5 Simple Steps to Divide Mixed Number Fractions Easily

Why Understanding Mixed Numbers is Essential

Mathematics often involves the use of fractions in everyday problem-solving, and mixed numbers, in particular, offer a unique approach to expressing quantities that are not whole. A mixed number, for example, 2 1⁄3, combines an integer (2) with a fraction (1⁄3), providing a clear visual of both whole and part. Understanding how to manage these mixed numbers, especially dividing them, can unlock a multitude of mathematical skills from measurement conversions to culinary precision.
📚 Note: Dividing mixed numbers involves several key steps, so patience and practice will enhance your understanding and confidence.
Step-by-Step Guide to Divide Mixed Numbers
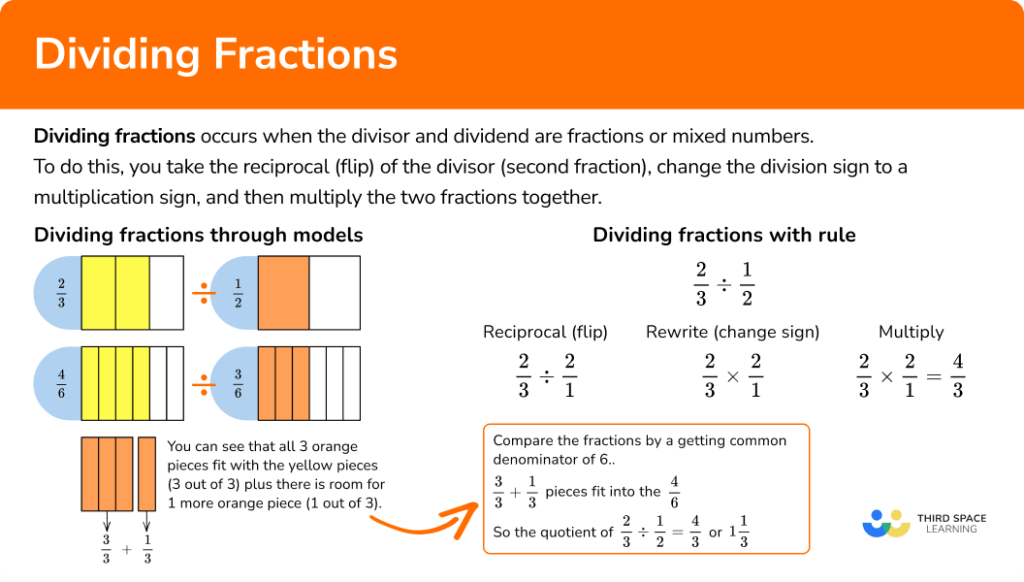
Here’s how to systematically divide mixed numbers:
- Convert to Improper Fractions: Begin by converting mixed numbers into improper fractions, which means the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator.
- Find the Reciprocal: Swap the numerator and the denominator of the second fraction, which is part of the division process.
- Multiply: Now, you multiply the first fraction by the reciprocal of the second fraction.
- Reduce if Possible: Simplify your answer to its lowest terms to make the result easier to understand.
- Convert Back to Mixed Numbers: Optionally, convert the result back to a mixed number for readability.
1. Convert Mixed Numbers to Improper Fractions

The first step in dividing mixed numbers is to convert them to improper fractions. To do this:
- Multiply the whole number part by the denominator of the fraction.
- Add the result to the numerator of the fraction.
- Place this new numerator over the original denominator.
Let’s use an example: Suppose you want to divide 5 3⁄4 by 1 1⁄2.
To convert 5 3⁄4:
- 5 * 4 = 20 (since the denominator is 4)
- Add the numerator: 20 + 3 = 23
- The improper fraction is 23⁄4.
To convert 1 1⁄2:
- 1 * 2 = 2 (since the denominator is 2)
- Add the numerator: 2 + 1 = 3
- The improper fraction is 3⁄2.
💡 Note: Improper fractions give a clear view of the quantity in terms of parts, making division easier.
2. Find the Reciprocal of the Divisor

The next step involves finding the reciprocal of the second fraction. The reciprocal simply means swapping the numerator and the denominator:
- For 3⁄2, the reciprocal is 2⁄3.
Now your division becomes a multiplication:
- 23⁄4 ÷ 3⁄2 becomes 23⁄4 × 2⁄3.
3. Multiply the Fractions

Now, multiply the numerator of the first fraction with the numerator of the reciprocal, and do the same with the denominators:
- (23 * 2) / (4 * 3) = 46⁄12.
4. Simplify the Result

If the product is not in its lowest terms, simplify by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD):
- The GCD of 46 and 12 is 2.
- 46⁄12 simplifies to 23⁄6.
🧮 Note: Simplifying fractions gives a more understandable result by reducing it to its smallest possible form.
5. Convert Back to Mixed Number (Optional)

If you want the result in mixed number format:
- Divide the numerator by the denominator: 23 ÷ 6 = 3 R5.
- The result is 3 5⁄6.
And there you have it! You’ve successfully divided two mixed numbers by converting to improper fractions, finding the reciprocal, multiplying, simplifying, and if needed, converting back to a mixed number.
Why This Skill Matters

The process of dividing mixed numbers is not just an academic exercise; it has real-world applications:
- Cooking and Baking: Recipes often call for dividing portions, adjusting ingredient amounts.
- Construction and Engineering: Accurate measurements and calculations are crucial for safety and design precision.
- Finance: Financial analysts often need to divide fractions when dealing with investment returns or asset allocation.
Why do I need to convert mixed numbers into improper fractions before dividing?

+
Converting to improper fractions allows for a smoother division process. Division of fractions inherently involves multiplication, which is easier with improper fractions due to their structural simplicity.
Can I skip any step in this process?
+
Each step in the process is integral to achieving the correct result. Skipping steps like finding the reciprocal could lead to incorrect answers, although for some experienced users, shortcuts might be possible.
What if I need to divide by a whole number?

+
Whole numbers can be treated as fractions with a denominator of 1. For example, dividing 23/4 by 5 would mean you're dividing by 5/1, where you proceed with steps 2 to 5 as usual.
How do I know when to simplify fractions?

+
Simplify when the numerator and denominator share common factors other than 1. If they don't, simplification isn't necessary but still helpful for clarity.
Is there an alternative method to this process?

+
Yes, there are other methods like using common denominators or decimal conversion, but the steps outlined above are the most commonly taught and used due to their systematic approach and precision.
Mastering the division of mixed numbers opens up a range of mathematical applications, from daily tasks to advanced problem-solving. Remember, each step in the process, from converting to improper fractions to finding reciprocals and simplifying, is essential. With practice, these steps will become second nature, allowing you to confidently tackle any fraction division problem with ease and accuracy.