Diploid and Haploid Chromosomes Worksheet Answers Revealed

In the fascinating world of genetics, understanding the difference between diploid and haploid chromosomes is fundamental. This understanding not only provides insights into how life is built from the most basic level but also has significant implications in fields like medicine, agriculture, and evolution. Today, let's delve into a comprehensive exploration of these two genetic states through a set of worksheet answers that will clarify the concept for both students and enthusiasts alike.
Understanding Diploid and Haploid

At the core of genetics, organisms are classified based on their chromosome number:
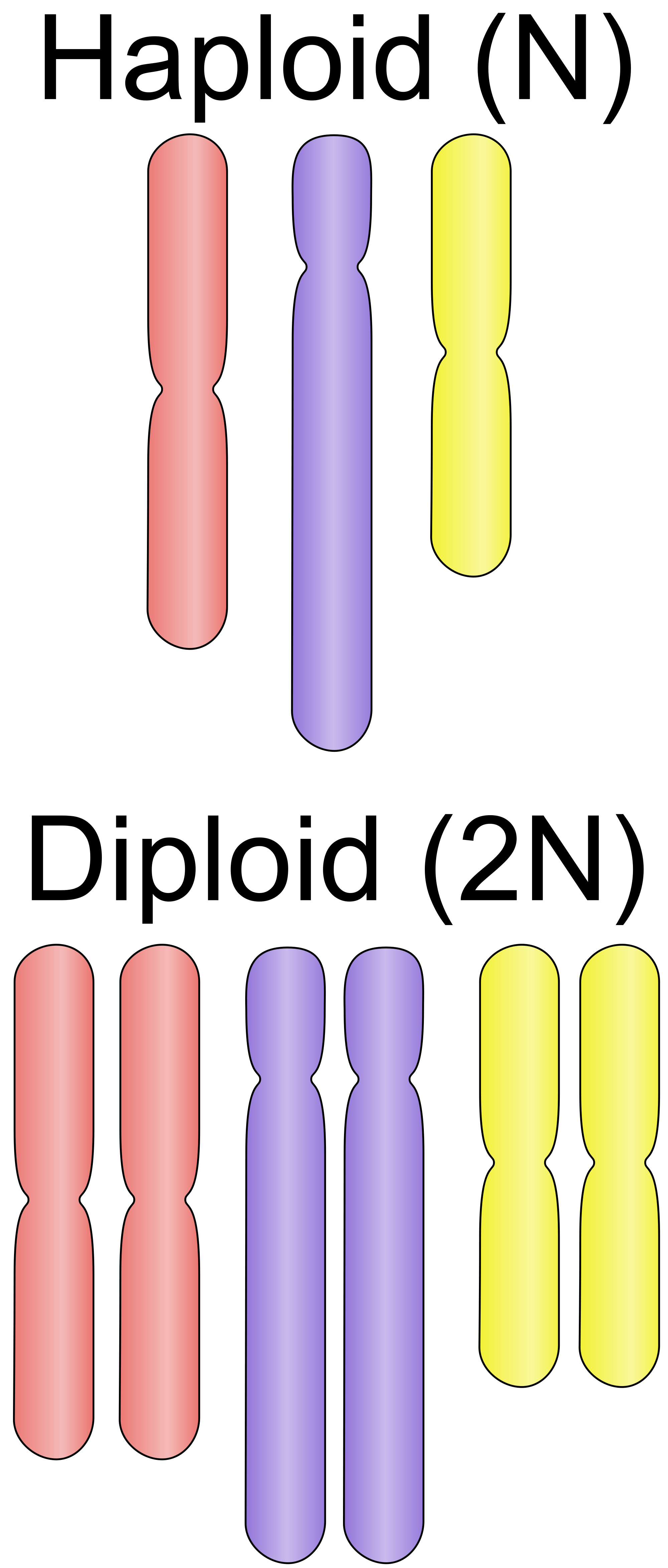
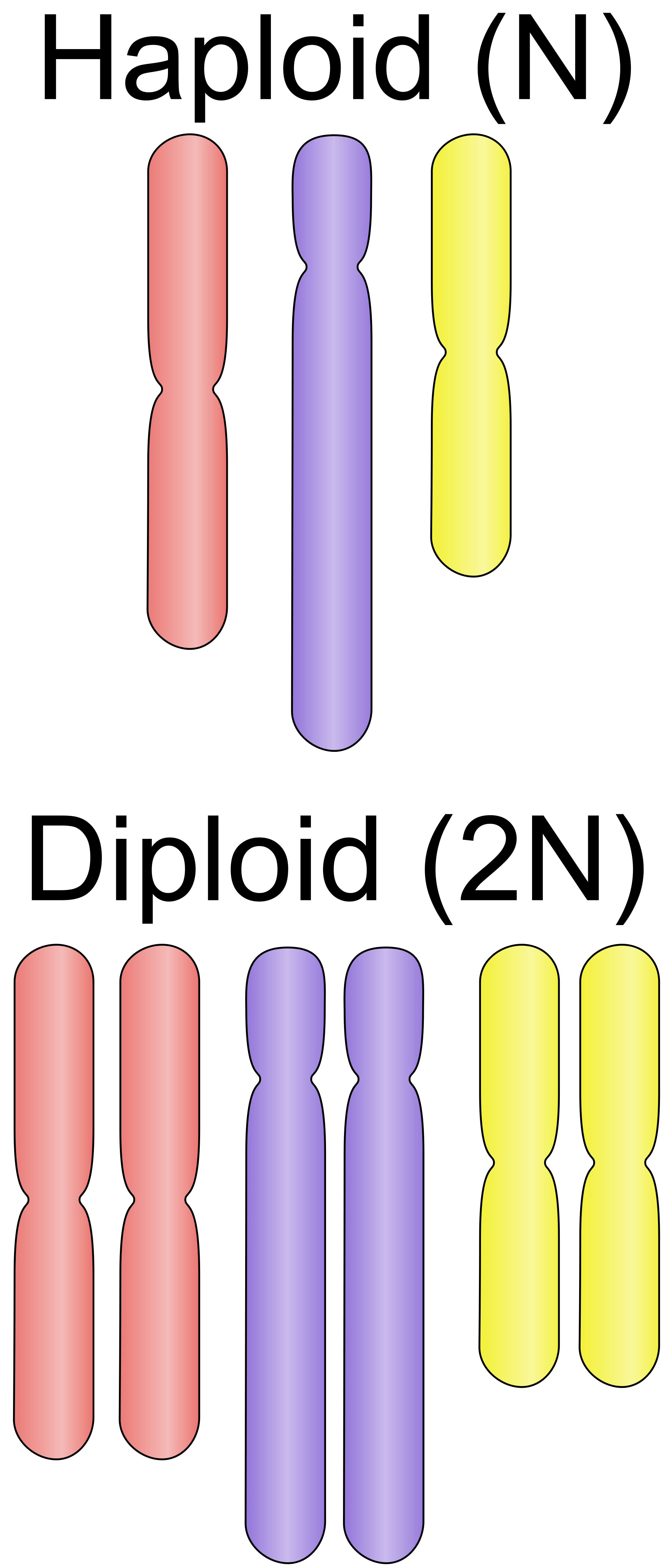
- Diploid (2n): These organisms have two sets of chromosomes; one set inherited from each parent. For humans, this means 46 chromosomes.
- Haploid (n): These cells contain only one set of chromosomes. This is typical of gametes (sperm and egg cells) in humans, with 23 chromosomes each.
