Does Australia Have Nuclear Weapons: The Truth Revealed

Introduction to Australia's Nuclear Policy

The question of whether Australia has nuclear weapons is a contentious issue that has been debated by politicians, policymakers, and the general public for decades. As a signatory to the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT), Australia has committed to not developing or acquiring nuclear weapons. However, there are still concerns and speculations about the country’s nuclear capabilities. In this article, we will delve into the history of Australia’s nuclear policy, its current nuclear status, and the implications of its nuclear stance.
Australia's Nuclear History

Australia’s nuclear history dates back to the 1950s, when the country was involved in British nuclear testing in the Monte Bello Islands and Emu Field. The tests were conducted between 1952 and 1963, and they raised concerns about the impact of nuclear radiation on the environment and human health. In the 1960s, Australia also considered developing its own nuclear weapons program, but it ultimately decided to sign the NPT in 1970.
Australia's Current Nuclear Status

Today, Australia is a party to the NPT and has committed to not developing or acquiring nuclear weapons. The country has also signed the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) and the Treaty of Rarotonga, which establishes a nuclear-free zone in the South Pacific. Australia’s nuclear policy is focused on promoting non-proliferation and disarmament, and it has been actively involved in international efforts to strengthen the NPT.
Speculations about Australia's Nuclear Capabilities

Despite Australia’s commitment to non-proliferation, there have been speculations about the country’s nuclear capabilities. Some have suggested that Australia could develop nuclear weapons in the future, either by itself or in collaboration with other countries. Others have pointed to the country’s advanced uranium enrichment capabilities and its possession of nuclear reactors as evidence of a potential nuclear weapons program.
However, these speculations are unfounded and lack concrete evidence. Australia’s nuclear reactors are used for peaceful purposes, such as generating electricity and producing medical isotopes. The country’s uranium enrichment capabilities are also strictly controlled and monitored by international organizations to ensure that they are not used for military purposes.
Why Australia Doesn't Need Nuclear Weapons

There are several reasons why Australia doesn’t need nuclear weapons:
- Geographic isolation: Australia is a continent-sized country with a relatively small population, surrounded by vast oceans. This makes it difficult for potential enemies to launch a conventional attack, let alone a nuclear one.
- Strong alliances: Australia has strong alliances with countries like the United States, the United Kingdom, and New Zealand, which provide a security umbrella and reduce the need for nuclear deterrence.
- Conventional military capabilities: Australia has a well-equipped and well-trained conventional military, which is capable of defending the country against most potential threats.
- International norms: Australia is a signatory to several international treaties and agreements that prohibit the development and use of nuclear weapons. Joining the nuclear club would undermine these norms and damage the country’s international reputation.
💡 Note: Australia's nuclear policy is guided by a commitment to non-proliferation and disarmament, and the country has consistently advocated for the abolition of nuclear weapons.
Implications of Australia's Nuclear Stance

Australia’s nuclear stance has significant implications for the country’s foreign policy, defense strategy, and international reputation. By committing to non-proliferation and disarmament, Australia:
- Enhances its international reputation: Australia’s commitment to non-proliferation and disarmament enhances its international reputation as a responsible and law-abiding country.
- Promotes regional stability: By not developing nuclear weapons, Australia helps to promote regional stability and reduce the risk of nuclear conflict in the Asia-Pacific region.
- Supports international cooperation: Australia’s nuclear policy supports international cooperation on non-proliferation and disarmament, and promotes a more peaceful and secure world.
Has Australia ever had nuclear weapons?

+
No, Australia has never had nuclear weapons. The country has been a signatory to the NPT since 1970 and has committed to not developing or acquiring nuclear weapons.
Why doesn't Australia need nuclear weapons?
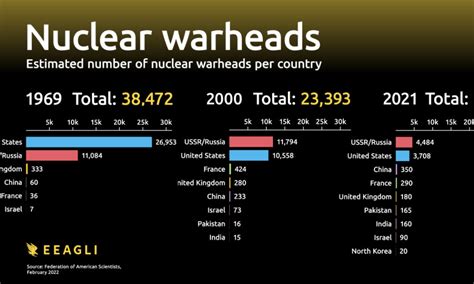
+
Australia doesn't need nuclear weapons because of its geographic isolation, strong alliances, conventional military capabilities, and commitment to international norms.
Is Australia's nuclear policy aligned with its regional interests?

+
Yes, Australia's nuclear policy is aligned with its regional interests. By committing to non-proliferation and disarmament, Australia helps to promote regional stability and reduce the risk of nuclear conflict in the Asia-Pacific region.
In conclusion, Australia’s nuclear policy is guided by a commitment to non-proliferation and disarmament. The country has consistently advocated for the abolition of nuclear weapons and has committed to not developing or acquiring nuclear weapons. While there may be speculations about Australia’s nuclear capabilities, the country’s nuclear stance is clear and aligns with its regional interests and international reputation.
Related Terms:
- Australia secret nuclear weapons
- Australia nuclear weapons testing
- Countries with nuclear weapons
- Does Australia have nuclear power
- Australia nuclear power