DNA Double Helix Coloring Fun: Biology Corner Answers

Unraveling the Mystery of DNA: An Artful Approach

Deoxyribonucleic Acid, or DNA, is the blueprint of life. Found in every cell's nucleus, this molecule holds the instructions for an organism's growth, function, and reproduction. Understanding DNA not only helps us appreciate the complexity of life but also enriches our grasp of molecular biology. One engaging method to delve into this subject is through the visual representation of DNA's double helix structure, specifically via the "DNA Double Helix Coloring Fun" activity from Biology Corner.
Why Use Coloring in Biology Education?

Coloring activities, like the one provided by Biology Corner, are not merely a break from traditional learning methods; they offer several educational benefits:
- Memory Enhancement: Coloring activates multiple areas of the brain, aiding in memory retention.
- Understanding Structure: Visualizing complex structures like DNA through color can simplify their comprehension.
- Engagement: It encourages active learning, where students learn by doing, rather than just reading.
- Detail Orientation: Coloring forces students to pay attention to minute details, essential for understanding molecular biology.
The DNA Coloring Fun Activity

The "DNA Double Helix Coloring Fun" activity from Biology Corner is designed to guide students through the intricacies of DNA's structure. Here’s how it unfolds:
- Provide the Worksheet: Start by distributing the DNA coloring worksheet to your students.
- Introduce the Concept: Briefly explain what DNA is, its significance, and why understanding its structure is essential.
- Coloring Process: Guide students through the process of coloring different parts of the DNA, which include:
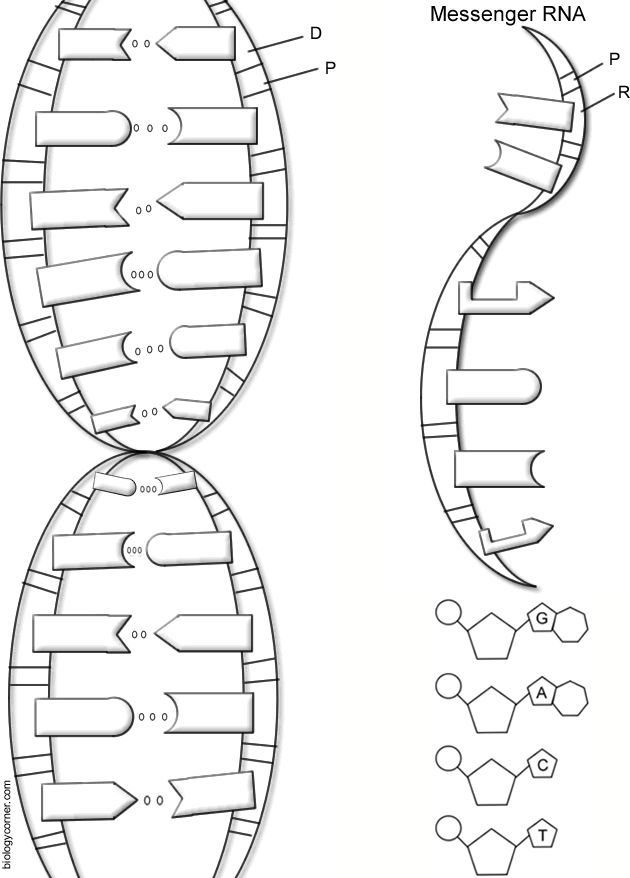
| Component | Color |
|---|---|
| Deoxyribose Sugar | Blue |
| Phosphate Group | Orange |
| Adenine (A) | Green |
| Thymine (T) | Yellow |
| Cytosine (C) | Red |
| Guanine (G) | Purple |
| Hydrogen Bonds | Black |

Students color each component, learning not just the aesthetic value but the fundamental structure of DNA in the process.
Key Learning Points from Coloring

Through this activity, students grasp the following key concepts:
- Antiparallel Strands: DNA consists of two antiparallel strands, where one runs in the 5' to 3' direction while the other runs 3' to 5'.
- Base Pairing: Adenine pairs with Thymine via two hydrogen bonds, and Cytosine pairs with Guanine through three hydrogen bonds, adhering to the rule of complementarity.
- Helical Nature: The structure of DNA is not merely linear but forms a right-handed double helix, allowing for efficient storage of genetic information.
- Backbone Composition: The sugar-phosphate backbone provides structural support, with deoxyribose sugars and phosphates forming the core of DNA’s structure.
🎨 Note: The exact colors suggested for each component are not strictly set in stone; they can be adapted to encourage creativity while still maintaining scientific accuracy.
Applying the Knowledge

Once the coloring activity is completed, students should:
- Reflect: Consider how the visual representation helps in understanding DNA’s function and structure.
- Discuss: Engage in discussions about the importance of DNA's structure, its replication, and its role in protein synthesis.
- Further Study: Explore related topics like DNA replication, genetic mutations, or gene expression, using the knowledge gained from this hands-on activity.
Engaging students through activities like the DNA Double Helix Coloring Fun not only makes learning about molecular biology enjoyable but also reinforces critical concepts in an intuitive manner. This approach fosters a deeper connection to the subject, making it memorable and engaging for learners of all levels. By blending art with science, educators can spark curiosity and promote a lifelong passion for discovery.
What is the significance of DNA’s double helix structure?

+
The double helix structure of DNA allows for efficient storage and transmission of genetic information. Its shape facilitates the unwinding process during replication and transcription, ensuring that the genetic code is accurately copied and read.
Why do we use color coding in DNA activities?
+
Color coding helps in distinguishing different components of DNA visually, making complex structures easier to understand. It aids in memory retention and enhances the learning experience by engaging multiple senses.
Can students use different colors than those suggested?

+
Absolutely, the colors suggested are merely for convenience and standardization. Encouraging students to use their own color schemes can promote creativity while still ensuring they learn the structural components of DNA.