanding is the ecology energy pyramid, which visually represents the transfer of energy through different trophic levels. This pyramid worksheet is not just a simple diagram; it's a profound educational tool that provides insights into energy efficiency, biomass conversion, and ecological balance. Let's delve into how to work with and understand this worksheet.
What is an Ecology Energy Pyramid?

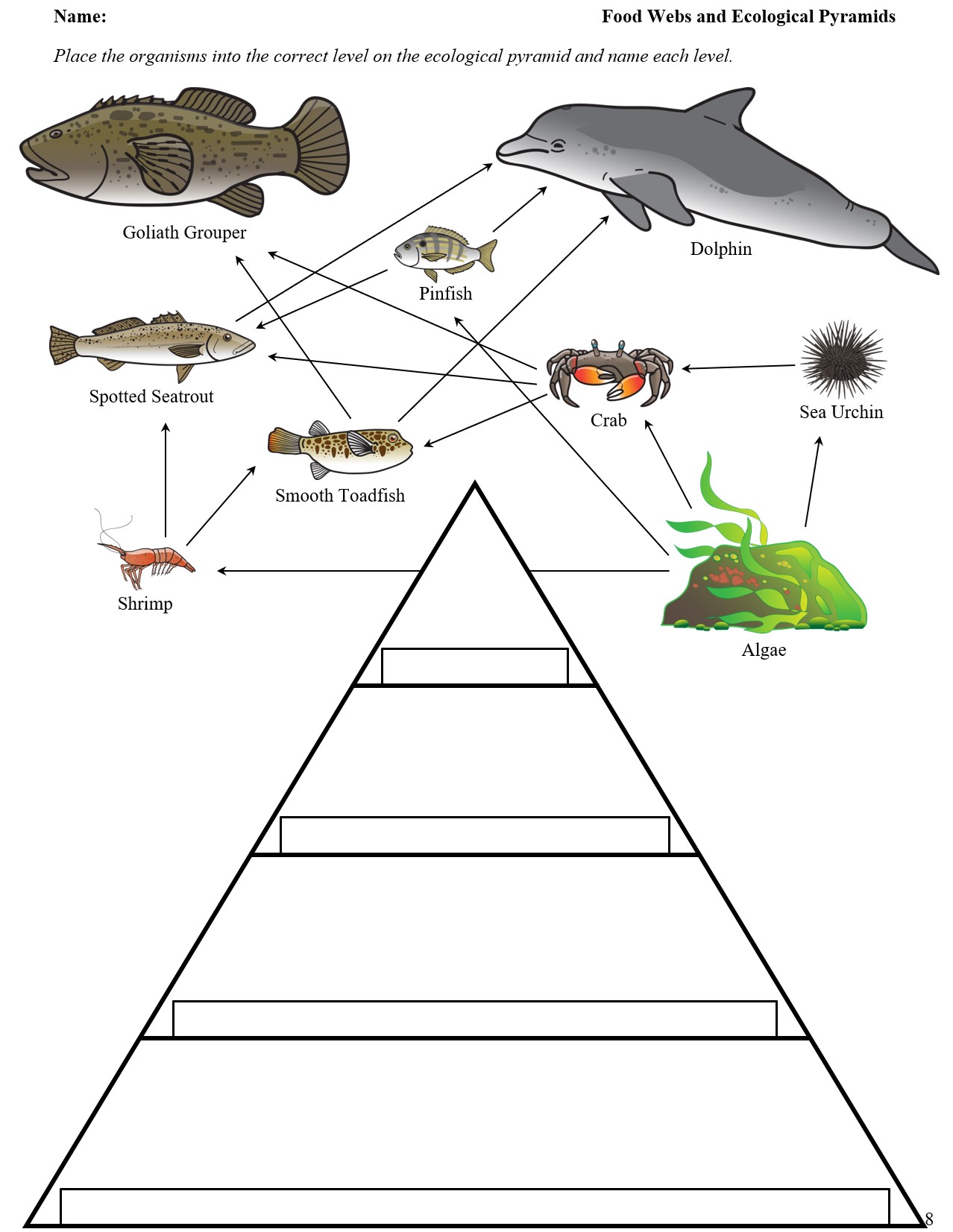
An energy pyramid, also known as a trophic pyramid or ecological pyramid, shows how energy is transferred from one trophic level (feeding level) to the next in an ecosystem. Here's how it generally works:
- Primary Producers (Base Level): This level comprises plants, algae, and some bacteria. They convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis.
- Primary Consumers (Herbivores): Animals that feed directly on producers, like rabbits, deer, and caterpillars.
- Secondary Consumers (Carnivores or Omnivores): Organisms that eat herbivores, including predators like wolves, birds of prey, and spiders.
- Tertiary Consumers (Top Carnivores): Predators at the top of the food chain, such as big cats, some fish species, and humans.
- Decomposers: Fungi and bacteria break down dead matter, returning nutrients to the soil for plants to use, completing the cycle.

