Double Digit Subtraction Worksheets: Master Regrouping Easily

When teaching young learners the art of double-digit subtraction, mastery over the concept of regrouping is essential. This subtraction technique, sometimes called "borrowing," is fundamental for understanding more complex arithmetic operations as students progress in their mathematical education. This long-form blog post delves into why worksheets are invaluable for this learning curve, how they facilitate the understanding of regrouping, and provides detailed steps to make learning fun and engaging.
Understanding Double-Digit Subtraction
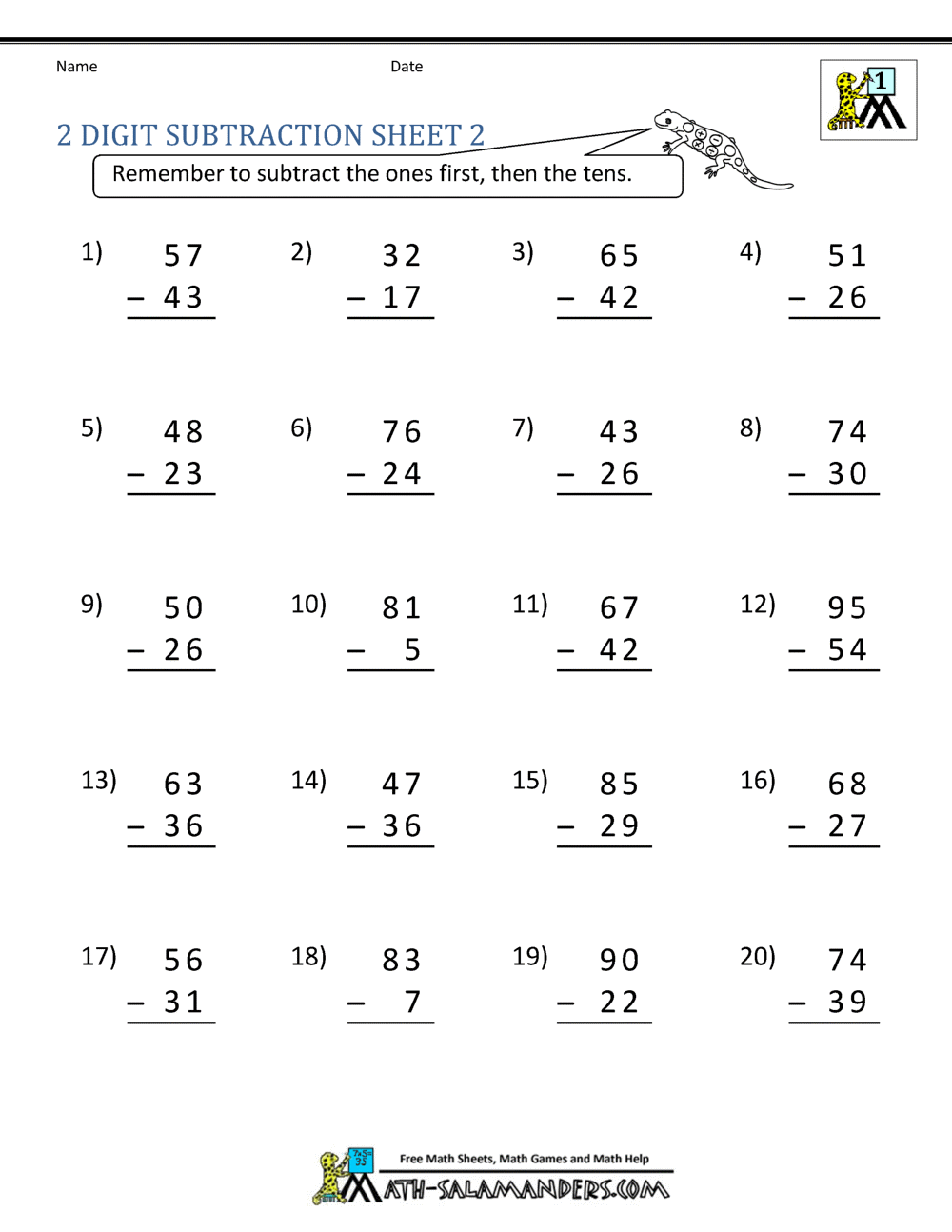
Double-digit subtraction involves taking away one number from another, where both numbers have two digits. Here’s what you need to grasp:
- Place value: Each digit in a number has a place value; the tens place is worth ten times more than the ones place.
- Regrouping or Borrowing: When the digit in the ones place of the minuend (the number being subtracted from) is smaller than the digit in the subtrahend (the number being subtracted), you need to borrow from the tens place.
Here’s how it looks in action: becomes (40+3-20+7). Since you can’t take 7 from 3, you regroup one ten (or 10 ones) from the tens place, so it becomes , which equals .
The Role of Worksheets in Teaching Subtraction

