Mastering Dosage Calculations: Worksheet With Answers

In today's healthcare environment, precise medication dosage calculation is not merely an academic exercise; it's a matter of life and death. Whether you're a nursing student, a healthcare practitioner, or someone administering medication in a clinical setting, mastering dosage calculations ensures both patient safety and effective treatment. This comprehensive guide will take you through various facets of dosage calculations with practical examples and worksheets to cement your understanding and proficiency.
Understanding the Basics of Dosage Calculation
The science of dosage calculation rests on understanding three fundamental elements:
- Formula Understanding: Familiarity with basic and advanced formulas used in calculating dosages.
- Unit Conversions: Ability to convert between different units of measure, a critical skill for drug administration.
- Dimensional Analysis: Utilizing this technique to make complex calculations manageable.
Essential Formulas for Dosage Calculations

Here are some key formulas you'll need to master:
- Dosage Formula: Amount of Drug / Volume of Drug x Desired Dose = Volume to administer
- Infusion Rate Calculation: Volume / Time = Infusion Rate
- BSA (Body Surface Area) Based Dosage: Mg/m² x BSA = Total Dose
- Concentration Conversion: Percentage Concentration to mg/ml: (% Strength x 10) = mg/ml
Unit Conversion Tables for Easy Reference

| Unit | Conversion |
|---|---|
| 1 kilogram (kg) | 1000 grams (g) |
| 1 gram (g) | 1000 milligrams (mg) |
| 1 milligram (mg) | 1000 micrograms (mcg) |
| 1 liter (L) | 1000 milliliters (ml) |

⚠️ Note: Understanding these conversions is crucial for drug administration accuracy, as errors can lead to serious consequences.
Dimensional Analysis in Dosage Calculations

Dimensional Analysis simplifies complex calculations by canceling out units until the desired units are achieved:
- Example: Convert 0.5 mg to mcg.
- 0.5 mg x (1000 mcg / 1 mg) = 500 mcg
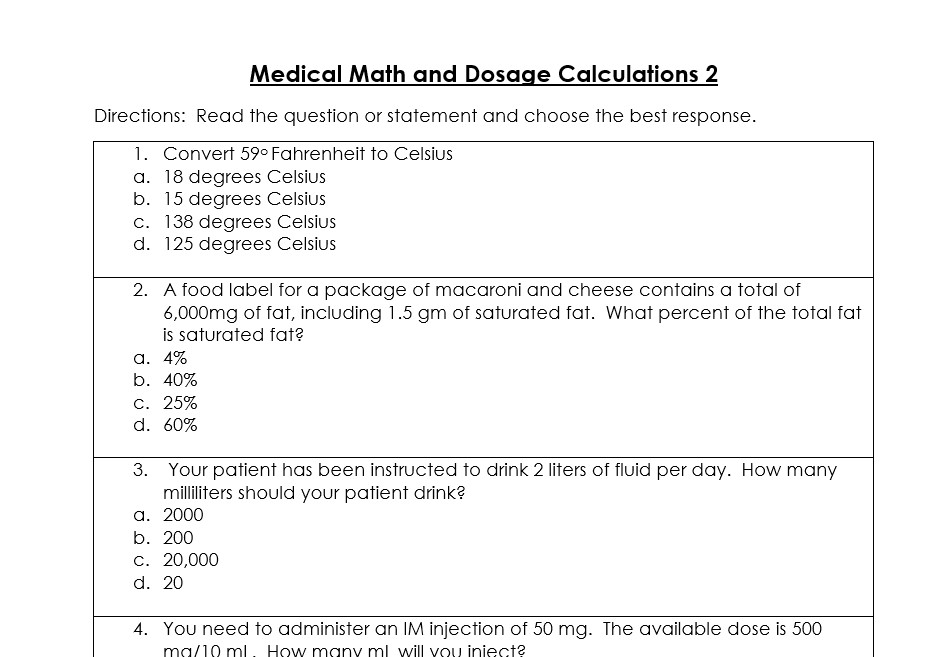
Practical Examples and Worksheets

Here are some practical exercises and their answers to help you sharpen your dosage calculation skills:
Example 1: Calculating Drug Amounts

A patient needs 500 mg of a drug. The concentration of the available solution is 250 mg/ml. How much should be administered?
- Calculation: 500 mg / (250 mg/ml) = 2 ml
Example 2: Infusion Rates

If 500 ml of IV fluid needs to be infused over 5 hours, what is the flow rate in ml/hr?
- Calculation: 500 ml / 5 hr = 100 ml/hr
Example 3: Conversions

Convert 2% Lidocaine solution to mg/ml.
- Calculation: (2% x 10) = 20 mg/ml
In Summary

Developing proficiency in dosage calculations is essential for healthcare professionals. By understanding basic formulas, mastering unit conversions, and employing dimensional analysis, you can confidently ensure correct drug administration. Regular practice through worksheets and real-life examples will enhance your calculation skills, making you an invaluable asset in any healthcare setting.
Why are dosage calculations important in healthcare?

+
Dosage calculations ensure that patients receive the correct amount of medication, which is critical for both effective treatment and patient safety. Errors in dosage can lead to overdoses, underdoses, or even death.
What are the common mistakes made during dosage calculations?

+
Common mistakes include misreading prescriptions, incorrect unit conversions, misplacing decimals, and not double-checking calculations.
How can I improve my skills in dosage calculations?

+
Practice regularly with worksheets, understand the principles behind the formulas, use mnemonic devices, and always verify calculations with another professional or through double-checking.