Diploid Cells
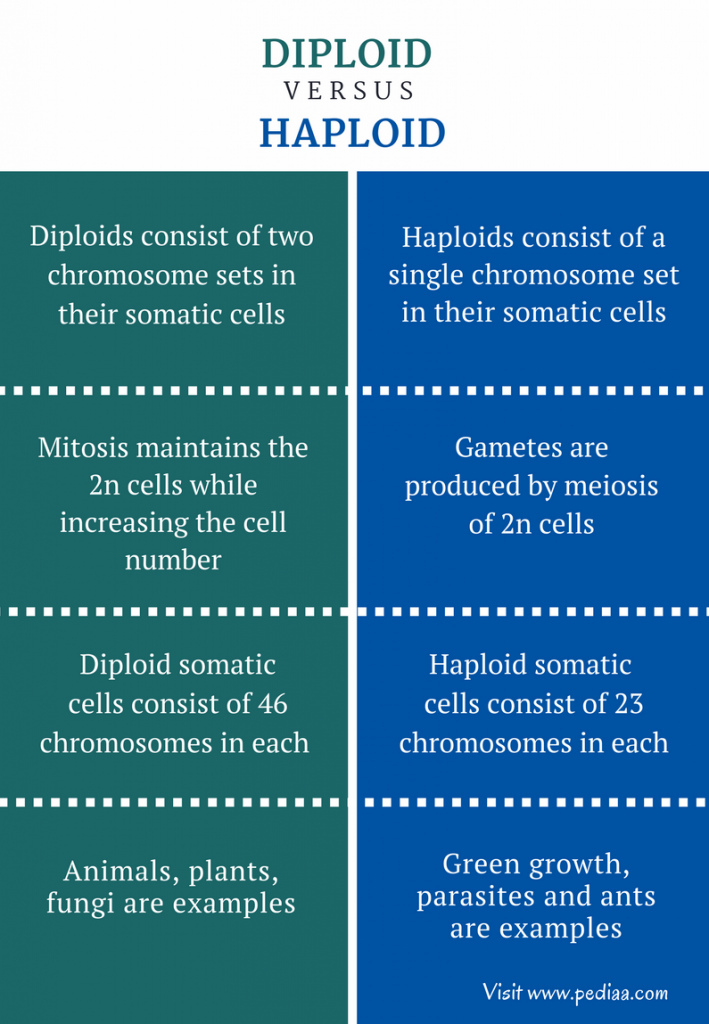
Diploid cells make up the majority of an organism's body cells. Here are some key points about diploid cells:
- Humans, like other sexually reproducing animals, have diploid somatic cells where they carry two homologous chromosomes for each type, one from each parent.
- During fertilization, the diploid condition is restored when two haploid gametes combine to form a zygote.
- The process ensuring the correct distribution of chromosomes during cell division is known as meiosis.
📌 Note: Diploid cells undergo mitosis for growth, repair, and normal functioning.
Haploid Cells
Haploid cells are specialized for the purpose of sexual reproduction:
- Gametes in animals or spores in plants carry only one set of chromosomes, ensuring that upon fusion, the offspring will have the correct number of chromosomes.
- Meiosis produces haploid cells, reducing the number of chromosomes by half.
- These cells contribute to genetic diversity through recombination during meiosis.
Worksheet Answers