Working with the Energy Pyramid Worksheet

The worksheet typically contains:
- A diagram of the pyramid with empty spaces for filling in the levels.
- Questions to answer about energy flow.
- Space to calculate the energy loss or efficiency between levels.
- Exercises to compare different ecosystems' energy pyramids.
Filling in the Pyramid

To accurately fill in an energy pyramid worksheet:
- Identify the producers (plants) and list them at the base.
- Determine the primary consumers (herbivores) and place them on the next level.
- Continue this process for secondary and tertiary consumers, ensuring to label each appropriately.
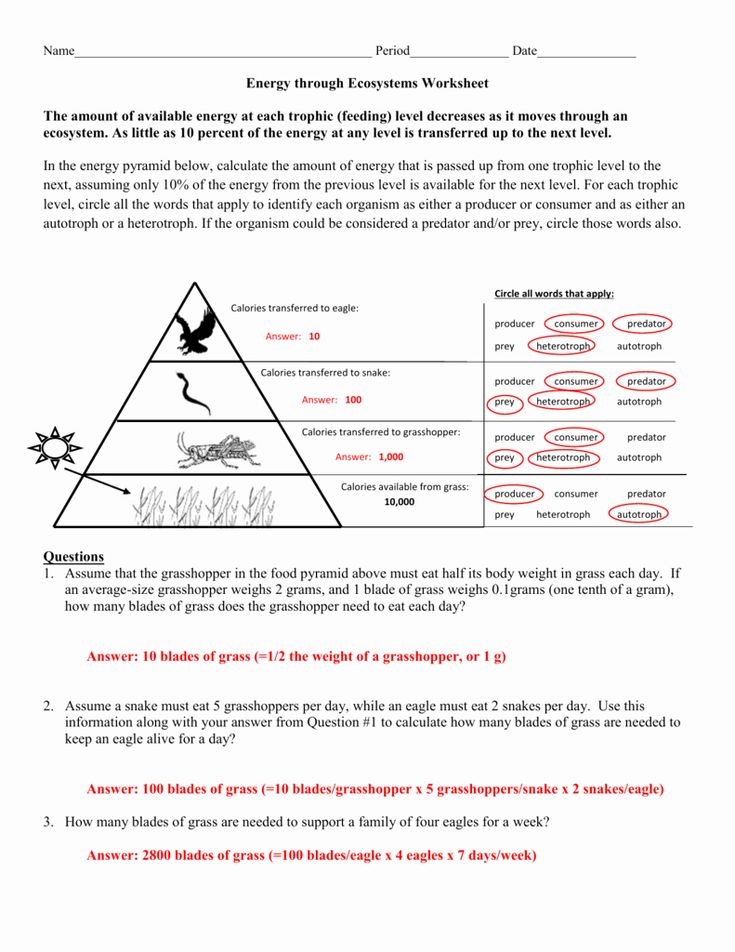
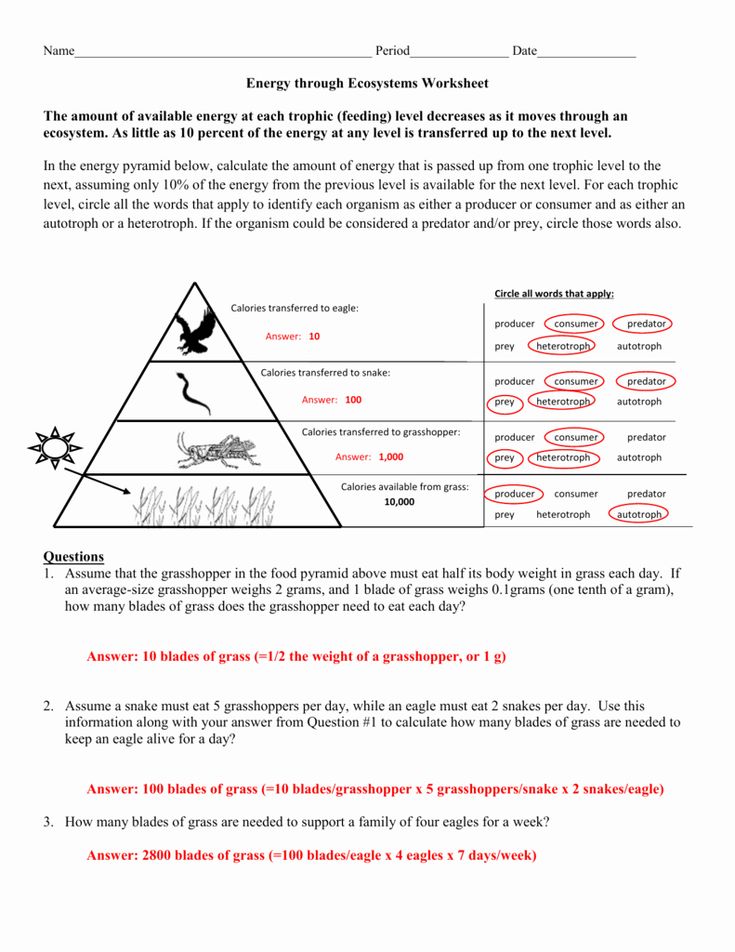
- Calculate or estimate the percentage of energy transferred from one level to the next. Generally, around 10% of the energy at one level is passed on to the next.
🌱 Note: Remember, each level contains less energy than the level below it, due to various energy losses like metabolic processes, movement, and reproduction.
Calculating Energy Loss
| Trophic Level | Energy (Kcal/m^2/year) | Energy Loss (10%) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Producers | 10,000 | 9,000 (Loss) |
| Primary Consumers | 1,000 | 900 (Loss) |
| Secondary Consumers | 100 | 90 (Loss) |
| Tertiary Consumers | 10 | 9 (Loss) |

