Distance vs Time Graph: Master Worksheet Fun

In the fascinating world of physics, the study of motion is fundamental. Among the tools to analyze motion, the Distance vs Time graph stands out as an intuitive and informative way to understand how objects move over time. This worksheet guide will dive deep into the mechanics of creating, interpreting, and gaining insights from these graphs, making learning fun and engaging. Whether you're a student looking to master physics or just someone curious about the nuances of motion, this guide will provide you with the necessary skills and understanding.
Understanding the Basics

Before we delve into the worksheets, let’s solidify the basics:
- Distance (y-axis): This is the total path an object has covered from its starting point.
- Time (x-axis): This represents the time elapsed from the start of the motion.

Graph Characteristics

Here are some key characteristics to look for in a Distance vs Time graph:
- Slope: The slope of the graph gives the speed of the object. A steeper slope indicates faster motion, and a flat line (zero slope) shows no motion.
- Curvature: Curves in the graph can represent acceleration or deceleration, with the concavity indicating the direction of acceleration.
- Straight Line: A straight line implies uniform (constant) speed or no change in speed over time.
- Vertical Position: The vertical position on the graph shows the distance traveled.
Worksheet #1: Creating a Basic Distance vs Time Graph

Here’s a basic exercise to familiarize yourself with these graphs:
- Step 1: Plot the following data points on graph paper or a digital tool:
Time (s) Distance (m) 0 0 2 10 4 20 6 30 
- Step 2: Connect the points with a line or curve, depending on the motion type.
- Step 3: Analyze the slope and shape of your graph to determine the object’s motion pattern.
Worksheet #2: Interpreting Real-World Scenarios

Now, let’s apply these graphs to real-life situations:
- Scenario 1: A car starting from rest accelerates uniformly to 60 km/h in 10 seconds. How would you plot this on a Distance vs Time graph?
- Scenario 2: A bike rider starts with a velocity of 15 m/s, then slows down to 5 m/s in 5 seconds. Plot and interpret this motion.

Worksheet #3: Calculations and Analysis

Here, we will delve into more quantitative aspects:
- Step 1: Using the graph from Scenario 1, calculate the average velocity of the car.
- Step 2: Determine the acceleration of the car using the slope formula for acceleration.
- Step 3: Discuss how to calculate the displacement if you know the initial velocity, time, and acceleration.
💡 Note: Remember that average velocity is the total displacement divided by the total time, whereas instantaneous velocity is represented by the slope of the tangent to the curve at any given time.
Mastering Distance vs Time Graphs

