5 Tips for Dividing Fractions and Mixed Numbers Easily

In the realm of mathematics, division of fractions and mixed numbers can often seem daunting, especially for those encountering these operations for the first time. However, with a few easy-to-remember tips and strategies, this task can become much simpler. Here, we delve into the nuances of dividing fractions and mixed numbers, offering practical advice to enhance your mathematical skills.
The Basics of Fraction Division

The foundation of dividing fractions and mixed numbers hinges on understanding the reciprocal or multiplicative inverse. When you want to divide by a fraction, you multiply by its reciprocal instead. Let’s explore how this works:
- To divide fractions, keep the first fraction as it is, change the division sign to multiplication, and then invert the second fraction (the divisor).
Example:

Suppose you need to divide (\frac{3}{4}) by (\frac{2}{5}). Here’s the step-by-step process:
- Keep (\frac{3}{4}) as it is.
- Change the division sign to multiplication: (\frac{3}{4} \times)
- Invert (\frac{2}{5}) to get (\frac{5}{2}).
- The expression becomes: (\frac{3}{4} \times \frac{5}{2}).
- Multiply the numerators and the denominators separately: (\frac{3 \times 5}{4 \times 2} = \frac{15}{8})
💡 Note: Ensure you understand the concept of reciprocals thoroughly before attempting to divide mixed numbers or fractions.
Handling Mixed Numbers
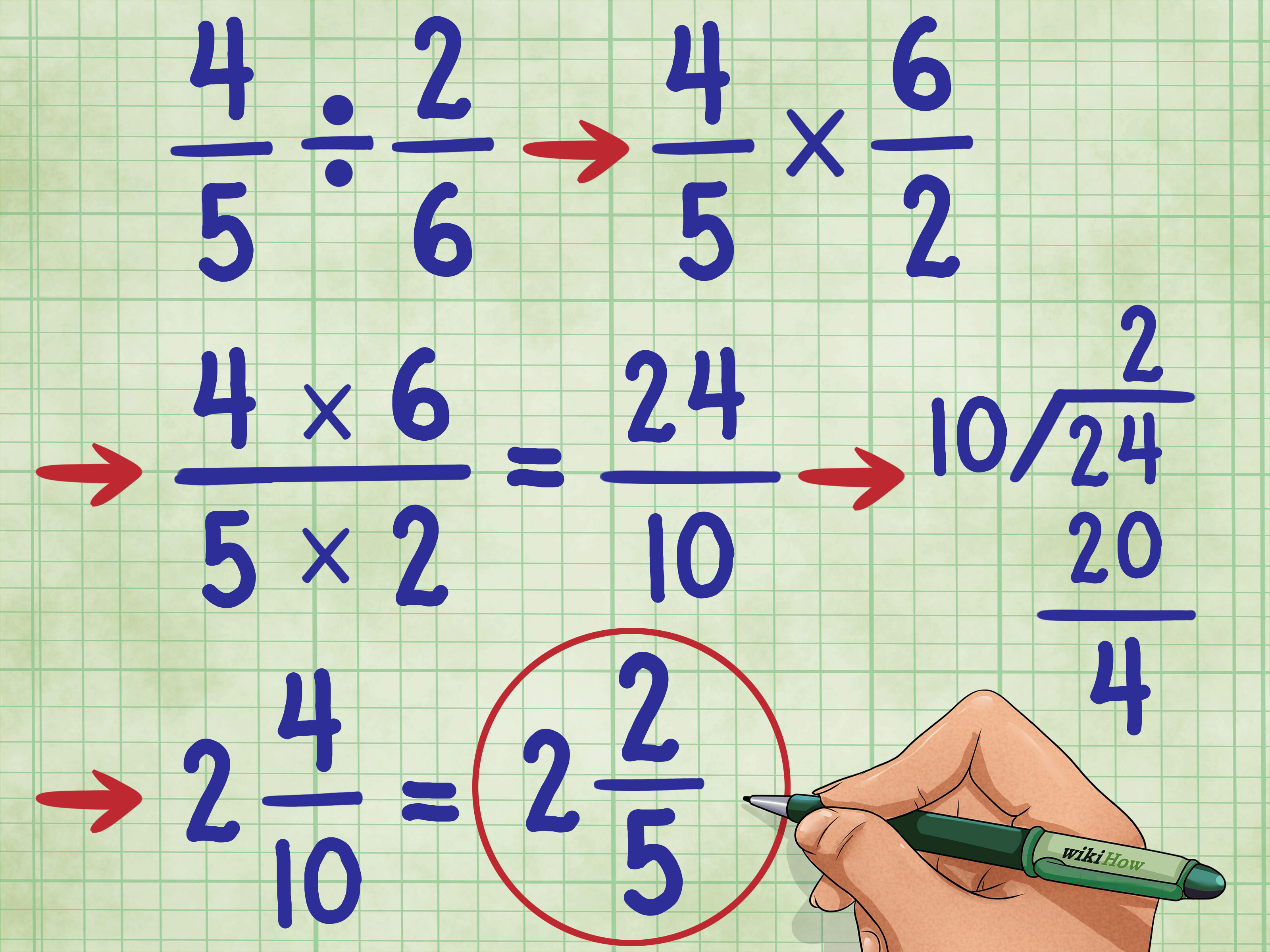
Before dividing mixed numbers, you must convert them to improper fractions. This conversion simplifies the calculation significantly:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator of the fraction part, then add the numerator to get the new numerator. The denominator remains the same.
Example:
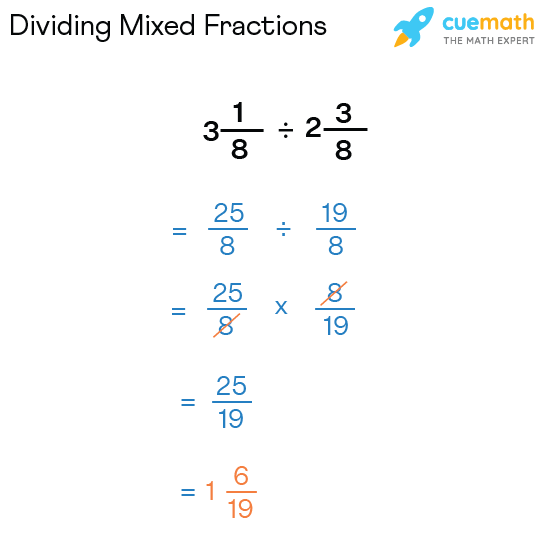
Divide the mixed number (2\frac{1}{3}) by (1\frac{1}{2}):
- Convert (2\frac{1}{3}) to (\frac{7}{3}) and (1\frac{1}{2}) to (\frac{3}{2}).
- Use the reciprocal method: (\frac{7}{3} \times \frac{2}{3} = \frac{14}{9}).
🧮 Note: This conversion step often eliminates common errors in division of mixed numbers.
Tips for Easy Division

