Diploid vs Haploid: Simplified Biology Worksheet for Students

Understanding Diploid and Haploid States
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on diploid and haploid states in biology. Understanding these terms is fundamental for students studying life sciences, as they are the building blocks of how organisms reproduce and develop. In this post, we'll explore what diploid and haploid mean, why they are significant, and how they relate to each other in different life forms.
The Basics of Chromosomes
To grasp the difference between diploid and haploid, one must first understand chromosomes:
- Chromosomes: These are thread-like structures made of DNA and proteins found in the nucleus of cells. They carry genetic information in the form of genes.
- Genes: Segments of DNA that code for specific proteins or traits.
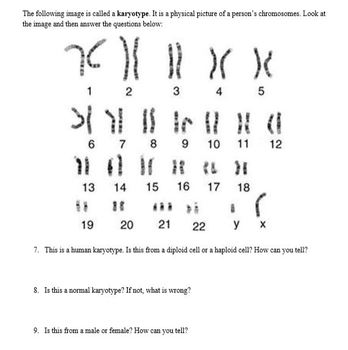
🧬 Note: Each organism has a specific number of chromosomes which can be unique to their species. Humans, for instance, have 46 chromosomes.
What is Diploid?

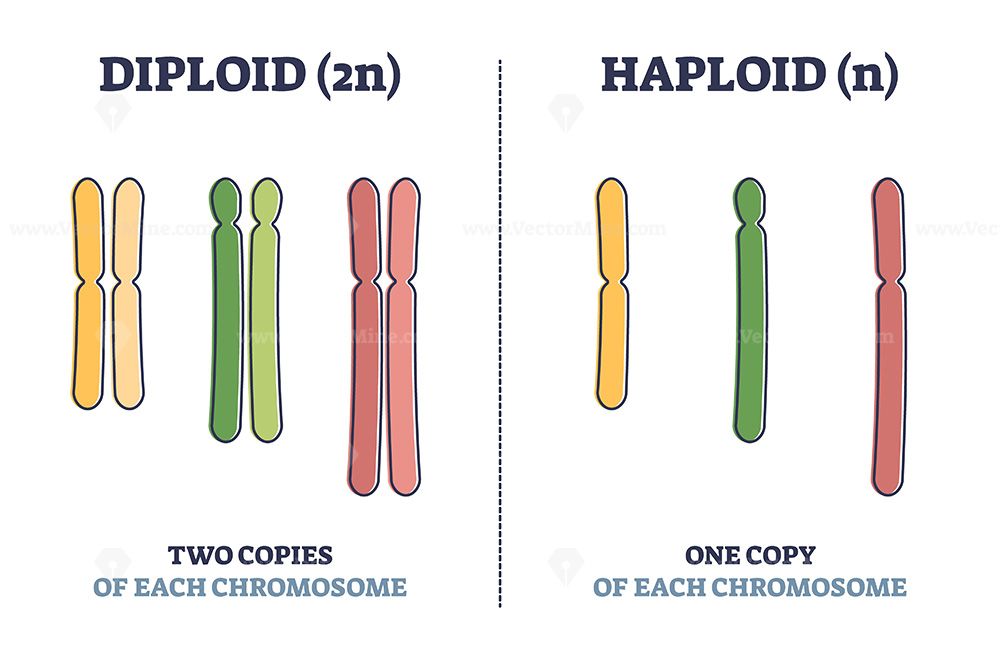
Diploid cells contain two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent:
- Humans are diploid organisms where most cells carry 23 pairs of chromosomes, totaling 46.
- In diploid cells, these chromosomes exist in pairs called homologous chromosomes.
Here's a quick comparison:
| Cell Type | Chromosome Sets | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Diploid | 2 sets (2n) | Human somatic cells |
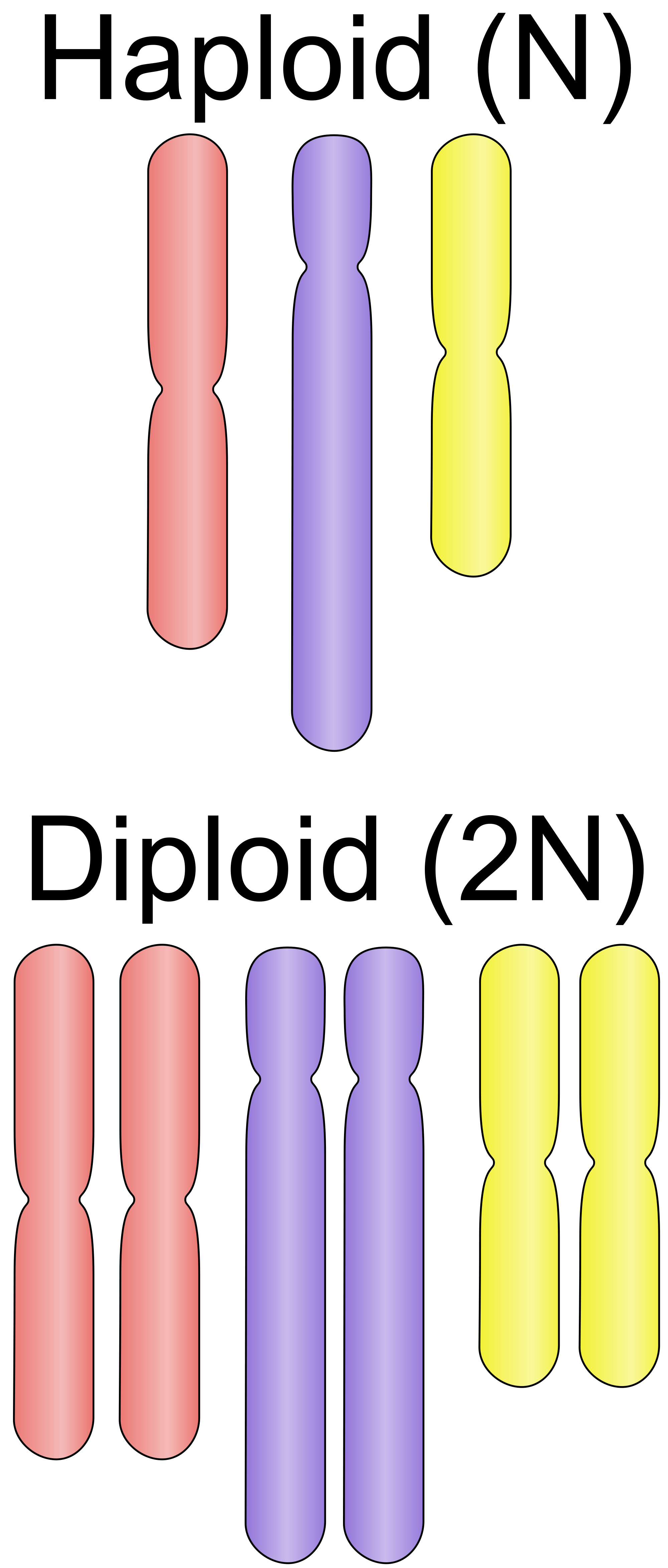
Diploid cells undergo mitosis to produce daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell, each with 46 chromosomes in humans.
What is Haploid?

