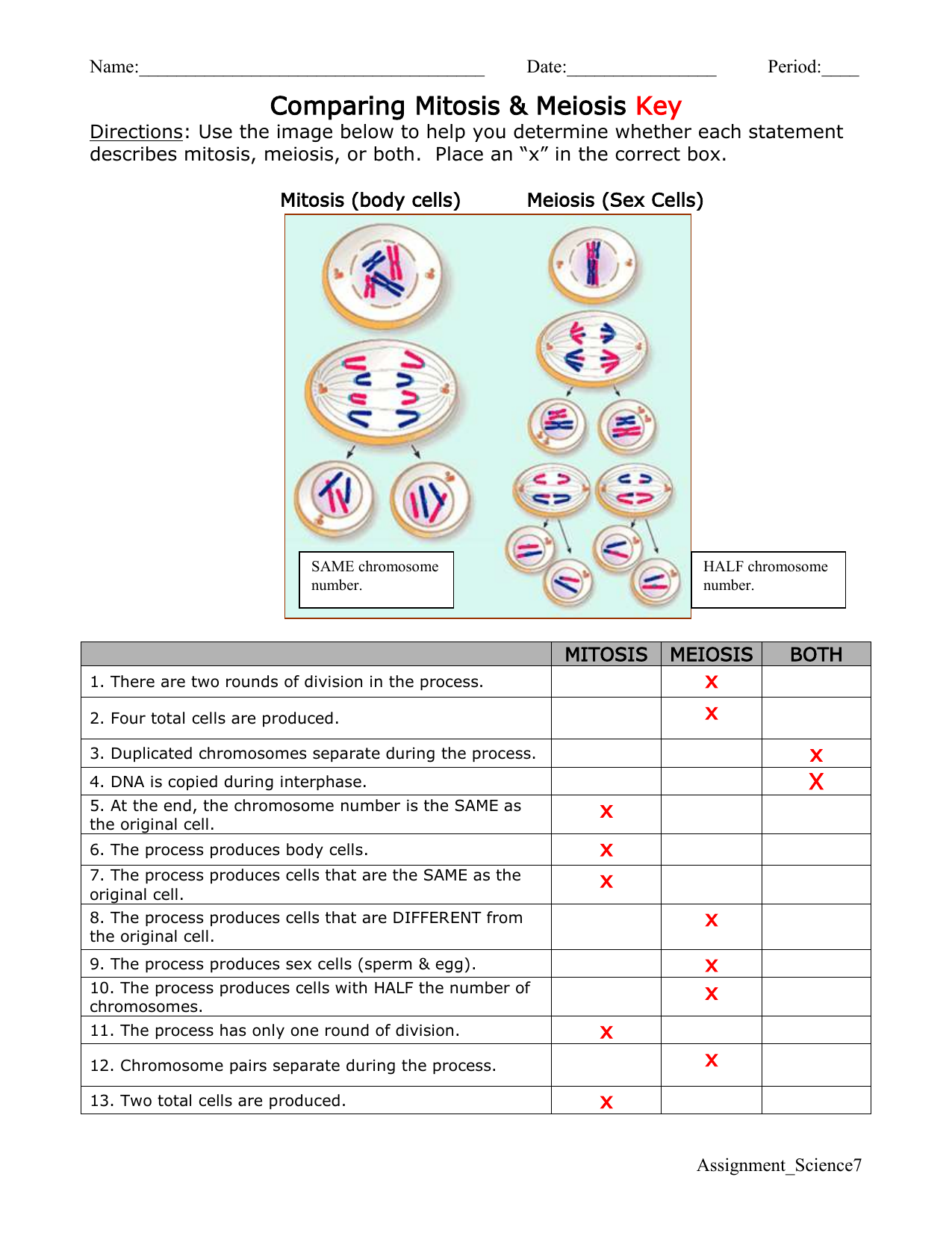
5 Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answers Revealed

In ecological studies, one tool that provides insight into the structure of ecosystems is the ecological pyramid. These pyramids visually represent the relationships between different trophic levels in terms of numbers, biomass, or energy. This blog post explores five ecological pyramids, their importance, and provides detailed worksheet answers that help deepen your understanding of these ecological dynamics.
What Are Ecological Pyramids?


