Reporting Inheritance to Food Stamps
Introduction to Reporting Inheritance to Food Stamps

When it comes to government assistance programs like food stamps, also known as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), there are strict guidelines that recipients must follow to maintain their eligibility. One of the critical aspects of these programs is the reporting of income and resources, which includes inheritance. Understanding how inheritance affects food stamp benefits is essential for recipients to avoid any potential issues with their eligibility. In this article, we will delve into the world of reporting inheritance to food stamps, exploring what constitutes inheritance, how it is reported, and its impact on SNAP benefits.
Understanding Inheritance and Its Impact on SNAP Benefits

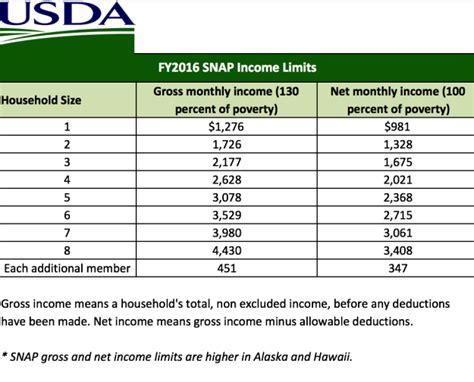
Inheritance refers to the assets or properties that an individual receives from a deceased person’s estate. This can include cash, real estate, stocks, bonds, and other valuables. When a SNAP recipient inherits assets, it can affect their eligibility for food stamps because the program is designed to support individuals with limited income and resources. The SNAP program has specific rules regarding the types of income and resources that are counted towards eligibility, and inheritance is one of them.
Types of Inheritance and Their Treatment Under SNAP

Not all types of inheritance are treated equally under the SNAP program. For instance: - Lump Sum Inheritance: A one-time payment received from an estate can be considered a resource and may affect eligibility. - Ongoing Inheritance: Regular payments, such as from a trust, may be considered income. - Inherited Real Estate: The value of inherited property can be counted as a resource, but there are exceptions, such as the recipient’s primary residence.
Reporting Inheritance to SNAP Authorities

Reporting inheritance to the SNAP authorities is crucial to maintain the integrity of the program and to ensure that recipients receive the correct amount of benefits. Failure to report inherited assets or income can lead to penalties, including the termination of benefits, repayment of incorrectly received benefits, and even criminal charges in severe cases. Recipients are required to report any changes in their income or resources, including inheritance, within a specified timeframe, usually 10 days from the date they receive the inheritance.
Steps to Report Inheritance

To report inheritance, SNAP recipients should follow these steps: - Gather Documentation: Collect all relevant documents related to the inheritance, such as wills, trusts, deeds, and bank statements. - Notify the Local SNAP Office: Reach out to the local SNAP office either in person, by phone, or through their official website, depending on the available contact methods. - Complete the Necessary Forms: Fill out any required forms to report the change in income or resources. This may include updating the application form or completing a change report form. - Submit the Documentation: Provide the gathered documents to support the report of inheritance.
📝 Note: It's essential to keep detailed records of all communications and submissions made to the SNAP office, including dates, times, and the names of the officials contacted.
Impact of Inheritance on SNAP Eligibility

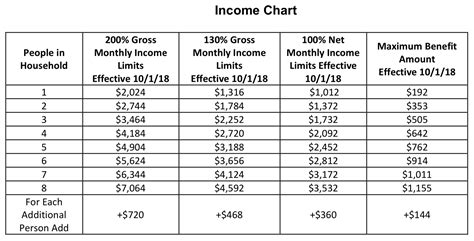
The impact of inheritance on SNAP eligibility depends on several factors, including the type and value of the inherited assets and the recipient’s current income and resource levels. Generally, if the inherited assets push the recipient’s total resources above the program’s limit, their eligibility for benefits may be reduced or terminated. However, there are exemptions and deductions that can be applied, such as the exclusion of the primary residence’s value.
| Resource Type | Counted Towards Eligibility? | Exemptions/Deductions |
|---|---|---|
| Cash | Yes | None |
| Real Estate (Primary Residence) | No | Excluded |
| Stocks/Bonds | Yes | Depends on the type and value |

Maintaining Eligibility After Receiving Inheritance

To maintain eligibility for SNAP benefits after receiving an inheritance, recipients should: - Seek Professional Advice: Consult with a financial advisor or a legal expert to understand the implications of the inheritance on their SNAP benefits. - Report Changes Promptly: Ensure that all changes in income or resources are reported to the SNAP office within the required timeframe. - Explore Exemptions and Deductions: Understand the exemptions and deductions available under the SNAP program to minimize the impact of the inheritance on eligibility.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

Reporting inheritance to food stamps is a critical aspect of maintaining eligibility for the SNAP program. Understanding the types of inheritance, how they are treated under SNAP, and the steps to report them is essential for recipients. By following the guidelines and seeking professional advice when needed, individuals can navigate the complexities of inheritance and SNAP benefits, ensuring they receive the support they are eligible for while complying with the program’s requirements.
What is considered inheritance under the SNAP program?

+
Inheritance under the SNAP program includes assets or properties received from a deceased person’s estate, such as cash, real estate, stocks, and bonds.
How do I report inheritance to the SNAP office?
+
To report inheritance, gather all relevant documents, notify the local SNAP office, complete the necessary forms, and submit the documentation. It’s also recommended to keep detailed records of all communications.
Can receiving an inheritance affect my SNAP benefits?

+
Yes, receiving an inheritance can affect your SNAP benefits. The impact depends on the type and value of the inherited assets and your current income and resource levels. It may reduce or terminate your eligibility for benefits, but there are exemptions and deductions that can be applied.