To better understand the distinctions and interactions between diploid and haploid states, let's go through some typical worksheet questions:
1. What does “n” represent in the context of chromosome number?

n represents the haploid number of chromosomes, which means one set of chromosomes. In humans, n = 23.
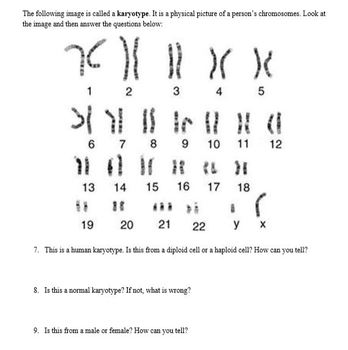
2. If a sperm cell has 23 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will a typical human zygote have?
The zygote will have 46 chromosomes (23 from sperm + 23 from egg).
3. Explain the difference between mitosis and meiosis regarding chromosome number.

- Mitosis results in daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (diploid).
- Meiosis, however, reduces the chromosome number by half, producing haploid cells.
4. Can a diploid cell directly become haploid?

No, diploid cells cannot directly become haploid. This transition requires the process of meiosis where DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division.
| Process | Resulting Chromosome Set |
|---|---|
| Mitosis | Diploid (2n) |
| Meiosis I | Two Haploid (n) |
| Meiosis II | Four Haploid (n) |

📝 Note: Meiosis introduces genetic variation through crossing over and independent assortment.
5. What happens if there is an error in meiosis?

An error in meiosis can lead to conditions like Down syndrome, where a person has an extra chromosome 21, resulting from nondisjunction.
Exploring diploid and haploid states through these questions and answers not only illuminates the complexities of genetic inheritance but also offers a glimpse into the control mechanisms life uses to ensure continuity. Each diploid or haploid cell holds immense potential for growth, repair, reproduction, and even evolution. Understanding these cellular building blocks is essential for appreciating the intricate mechanisms that govern life at the most fundamental level.
The journey through diploid and haploid chromosomes reveals not just the mechanics of genetics but the elegance of biological systems. Whether for academic pursuit or general interest, the insights gained from exploring these topics foster a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of life itself.
What is the significance of haploid cells in reproduction?
+
Haploid cells, like gametes, carry only one set of chromosomes. This ensures that when two gametes fuse during fertilization, the resultant zygote has the correct diploid number of chromosomes, preventing genetic anomalies.
Why don’t all cells in the body undergo meiosis?

+
Meiosis is specifically designed for sexual reproduction to create genetic diversity. Most body cells (somatic cells) require the maintenance of the correct chromosome number through mitosis for growth, repair, and other functions. Meiosis would disrupt this balance.
How does nondisjunction affect the chromosome number in offspring?

+
Nondisjunction during meiosis can result in an abnormal number of chromosomes in gametes. If a gamete with an extra or missing chromosome fertilizes with a normal gamete, the offspring may have conditions like Down syndrome or Turner syndrome.