To truly master these graphs, practice is key. Here are some tips:
- Regularly draw and analyze Distance vs Time graphs from different scenarios.
- Understand how different motions (constant speed, acceleration, deceleration) look on the graph.
- Learn how to calculate distances, velocities, and accelerations using the graph data.
- Engage with simulations or real-time experiments to see graphs in action.
By working through these worksheets, you've not only learned how to read and interpret Distance vs Time graphs but also understood how these graphs are fundamental in analyzing the kinematics of objects. From everyday commuting to astronomical bodies, these graphs help us visualize and calculate motion with precision. With this knowledge, you're well-equipped to tackle more complex physics problems or even real-life scenarios where understanding motion is crucial. Remember, every journey, both in life and in physics, can be mapped on these graphs, providing insights into where you've been, where you are, and where you might be going.
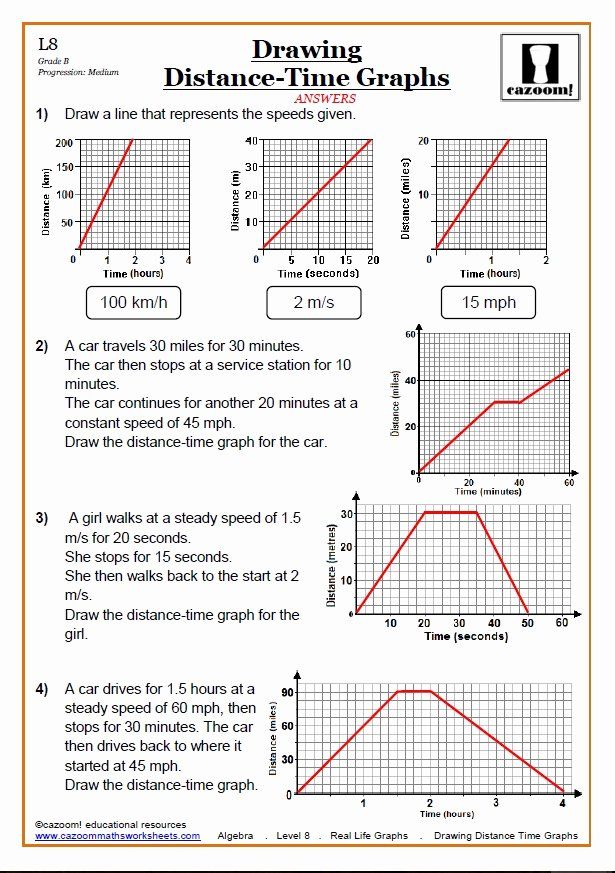
Why is the slope of a Distance vs Time graph important?
+
The slope of a Distance vs Time graph represents the velocity of the object. The steeper the slope, the faster the object is moving. It provides a clear visual representation of how fast something is traveling.
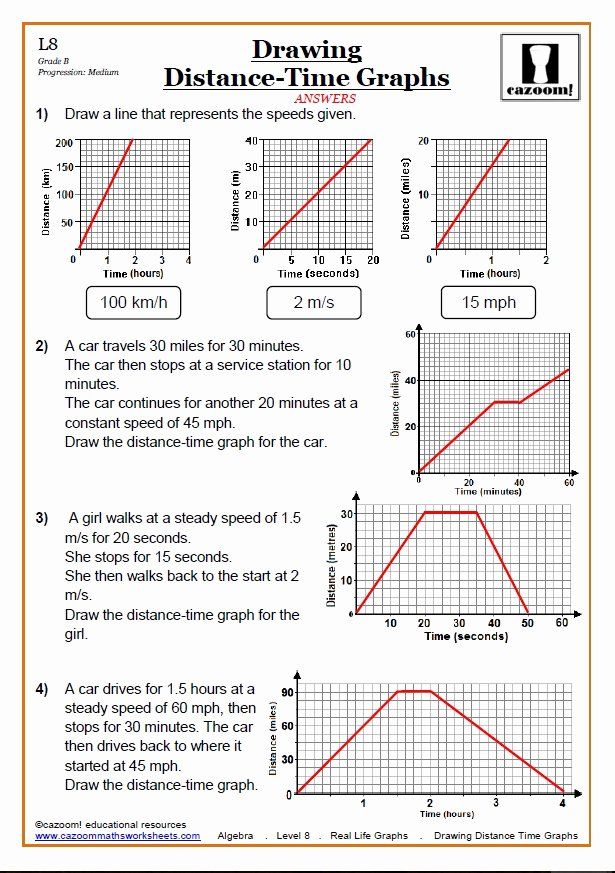
What does a curved line on a Distance vs Time graph indicate?
+
A curved line indicates that the object is accelerating or decelerating. The concavity of the curve (upward or downward) shows whether the acceleration is positive or negative.
Can you find acceleration from a Distance vs Time graph?

+
Yes, but indirectly. The acceleration is not directly shown on the graph; however, you can estimate it by calculating the change in velocity over time. This can be done by finding the slope of the velocity-time graph, which is derived from the Distance vs Time graph.
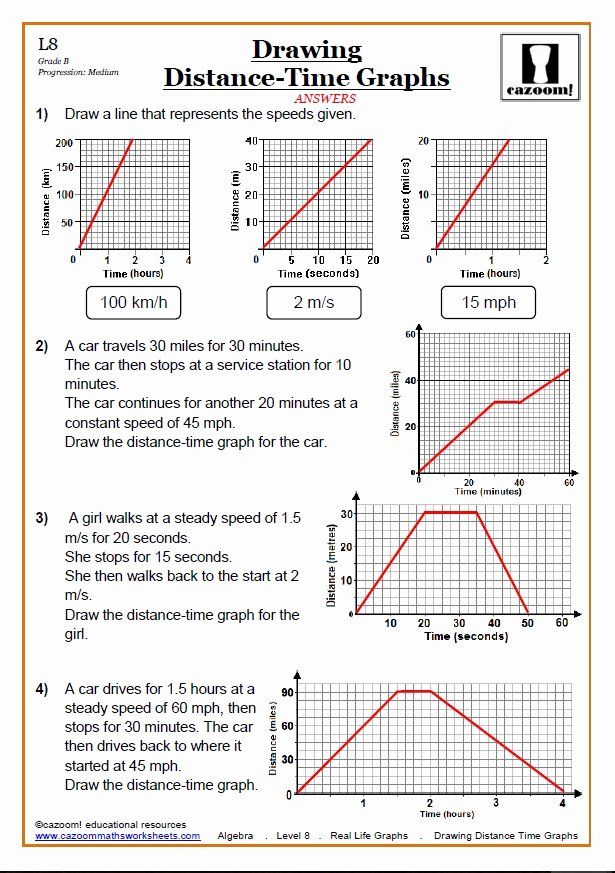
How do you interpret a flat line in a Distance vs Time graph?
+
A flat line (zero slope) means that the object is not moving; its speed is zero, and the distance from the starting point remains constant.
What are common mistakes when plotting these graphs?

+
Common mistakes include mislabeling axes, confusing distance with displacement, or not plotting data points accurately. Another error is assuming a straight line implies constant velocity when it might just mean constant speed but varying direction.