5 DNA Worksheet Answers Every Student Needs
Understanding DNA is crucial for students delving into genetics, biology, and various other scientific fields. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the fundamental blueprint for life, dictating the development and functioning of all known living organisms. Here are five common DNA worksheet answers that every student needs to know to grasp the basics of genetics and molecular biology.
What is DNA?

DNA, short for Deoxyribonucleic Acid, is an essential molecule found in the cells of all living organisms, with some exceptions like certain viruses which use RNA. It contains the genetic instructions used in the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of living things. Here are some key points:
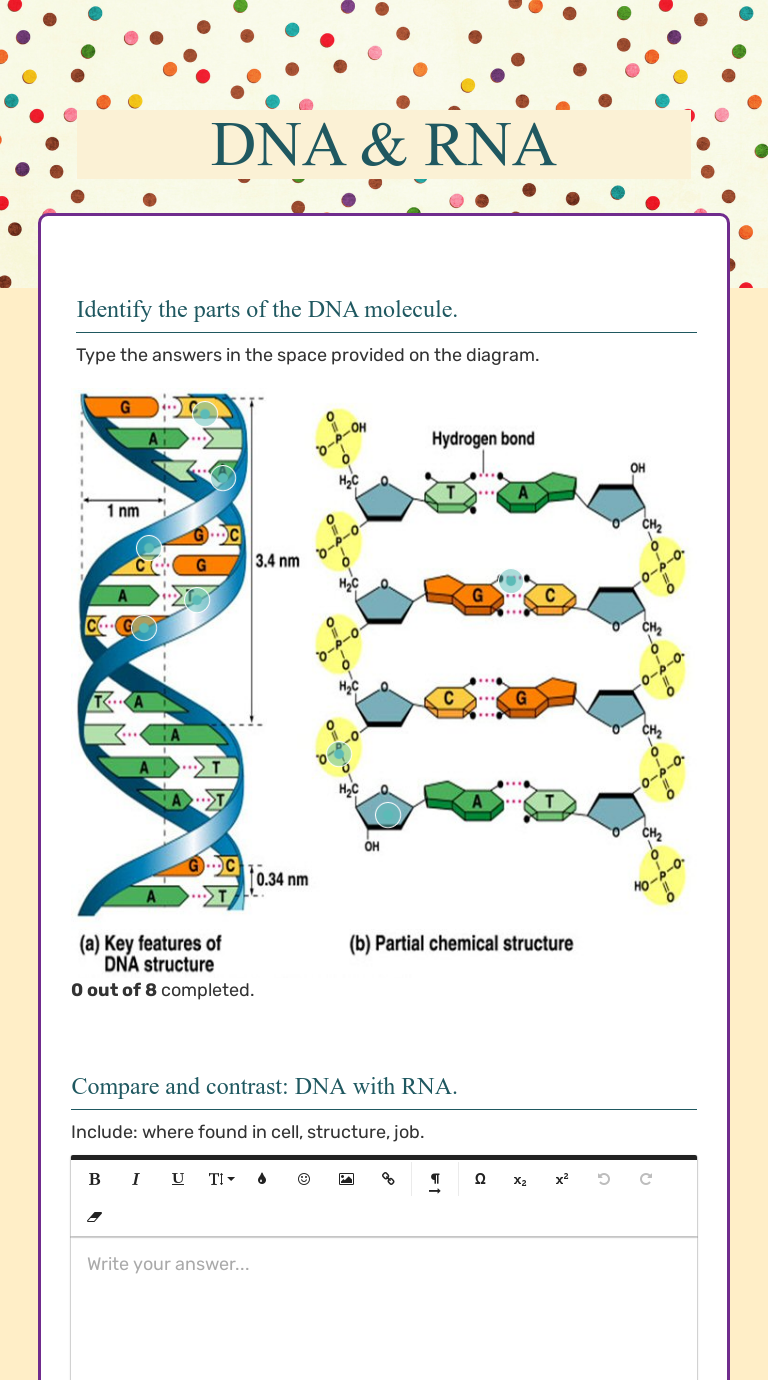
- DNA is structured as a double helix, resembling a twisted ladder.
- The rungs of the ladder are made up of base pairs, which are adenine (A) with thymine (T) and cytosine (C) with guanine (G).
- The backbone of the ladder consists of sugars and phosphates.
🔍 Note: Remember that the base pairing rules are A-T and C-G. These rules are fundamental for DNA replication and transcription.
What is a Gene?

A gene is a segment of DNA that provides the instructions for making a specific protein or RNA molecule. Here's a brief overview:
- Genes are located on chromosomes within the nucleus of a cell.
- Each gene codes for a particular trait or function through the production of proteins.
- The number and arrangement of genes determine everything from eye color to the complexity of an organism's behavior.
How is DNA Replicated?

DNA replication is the process by which a cell copies its DNA before cell division to ensure each new cell receives an identical copy of the genome. Here's how it works:
- Unwinding: The double helix unwinds, and the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs break.
- Complementary Pairing: Each strand serves as a template for making a new complementary strand. A always pairs with T, and C with G.
- Enzyme Action: DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the growing new strand, following the rules of base pairing.
- Proofreading: Enzymes proofread the new strands to correct any errors in replication.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Unwinding | The double helix is unwound by the enzyme helicase. |
| Complementary Pairing | Each old strand binds with new nucleotides following the base pairing rules. |
| Enzyme Action | DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to create new strands. |
| Proofreading | Enzymes like exonuclease correct any mistakes in the new strands. |

🔍 Note: DNA replication is semi-conservative; each daughter cell gets one original and one newly synthesized DNA strand.
What are Mutations?

Mutations are changes to the genetic material (DNA). They can occur naturally or be induced by environmental factors like radiation or chemicals. Here are some types of mutations:
- Point Mutations: Alterations at a single nucleotide base.
- Insertions/Deletions: Addition or removal of nucleotides.
- Chromosomal Mutations: Large-scale changes in chromosome structure or number.
Mutations can lead to variations in traits, diseases, or even the evolution of species if they provide a survival advantage.
Why is DNA Important?

DNA's importance cannot be overstated:
- It dictates the physical structure, development, and behavior of organisms.
- It provides the mechanism for inheritance, allowing traits to be passed from one generation to the next.
- It is central to processes like evolution through natural selection due to its capacity for variation via mutation.
DNA is also essential in biotechnology, allowing for genetic engineering, gene therapy, and forensic analysis.
In summary, understanding DNA is fundamental for students to comprehend how life works at its most basic level. From genes to replication, mutations to the very structure of DNA, this molecule’s complexity underscores the intricate design of life. Whether you’re studying for an exam or just curious about the building blocks of life, knowing these core concepts will provide a strong foundation in biology and beyond.
What is the difference between DNA and RNA?

+
DNA has a double-stranded structure, uses thymine, and remains in the nucleus. RNA is generally single-stranded, uses uracil instead of thymine, and can move out of the nucleus to the ribosomes for protein synthesis.
Why are mutations important?

+
Mutations introduce genetic diversity, which can lead to evolution. They can also cause diseases, but they’re crucial for adaptation, allowing organisms to better survive changes in their environments.
How does DNA replication ensure accuracy?

+
DNA replication includes proofreading mechanisms where enzymes like DNA polymerase correct any errors as the new strand is formed, ensuring high fidelity in genetic transmission.