Worksheets are the backbone of mastering arithmetic, and when it comes to double-digit subtraction, they play several critical roles:
- Repetition: Repetitive practice helps solidify the concept.
- Practical Application: Provides real-life problems to enhance understanding.
- Visual Learning: Helps students see the steps involved in regrouping visually.
- Feedback: Worksheets allow for immediate feedback, enabling corrections on the spot.
Steps to Master Regrouping Through Worksheets
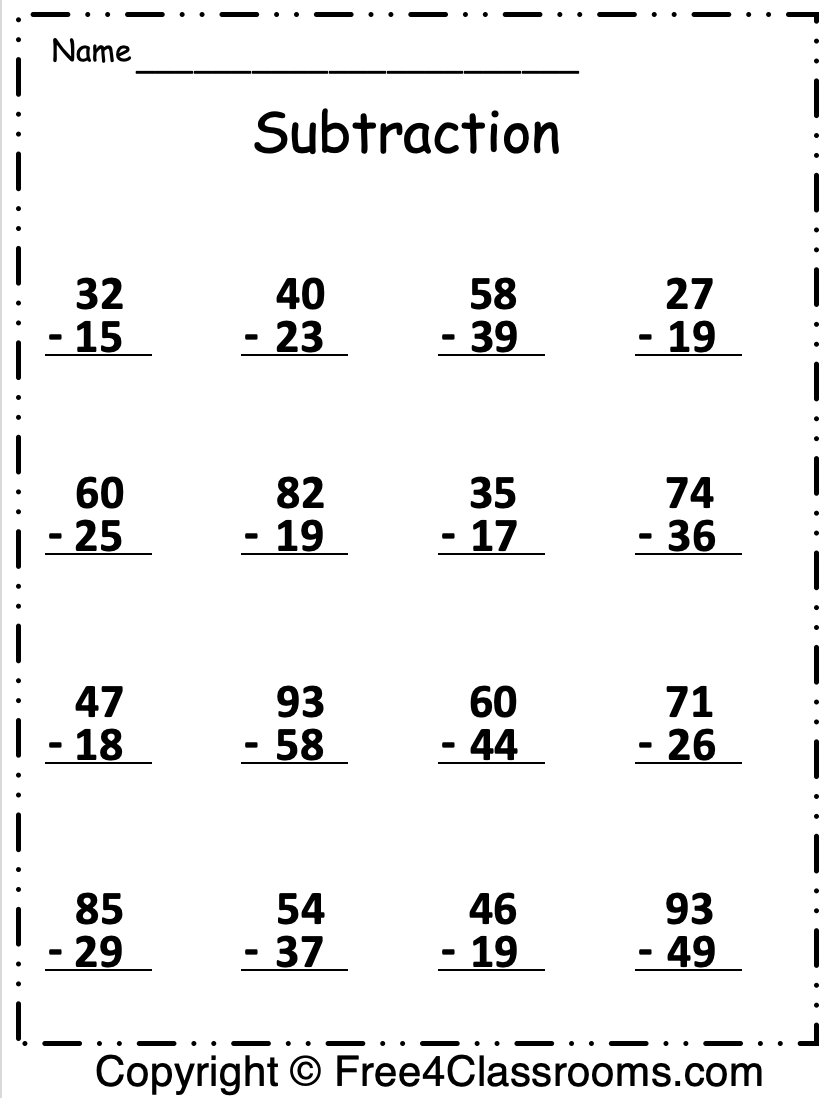
Here are detailed steps to ensure that students master double-digit subtraction with regrouping:
Step 1: Ensure Basic Understanding

