Mastering Division: Fun Worksheet for Kids

Are you looking for a fun and engaging way to teach your child the basics of division? Division is one of those fundamental math concepts that can seem daunting to kids at first. However, with the right approach, it can become an enjoyable learning experience. Here, we'll explore creative and interactive methods to help your young mathematicians master division through a fun worksheet designed specifically for kids.
The Importance of Division in Early Education

Before diving into the worksheet, let’s understand why division is crucial in early math education:
- Foundational Skill: Division is one of the four basic arithmetic operations. It helps in breaking down quantities into equal parts or groups, which is essential for understanding fractions, ratios, and other advanced topics.
- Real-Life Applications: Division skills are applied in daily life, from sharing items equally among friends to understanding recipes or calculating distances.
- Logical Thinking: It promotes analytical and logical reasoning as children learn to distribute numbers evenly.
Designing a Division Worksheet for Kids

A worksheet needs to be both educational and entertaining to keep children engaged. Here are key elements to include:
- Visual Aids: Use images or pictograms to represent division problems visually.
- Coloring and Drawing: Allow space for kids to color or draw as part of solving problems.
- Interactive Games: Incorporate games like ‘Match the Squares’ or ‘Cut and Share’ where kids physically interact with the worksheet.
- Puzzles: Use number puzzles that require division to solve, making the learning process fun and challenging.
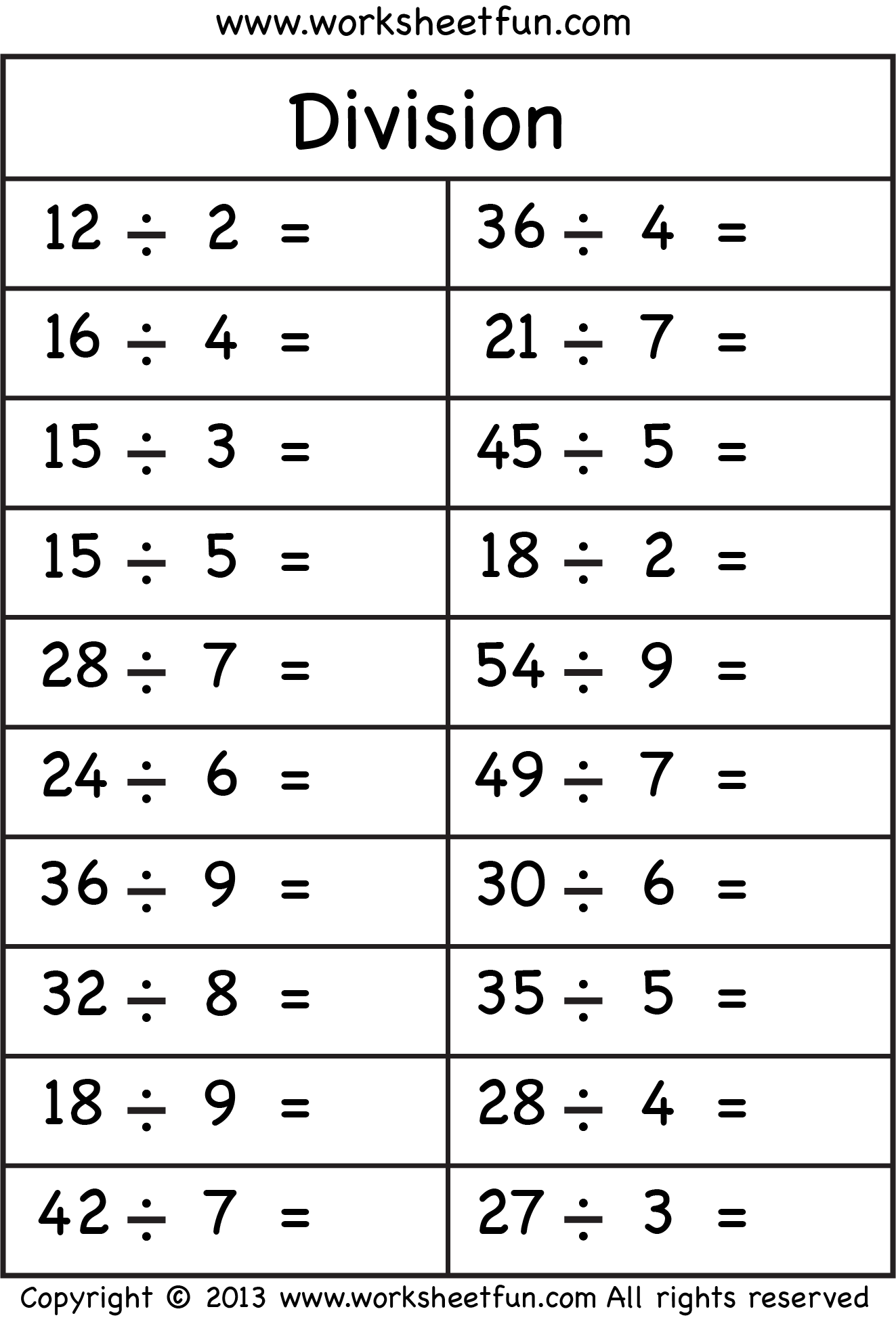
Sample Division Worksheet