Understanding the energy loss helps students appreciate why there are fewer top predators compared to herbivores or why plants are so critical to an ecosystem's energy flow.
Comparing Ecosystems
Worksheets might include exercises where you:
- Compare the energy pyramids of different ecosystems like a desert, forest, or ocean.
- Discuss how factors like temperature, available sunlight, or nutrients affect the pyramid shape.
Energy Efficiency and Biomass
The pyramid’s structure also highlights energy efficiency and biomass:
- Energy is lost as heat during metabolic processes, in unproductive activities, or through feces.
- Biomass reduces at each level as less energy is available for growth and survival.
🔥 Note: The energy loss at each level significantly influences population sizes; the higher the level, the fewer individuals due to less available energy.
Practical Applications

The energy pyramid isn’t just a theory; it has real-world implications:
- Conservation Efforts: Understanding energy transfer helps conservationists preserve biodiversity by protecting critical food chains.
- Agriculture and Farming: Knowing the energy pyramid informs strategies for managing livestock, crop rotation, and resource allocation.
- Climate Change: Energy pyramids can shift with changes in climate, affecting entire ecosystems.
This foundational knowledge sheds light on how ecosystems operate, how they can be disrupted, and how humans can manage their impact on nature more sustainably.
In essence, the ecology energy pyramid is more than a diagram; it's a window into the complex energy dynamics of nature. By filling out this worksheet, students not only learn about energy transfer but also gain insights into the delicate balance of life on Earth. This educational tool fosters a deeper appreciation for the environment and encourages responsible interaction with natural systems.
Why is energy transfer between trophic levels so inefficient?
+
The inefficiency in energy transfer between trophic levels is mainly due to metabolic losses. Organisms lose energy as heat during cellular respiration, which is the primary way living things generate energy from food. Additional losses occur through movement, reproduction, and the production of waste materials, significantly reducing the energy available to the next level in the food chain.
Can ecosystems exist without a clear pyramid structure?

+
Yes, ecosystems can have variations in their trophic structure. For instance, in some marine ecosystems, the pyramid might be inverted due to phytoplankton’s short lifespan and fast reproductive rates. However, the basic principle of energy flow remains the same; higher trophic levels will always have less energy available.
How does human activity affect the energy pyramid?

+
Human activities like deforestation, pollution, and over-fishing can disrupt the energy pyramid by altering habitat, reducing primary producers, or diminishing the population of key species, which can lead to imbalances in energy flow and potentially ecosystem collapse.
What role do decomposers play in the energy pyramid?

+
Decomposers like bacteria and fungi play a critical role in ecosystems by breaking down dead matter and waste. They release nutrients back into the environment, which allows primary producers to use them again, essentially recycling the energy and nutrients that have been lost through higher trophic levels.



