5 Tips to Master Ecological Pyramid Worksheets Easily

Understanding Ecological Pyramids

Before diving into how to master ecological pyramid worksheets, it's essential to understand what ecological pyramids are. These diagrams illustrate the structure of an ecosystem by representing how energy, biomass, or numbers of organisms are distributed among different trophic levels. Typically, there are three types of ecological pyramids:
- Pyramid of Energy - Shows the flow of energy from one trophic level to the next, always depicting a decrease in energy.
- Pyramid of Biomass - Represents the total weight or mass of living material at each trophic level, which can vary in shape.
- Pyramid of Numbers - Displays the number of individual organisms at each trophic level, also varying in shape.

Tips for Mastering Ecological Pyramids

1. Grasp the Concept of Trophic Levels

Start with understanding that each level in an ecological pyramid represents a different trophic level. Here's a simple guide:
- Producers: Plants and algae that convert sunlight into energy.
- Primary Consumers: Herbivores that eat plants.
- Secondary Consumers: Carnivores or omnivores feeding on primary consumers.
- Tertiary Consumers: Top predators in the food chain.
🌿 Note: Always keep in mind the energy transfer efficiency between trophic levels; roughly 10% of the energy is passed up the pyramid.
2. Analyze Pyramid Shapes and Interpretations

Not all ecological pyramids are triangular; some might be inverted or even diamond-shaped. Here’s how to interpret these variations:
| Pyramid Type | Shape | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | Upright | Energy always decreases as it moves up trophic levels due to inefficiency in transfer. |
| Biomass | Variable | Biomass might decrease or increase, depending on the ecosystem’s dynamics. |
| Numbers | Inverted or Upright | Numbers can decrease with increasing trophic levels or might show different patterns in ecosystems with large producers like trees. |
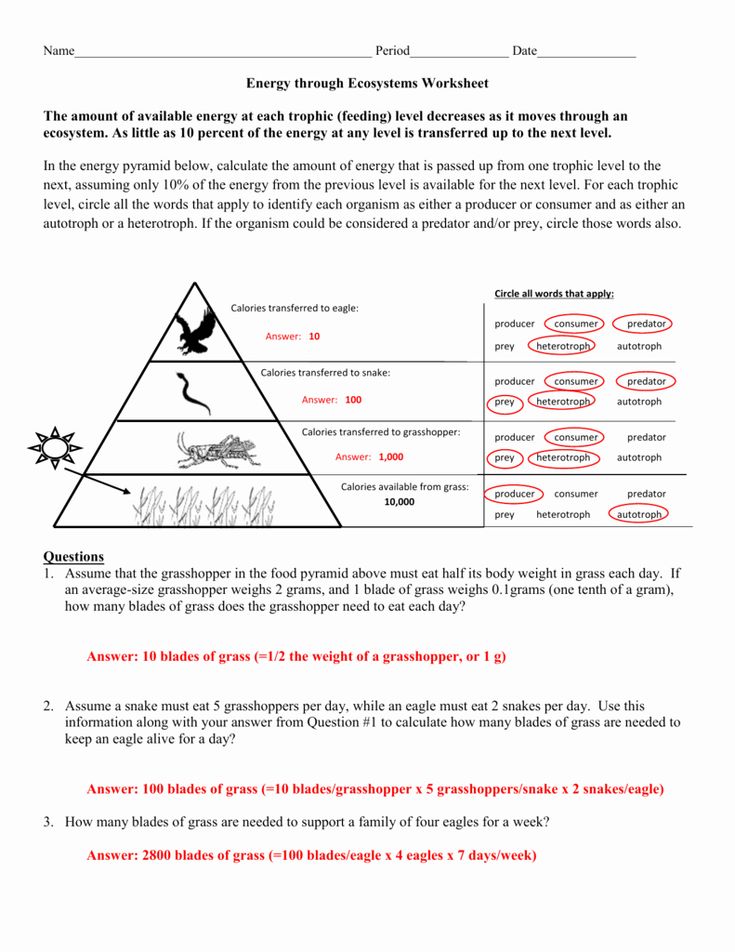