| Activity | Description |
|---|---|
| Cookie Sharing | There are 12 cookies, and 3 friends. How many cookies does each friend get? Draw or color the cookies. |
| Fruit Basket | Divide 18 fruits into 3 baskets. Use drawings or cutouts to show how you would share the fruits. |
| Match the Squares | Match the number of boxes with the correct number of objects to be shared inside each box. |

🌟 Note: When designing your worksheet, consider the age group of your child. Younger children might need larger, more colorful illustrations, while older children can handle more complex division problems.
Here are a few tips on how to make the worksheet even more engaging:
- Include storylines or scenarios where division is necessary. For instance, using characters or animals trying to divide resources equally.
- Provide space for creativity by allowing kids to color, paste stickers, or draw their solutions.
- Introduce variations in difficulty to keep the interest high. Start with simple division and progress to more complex problems within the same worksheet.
Explaining Division Concepts Through Worksheets
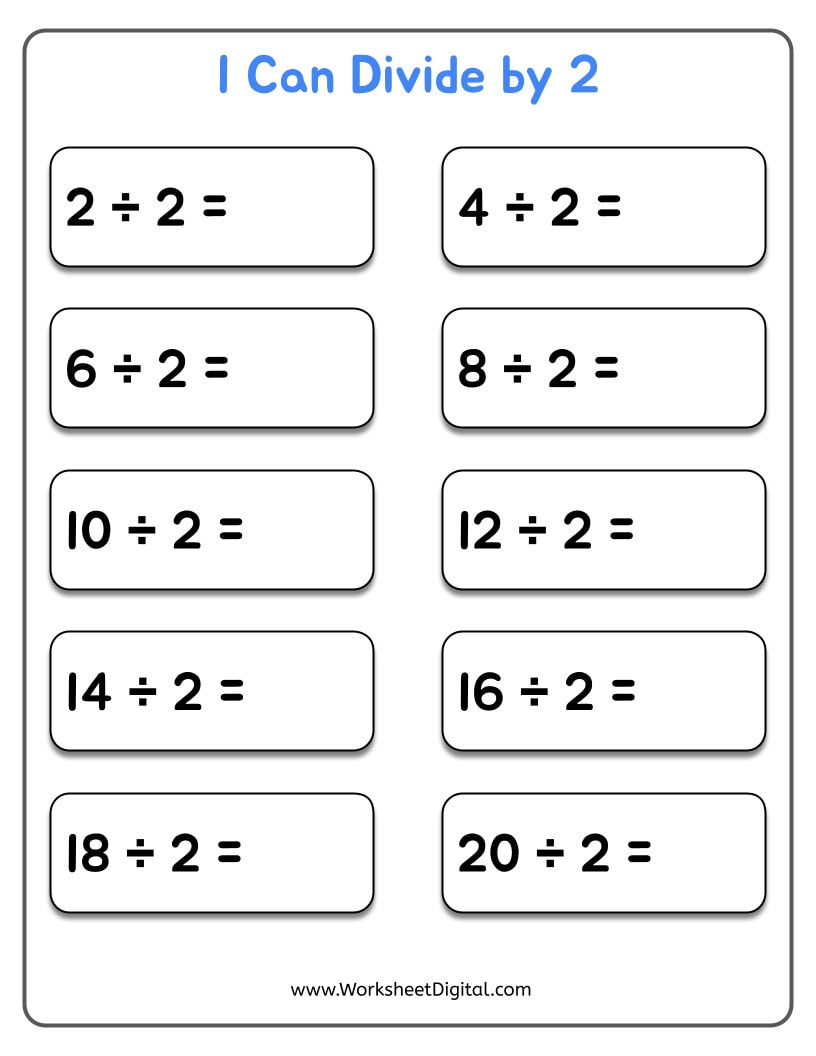
Worksheets can be a powerful tool for teaching division if they're structured to explain the concept:
- Equal Sharing: The basis of division. Demonstrate how to share objects or items equally among a group.
- Repeated Subtraction: A method to divide by repeatedly taking away the same number until you reach zero, thus learning the dividend.
- Visual Division: Use dots or grid papers to visually demonstrate division problems. This helps kids see division as breaking down a whole into parts.
Making Division Fun Beyond the Worksheet