Here are some actionable tips to make division of fractions and mixed numbers effortless:
- Know Your Reciprocals: Understanding that any fraction’s reciprocal is achieved by swapping its numerator and denominator is crucial.
- Simplify Where Possible: Before or after the division, simplify fractions by canceling out common factors to reduce the complexity of the calculation.
- Visualize the Process: Sometimes drawing simple diagrams or using physical objects to represent fractions can help in understanding the concept better.
- Practice with Real-Life Scenarios: Try to find practical applications like cooking measurements, where you might divide fractions naturally.
- Use Cross-Cancellation: In more complex problems, cross-cancellation can save time and reduce the likelihood of errors.
Using Cross-Cancellation:

| Fraction 1 | Operator | Fraction 2 |
|---|---|---|
| (\frac{8}{9}) | ÷ | (\frac{16}{3}) |
| Can cancel 8 with 16 to 1 and 3 with 9 to 3: | → | (\frac{1}{3}) ÷ (\frac{2}{1}) |
| After cross-cancellation: | = | (\frac{1}{3}) x (\frac{1}{2} = \frac{1}{6}) |

✨ Note: Cross-cancellation is particularly useful in situations where simplification is difficult in the numerator or the denominator.
Solving Common Pitfalls

Students often encounter several pitfalls when dividing fractions and mixed numbers:
- Forgot to Flip the Second Fraction: Always remember to invert the second fraction before multiplying.
- Mixed Numbers Confusion: Convert mixed numbers to improper fractions for accurate calculation.
- Order of Operations: Follow the order of operations when multiple operations are involved.
Overcoming Mistakes:
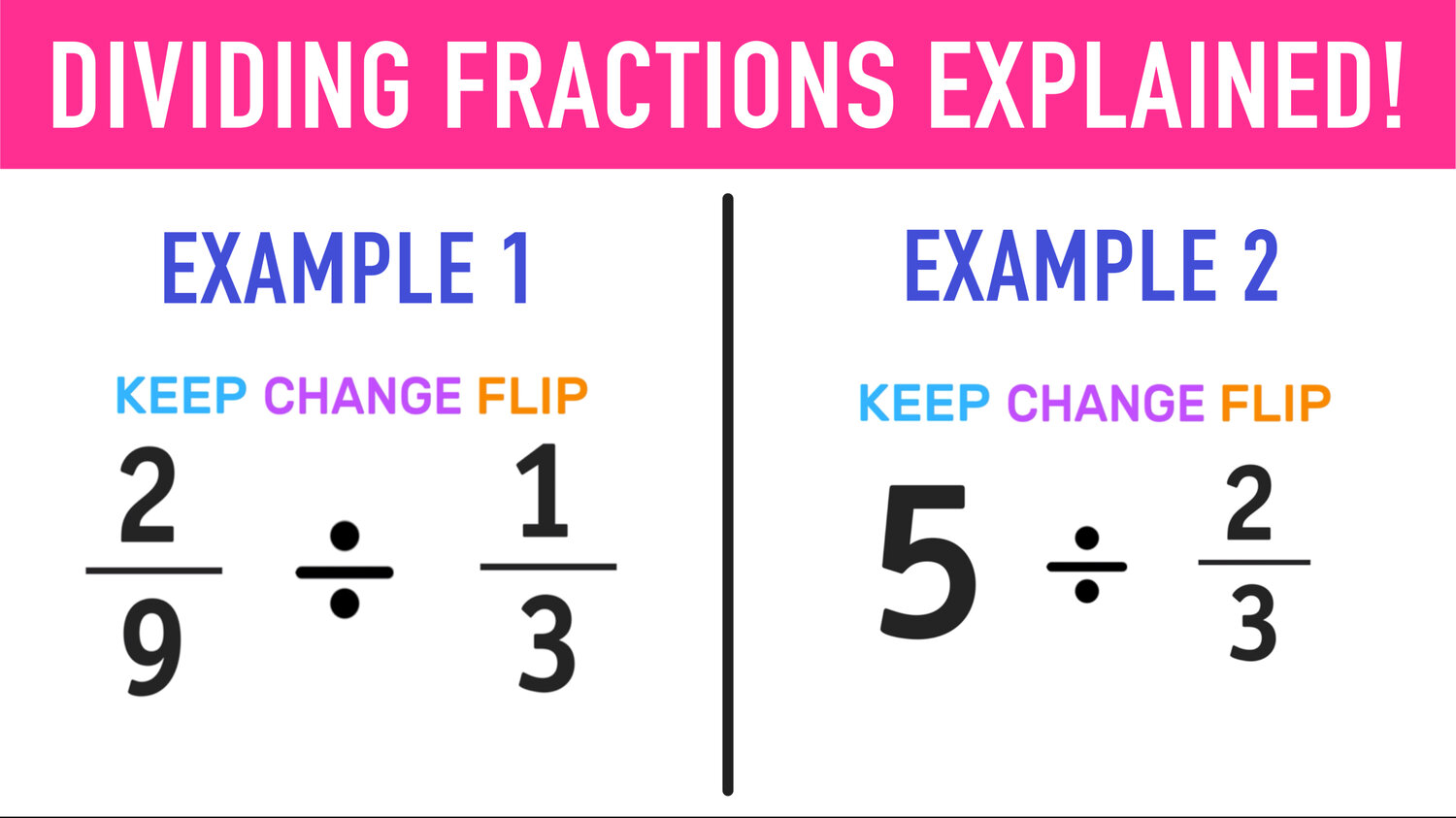
Regular practice and using mnemonic devices or simple acronyms like “Keep Change Flip” can help in remembering the steps for fraction division.
In summary, dividing fractions and mixed numbers becomes significantly easier with the right approach. By understanding the reciprocal method, practicing with real-life examples, and learning to sidestep common mistakes, one can master this arithmetic operation with confidence. Keep these tips handy, and you’ll find that dividing fractions and mixed numbers is not just possible, but also can be enjoyable and logical.
Why do we flip the second fraction when dividing?

+
Dividing by a fraction is equivalent to multiplying by its reciprocal. Flipping the second fraction turns division into multiplication, which is a simpler operation.
Can I use cross-cancellation with mixed numbers?

+
Yes, you can use cross-cancellation after converting mixed numbers into improper fractions to simplify the multiplication or division.
What if my division results in a mixed number?

+
After performing the division, you may need to convert the improper fraction back into a mixed number for a clearer representation, especially in practical scenarios.
How can I simplify fraction division even further?

+
Simplify by canceling out common factors before multiplication. You can also learn about least common denominators for more complex situations.