Before diving into worksheets:
- Ensure students understand place value.
- Explain what regrouping means and why it’s necessary.
Step 2: Introduce Worksheets

Start with simple worksheets to get familiar with the subtraction process:
- Begin with no-regrouping problems to build confidence.
- Then transition to single-digit borrowing problems.
- Move on to worksheets that involve regrouping in both digits.
Here’s an example of how a worksheet might look:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| 63-27 | 36 |
| 51-18 | 33 |
| 82-39 | 43 |

Step 3: Visualize the Process

Visual aids can help tremendously:
- Use number lines to show borrowing.
- Draw money or base ten blocks to illustrate the process.
Step 4: Practice with Variety

Include various formats in your worksheets:
- Word problems for contextual understanding.
- Mixed operations to see subtraction in a broader mathematical context.
- Timed exercises to improve speed and accuracy.
✏️ Note: Always ensure that the problems are age-appropriate to keep the practice engaging and not overwhelming.
Step 5: Error Analysis
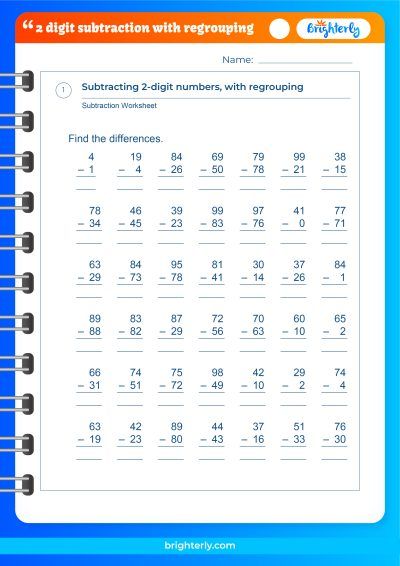
Have students explain their answers:
- They identify where they’ve gone wrong.
- Discuss common mistakes and how to avoid them.
Step 6: Reinforcement
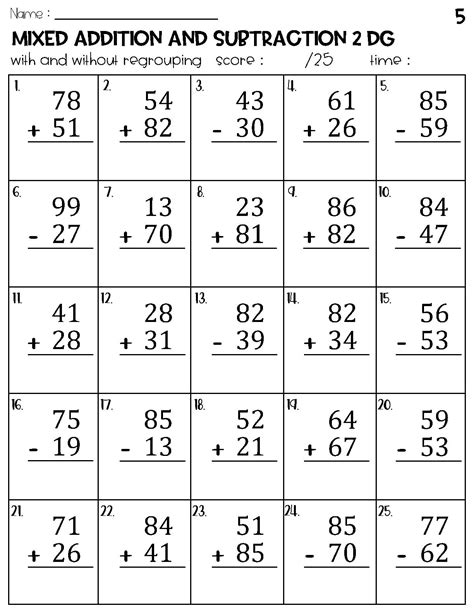
Ensure continuous practice:
- Incorporate subtraction in games or daily activities.
- Regularly return to subtraction practice.
To sum up, double-digit subtraction with regrouping can be a challenging leap for students, but with the structured and engaging approach of using worksheets, the learning process can be streamlined. By following the steps mentioned, teachers and parents can facilitate an environment where students not only grasp the concept of regrouping but enjoy the journey towards mathematical proficiency.
What age should children start learning double-digit subtraction?
+
Children typically begin learning double-digit subtraction in second grade, around 7-8 years old.
Are worksheets the only way to teach double-digit subtraction?

+
No, while worksheets are effective for practice, teaching can also be supplemented with interactive games, real-life problems, and visual tools.
How can I help my child if they struggle with regrouping?

+
Break down the process, use visual aids like base ten blocks, practice regularly, and provide positive reinforcement to build confidence.