On the other hand, haploid cells have only one set of chromosomes:
- These cells are typically gametes (sperm and egg cells in animals, pollen, and ovules in plants).
- In humans, a haploid cell contains 23 chromosomes.
The process of reducing the chromosome number from diploid to haploid is called meiosis, where cells undergo two rounds of cell division to create sex cells.
| Cell Type | Chromosome Sets | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Haploid | 1 set (n) | Human gametes |
Why Diploid and Haploid States Matter?

These terms are crucial in understanding:
- Genetic Variation: Meiosis, which leads to haploid gametes, introduces genetic diversity.
- Reproduction: Haploid cells fuse during fertilization to restore the diploid number, creating a unique offspring.
- Biological Processes: Diploid cells perform mitosis for growth and tissue repair, while haploid cells are pivotal in reproduction.
Let's delve into some notes:
🌿 Note: In plants, the alternation of generations between haploid and diploid stages is known as the sporophyte and gametophyte phase.
Life Cycles and Diploid-Haploid Transitions

Organisms have life cycles that involve transitions between diploid and haploid states:
- Sexual Reproduction: In animals, humans begin with a diploid zygote that grows through mitosis. Gametes (haploid) are formed through meiosis.
- Asexual Reproduction: Some organisms reproduce asexually, where only diploid cells are involved, maintaining genetic stability.
- Plants: The life cycle includes both haploid and diploid phases, with sporophytes (diploid) producing spores (haploid) that grow into gametophytes.
Genetic Significance

Diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes, which allows:
- Heterozygosity: Having different alleles for a gene, providing the potential for phenotypic diversity.
- Backup Genes: If one copy of a gene is damaged, the other can still function.
Haploid cells, however, simplify genetic information for:
- Genetic Recombination:** During meiosis, homologous chromosomes exchange segments in a process known as crossing over.
- Monohybrid Cross: It's easier to study the effect of single genes due to their singular presence.
To conclude, understanding diploid and haploid states is pivotal for comprehending how life evolves, adapts, and reproduces. It's not just about the numbers; it's about the dance of life itself where every cell has a role. Whether we're studying evolution, genetics, or medical conditions, the concept of ploidy level influences outcomes in surprising ways. The balance between diploid stability and haploid diversity is what keeps the biosphere thriving.
From the foundations of genetics to the complex intricacies of reproduction, diploid and haploid cells play their part in the grand symphony of life, each contributing uniquely to the chorus of biological systems.
Why are some cells diploid and others haploid?

+
Diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes, providing genetic stability and allowing for heterozygosity. Haploid cells are formed through meiosis to introduce genetic diversity during reproduction, ensuring each offspring has a unique set of traits.
What is the importance of meiosis?

+
Meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction as it reduces the chromosome number by half, ensuring that when gametes fuse during fertilization, the diploid state is restored. It also shuffles genetic information, promoting genetic diversity in populations.
Can diploid organisms ever have haploid cells?

+
Yes, during the process of gamete formation through meiosis, diploid organisms produce haploid cells or gametes which are then used in sexual reproduction.