Before we delve into specific pyramids, let’s briefly understand what ecological pyramids are:
- Definition: Ecological pyramids are graphical representations showing the proportion of different ecosystem components at each trophic level.
- Types: There are primarily three types:
- Pyramid of Numbers - Shows the number of individuals at each trophic level.
- Pyramid of Biomass - Represents the total living weight of organisms at each trophic level.
- Pyramid of Energy - Illustrates the flow of energy transfer through the ecosystem.
Pyramid of Numbers

The pyramid of numbers often illustrates the number of organisms at each trophic level from producers to top predators:
- In a typical grassland, this pyramid would be shaped like an upright triangle where there are:
- Millions of blades of grass (producers).
- Thousands of herbivores like grasshoppers.
- Hundreds of secondary consumers like mice.
- A few tertiary consumers such as snakes or birds of prey.
- In some ecosystems, like an oak forest, the pyramid might be inverted due to the small number of large producers like oaks supporting many smaller herbivores and consumers.
Worksheet Example:
| Trophic Level | Number of Organisms | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Tertiary Consumers | 5 | Owls |
| Secondary Consumers | 300 | Mice |
| Primary Consumers | 1000 | Grasshoppers |
| Producers | 100,000 | Blades of Grass |

🔔 Note: Remember that the pyramid of numbers might not always form an upright triangle due to variations in organism sizes and life cycles.
Pyramid of Biomass

The biomass pyramid quantifies the amount of living organic matter at each trophic level:
- Grassland Example: The pyramid would typically be upright with the following biomass proportions:
- High biomass at the producer level (plants).
- Decreasing biomass as you move up through herbivores to carnivores.
- Ocean Example: Here, phytoplankton, which are primary producers, have a low biomass compared to the large biomass of fish or whales, often leading to an inverted pyramid.
Worksheet Example:
| Trophic Level | Biomass (kg/hectare) |
|---|---|
| Top Carnivores | 1 |
| Herbivores | 20 |
| Producers | 800 |
🔔 Note: Biomass levels can fluctuate seasonally, especially in environments with pronounced seasonal changes.
Pyramid of Energy

This pyramid is perhaps the most accurate in depicting ecological flow:
- At each level, approximately 10% of the energy is transferred to the next higher trophic level due to:
- Heat loss
- Energy used for respiration
- Inefficiency in digestion
- Decomposition processes
- An example:
- Primary Producers might capture 1,000,000 kJ of solar energy.
- Primary Consumers consume and retain only 100,000 kJ of this energy.
- Secondary Consumers will then retain roughly 10,000 kJ.
- This pattern continues up the food chain.
Worksheet Example:
| Trophic Level | Energy (kJ/year) |
|---|---|
| Top Carnivores | 100 |
| Carnivores | 1,000 |
| Herbivores | 10,000 |
| Producers | 100,000 |
🔔 Note: The rule of 10% energy transfer between trophic levels is an oversimplification. Actual transfer rates can vary greatly.
Comparing Ecological Pyramids

Here’s a comparison of how these pyramids can differ in the same ecosystem:
- Pyramid of Numbers: Can be inverted in ecosystems with a few large producers supporting numerous small consumers.
- Pyramid of Biomass: Often upright but can be inverted in aquatic ecosystems where phytoplankton's biomass is less than that of larger organisms like fish or whales.
- Pyramid of Energy: Always upright due to the consistent loss of energy through metabolic processes and inefficiencies.
When we study these pyramids together, we gain:
- Quantitative data on ecosystem productivity.
- Insights into sustainability - ecosystems with low productivity at higher trophic levels might be more prone to disruption.
- Ecosystem stability and potential disturbances.
In conclusion, ecological pyramids provide a powerful visual and quantitative tool to understand energy flow, population structures, and ecological efficiency within various ecosystems. By examining the pyramids of numbers, biomass, and energy, we can:
- Assess how energy transfers influence organism abundance and size.
- Gain insight into food webs, ecological interactions, and the potential impacts of human activities.
- Understand the resilience and fragility of different ecosystems, informing conservation strategies and sustainable practices.
Why is the Pyramid of Energy Always Upright?

+
The Pyramid of Energy is always upright due to the energy transfer inefficiency between trophic levels, where only about 10% of the energy available at one level moves to the next. The rest is lost as heat, used in metabolic processes, or not consumed.
Can an Ecosystem Survive with an Inverted Biomass Pyramid?

+
Yes, ecosystems with inverted biomass pyramids, like oceans, can survive. The large biomass of consumers like fish and whales is supported by rapidly reproducing producers with less total biomass, like phytoplankton.
What Impact Does Human Activity Have on Ecological Pyramids?
+
Human activities, especially pollution, habitat destruction, and over-fishing, can disrupt the balance within these pyramids by altering the biomass, population numbers, and energy flow. This often leads to reduced biodiversity and ecosystem instability.