Educational activities don't have to be confined to a worksheet. Here are some additional ways to reinforce division skills:
- Physical Objects: Use everyday items like toys, candies, or fruits to create division scenarios.
- Math Games: Incorporate board games or card games that involve division to make learning interactive.
- Cooking: Let kids help measure ingredients for recipes where division is required to halve or quarter quantities.
While the worksheet itself is a structured tool, making division a part of daily activities can solidify understanding:
- Group Tasks: Set up situations where children have to divide a task or items amongst themselves, like setting the table for dinner.
- Story Problems: Engage kids with math stories where characters divide their treasure, time, or food. Ask them to solve the problem at the end of the story.
🧠 Note: Remember, the aim is to make division enjoyable, not to turn every activity into a high-pressure test.
Incorporating these playful methods into your child's learning can make the sometimes complex arithmetic operation of division not just understandable but also enjoyable. Through this worksheet and other activities, children can experience the satisfaction of mastering division in a way that feels less like schoolwork and more like play.
This playful approach to division fosters:
- Interest in Math: By making the process fun, kids are more likely to engage with math subjects.
- Confidence: As children see they can solve division problems through play, their confidence in their math abilities grows.
- Critical Thinking: They learn to break down problems into smaller parts and find patterns, which are essential skills beyond just division.
In this final reflection, we can acknowledge that teaching division to kids through engaging worksheets and activities not only builds mathematical competence but also enhances cognitive abilities, creativity, and problem-solving skills. By blending fun with learning, we're not only teaching division but also encouraging a lifelong love for learning, exploration, and critical thought.
How can I make a division worksheet more engaging for my child?

+
Incorporate activities like coloring, puzzles, and scenarios that children can relate to, such as sharing toys or dividing cookies. Adding a narrative or game-like elements can also make the worksheet more exciting.
What age is appropriate to start teaching division?
+
Division can be introduced as young as 6 or 7 years old, especially through the concept of sharing. However, formal division can be introduced around 8 or 9 when children start understanding multiplication as repeated addition.
Can division worksheets help with other math skills?

+
Yes, division worksheets can enhance understanding of fractions, ratios, patterns, and problem-solving strategies. They also help with logical thinking and can prepare children for algebra by familiarizing them with the inverse operations of multiplication.