3. Understand Calculations
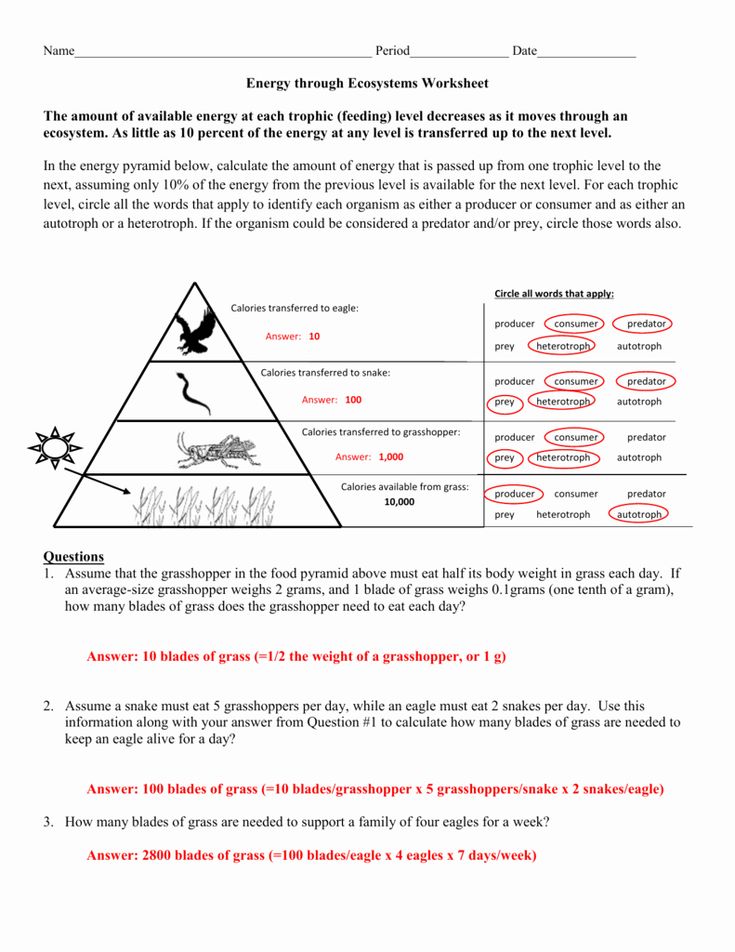
Many ecological pyramid worksheets require you to calculate values like:
- Energy flow between trophic levels.
- Biomass changes.
- Estimated number of organisms.
Here’s how to approach these calculations:
- Use the formula for energy transfer: Energy at level n = Energy at level n-1 x 10%
- Estimate biomass changes by understanding how much biomass is lost as waste or as unusable energy.
- Number of organisms at each level can be calculated based on food consumption rates and efficiencies.
4. Practice Drawing and Labeling Pyramids

Mastering the art of drawing ecological pyramids is crucial:
- Draw each trophic level, ensuring they reflect the correct shape.
- Label each level with the appropriate organisms, energy, biomass, or numbers.
- Ensure proportionality in your drawings; for instance, if one level has significantly more biomass than another, the difference should be visually evident.
5. Use Real-World Examples

Connecting theoretical knowledge with real-world scenarios can enhance understanding:
- Use case studies or examples from textbooks or online resources.
- Analyze the pyramid of an ecosystem you’re familiar with or one you’ve studied in your coursework.
- Apply the concepts of the ecological pyramid to food chains or webs you’ve encountered.

In this comprehensive guide, we've explored the fundamentals of ecological pyramids and provided practical tips to master worksheets related to these diagrams. Understanding trophic levels, interpreting different pyramid shapes, mastering calculations, practicing drawing and labeling, and using real-world examples are key to excelling in ecological pyramid work. Remember, practice and application are crucial for reinforcing these concepts, so take every opportunity to engage with worksheets and real-life examples.
By embracing these strategies, you'll not only improve your ability to work with ecological pyramids but also deepen your understanding of how ecosystems function, which is valuable knowledge in various fields from biology to environmental science.
What do the different shapes of ecological pyramids indicate?

+
The shape of an ecological pyramid indicates the distribution of energy, biomass, or numbers at each trophic level. An upright pyramid typically shows a decrease in these factors as you ascend the food chain, while inverted or irregular shapes can indicate that lower trophic levels are more abundant in terms of mass or numbers, often due to the type of ecosystem or the nature of the organisms involved.
How can I accurately calculate the energy transfer between trophic levels?

+
The rule of thumb for energy transfer is that only about 10% of the energy at one trophic level is transferred to the next. Use the formula: Energy at level n = Energy at level n-1 x 10%. This percentage accounts for the energy loss through heat, waste, and other inefficiencies.
Why do ecological pyramids sometimes appear inverted?

+
Ecological pyramids can appear inverted, particularly in terms of numbers, when there are fewer producers (like large trees in a forest) compared to a large number of consumers. In terms of biomass, an inverted pyramid might occur in aquatic ecosystems where phytoplankton biomass is less than the biomass of the herbivorous zooplankton feeding on them.



